J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Nov;27(11):1444-1446. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1444.
Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica without Extracutaneous Abnormalities: A Case Study Involving a Preterm Baby
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drsshong@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2157962
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1444
Abstract
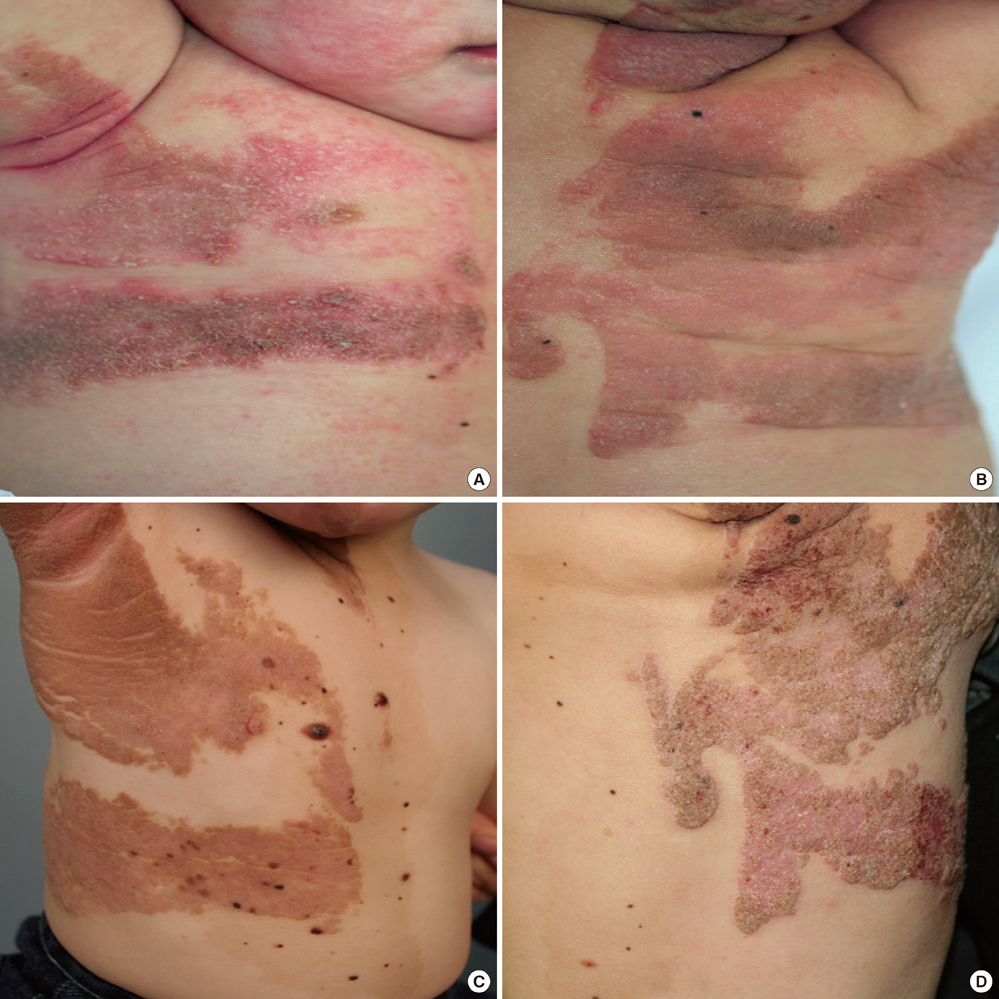
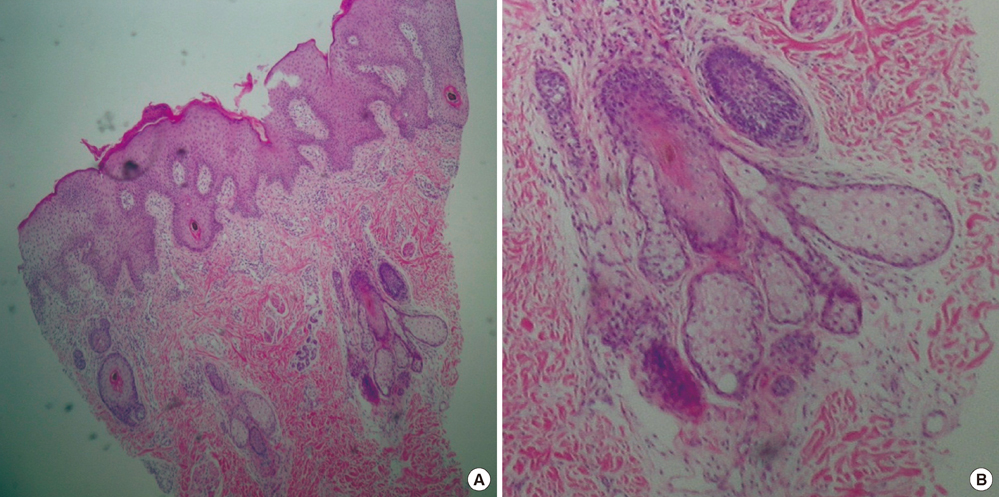
- Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (PPK) is a rare syndrome defined by the association of an organoid nevus occasionally with sebaceous differentiation, a speckled lentiginous nevus, and other extracutaneous anomalies. A preterm male infant of only 830 g at 27 week gestational age had an organoid nevus showing sebaceous differentiation. Also, he had multiple speckled-lentiginous nevus. Correlating the observed clinical presentation with the histopathological findings, the diagnosis of PPK was established. There have been less than 10 cases of PPK without extracutaneous manifestation. We present an uncommon case of a preterm patient with PPK who had no extracutaneous abnormalities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Happle R, Hoffmann R, Restano L, Caputo R, Tadini G. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a melanocytic-epidermal twin nevus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996. 65:363–365.2. Happle R. Mosaicism in human skin. Understanding the patterns and mechanisms. Arch Dermatol. 1993. 129:1460–1470.3. Chantorn R, Shwayder T. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a further case without extracutaneous anomalies and review of the condition. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011. 28:715–719.4. Happle R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes Part I. Well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010. 63:1–22.5. Boente MC, Pizzi de Parra N, Larralde de Luna M, Bonet HB, Santos Muñoz A, Parra V, Gramajo P, Moreno S, Asial RA. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: another epidermal nevus syndrome and a distinctive type of twin spotting. Eur J Dermatol. 2000. 10:190–194.6. Hermes B, Cremer B, Happle R, Henz BM. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a patient with the rare melanocytic epidermal twin nevus syndrome. Dermatology. 1997. 194:77–79.7. Wollenberg A, Butnaru C, Oppel T. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (Happle) in a 23-year-old man. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002. 82:55–57.8. Kinoshita K, Shinkai H, Utani A. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica without extracutaneous abnormalities. Dermatology. 2003. 207:415–416.9. Polat M, Yalçin B, Ustün H, Caliskan D, Alli N. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica without extracutaneous abnormalities. Eur J Dermatol. 2008. 18:363–364.10. Martínez-Menchón T, Mahiques Santos L, Vilata Corell JJ, Febrer Bosch I, Fortea Baixauli JM. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a 20-year follow-up with malignant degeneration of both nevus components. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005. 22:44–47.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica
- Extracutaneous mastocytoma of colon: a case report and literature review
- Nursing support perceived by mothers of preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit in South Korea
- Parental Role Stress and Perception of the Newborn in Mothers of Preterm Babies
- A Case of Dexamethasone induced Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Neonate with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia