J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Jan;28(1):25-35. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.25.
Social Inequality in Birth Outcomes in Korea, 1995-2008
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Environmental Health, Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. sonmia@kangwon.ac.kr
- 3Department of Statistics, College of Natural Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2157997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.25
Abstract
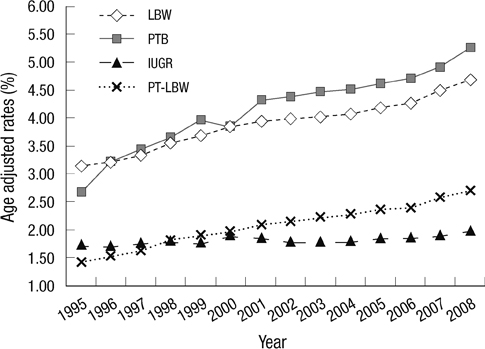
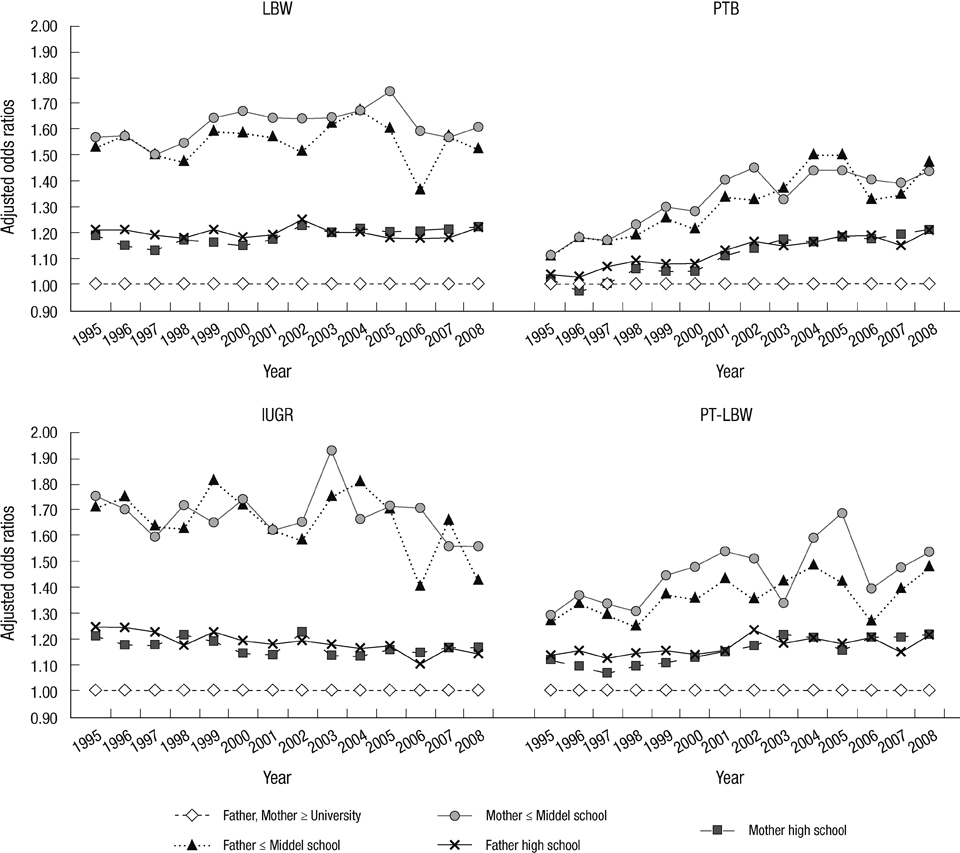
- Social inequality in adverse birth outcomes has been demonstrated in several countries. The present study examined the separate and joint effects of parental education and work in order to investigate the causal pathways of social class effects on adverse birth outcomes in Korea. The occurrence of low birth weight, preterm births, and intrauterine growth retardation was examined among 7,766,065 births in Korea from 1995 to 2008. The effect of social inequality, as represented by parental education and work, was examined against adverse birth outcomes using multivariate logistic regression after controlling for other covariates. Parental education had the most significant and greatest effect on all three adverse outcomes, followed by parental work and employment, which had lesser effects. For adverse birth outcomes, the gap between educational levels increased steadily in Korea from 1995 to 2008. Throughout the analysis, the effect of maternal manual work on adverse birth outcomes was apparent in the study results. Given this evidence of social inequality in education and employment, social interventions should aim at more in-depth and distal determinants of health.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kramer MS, Seguin L, Lydon J, Goulet L. Socio-economic disparities in pregnancy outcome: why do the poor fare so poorly? Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2000. 14:194–210.2. Sanjose S, Roman E, Beral V. Low birthweight and preterm delivery, Scotland, 1981-84: effect of parents' occupation. Lancet. 1991. 338:428–431.3. Rodriguez C, Regidor E, Gutierrez-Fisac JL. Low birth weight in Spain associated with sociodemographic factors. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995. 49:38–42.4. Olsen P, Laara E, Rantakallio P, Jarvelin MR, Sarpola A, Hartikainen AL. Epidemiology of preterm delivery in two birth cohorts with an interval of 20 years. Am J Epidemiol. 1995. 142:1184–1193.5. Gruenwald P, Funakawa H, Mitani S, Nishimura T, Takeuchi S. Influence of environmental factors on foetal growth in man. Lancet. 1967. 1:1026–1028.6. Butler NR, Alberman ED. Perinatal problems: the second report of the 1958 British perinatal mortality survey under the auspices of the national birthday trust fund. 1969. Edinburgh: Livingstone.7. Eastman NJ, Jackson E. Weight relationships in pregnancy. I. The bearing of maternal weight gain and pre-pregnancy weight on birth weight in full term pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1968. 23:1003–1025.8. Mengert WF. Fetal and neonatal mortality cause and prevention. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1948. 55:660–668.9. Anderson NA, Brown EW, Lyon RA. Cause of prematurity. Am J Dis Child. 1941. 61:72.10. Shwartz S. Prenatal care, prematurity, and neonatal mortality. A critical analysis of prenatal care statistics and associations. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1962. 83:591–598.11. Robinson JS, Moore VM, Owens JA, McMillen IC. Origins of fetal growth restriction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2000. 92:13–19.12. Rogers LK, Velten M. Maternal inflammation, growth retardation, and preterm birth: insights into adult cardiovascular disease. Life Sci. 2011. 89:417–421.13. Ancel PY, Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Di Renzo GC, Papiernik E, Breart G. Europop Group. Social differences of very preterm birth in Europe: interaction with obstetric history. Am J Epidemiol. 1999. 149:908–915.14. Lee SY, Hong SC. Difference in incidence rate of low birth weight among the parental social strata in Korea. Health Soc Sci. 2003. 13:61–79.15. Park JH, Lee BE, Park HS, Ha EH, Lee SW, Kim YJ. Association between pre-pregnancy body mass index and socioeconomic status and impact on pregnancy outcomes in Korea. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011. 37:138–145.16. Son M. The effects of the parents' social class on low birthweight among the birth, 1995-2001. Korean J Health Policy Adm. 2004. 14:148–168.17. Hwang S, Jang J. The relationship between the supply and policy change in women's labour. 2003. Seoul, Korea: Korea Labour Institute.18. Son M. Occupational class and health: the differentials in mortality, morbidity and workplace injury rates by occupation, education, income and working conditions in Korea. 2001. London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, University of London;244–268. PhD thesis.19. Mamelle N, Laumon B, Lazar P. Prematurity and occupational activity during pregnancy. Am J Epidemiol. 1984. 119:309–322.20. Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Kaminski M. Pregnant women's working conditions and their changes during pregnancy: a national study in France. Br J Ind Med. 1987. 44:236–243.21. McDonald AD, McDonald JC, Armstrong B, Cherry NM, Nolin AD, Robert D. Prematurity and work in pregnancy. Br J Ind Med. 1988. 45:56–62.22. Homer CJ, Beresford SA, James SA, Siegel E, Wilcox S. Work-related physical exertion and risk of preterm, low birthweight delivery. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1990. 4:161–174.23. Henriksen TB, Hedegaard M, Secher NJ. Standing and walking at work and birthweight. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1995. 74:509–516.24. Hickey CA, Cliver SP, Mulvihill FX, McNeal SF, Hoffman HJ, Goldenberg RL. Employment-related stress and preterm delivery: a contextual examination. Public Health Rep. 1995. 110:410–418.25. Kim YA, Park JH. Impact of changes in maternal age and parity distribution on low birth weight incidence rate. Korean J Prev Med. 1989. 22:276–282.26. Park MS, Park SH, Han JH, Kim EI. A study on factors affecting on low birth weight infants. J Reprod Med Popul. 1996. 9:5–14.27. Park SH, Han JH, Kim SM, Ku SY, Kim SH. Risk factors of preterm delivery in pregnant women aged 35 years or older: analysis of birth certificate data in 1996. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 42:1416–1421.28. Romo A, Carceller R, Tobajas J. Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR): epidemiology and etiology. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2009. 6:Suppl 3. 332–336.29. Launer LJ, Villar J, Kestler E, de Onis M. The effect of maternal work on fetal growth and duration of pregnancy: a prospective study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990. 97:62–70.30. Teitelman AM, Welch LS, Hellenbrand KG, Bracken MB. Effect of maternal work activity on preterm birth and low birth weight. Am J Epidemiol. 1990. 131:104–113.31. Klebanoff MA, Shiono PH, Carey JC. The effect of physical activity during pregnancy on preterm delivery and birth weight. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990. 163:1450–1456.32. Oh EJ, Min HJ, Kim JH. Career choice and labor market transition of the married women by level of education. J Vocat Educ Train. 2009. 12:141–162.33. Kim MR. The change of people's life during 6 years of neoliberalism. 95, Situation and Labor, Korean Institute of Labor Study and Policy. 2004. Seoul, Korea: 1–59.34. Kim AE. The social perils of the Korean financial crisis. J Contemp Asia. 2004. 34:221–237.35. Shin KY. Inequalities in social class in Korea. Econ Soc. 2003. 59:32–54.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of the Parents' Social Class on Infant and Child Death among 1995-2004 Birth Cohort in Korea
- Role of Parental Social Class in Preterm Births and Low Birth Weight in Association with Child Mortality:A National Retrospective Cohort Study in Korea
- An Exploratory Study of Health Inequality Discourse Using Korean Newspaper Articles: A Topic Modeling Approach
- Historical Advances in Health Inequality Research
- Concept Analysis of Health Inequalities