J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Dec;20(6):1073-1075. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.1073.
A Case of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Caused by Penicillium species in a Home Environment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine and Allergy, Soonchunhyang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Korean National Tuberculosis Association, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2157766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.1073
Abstract
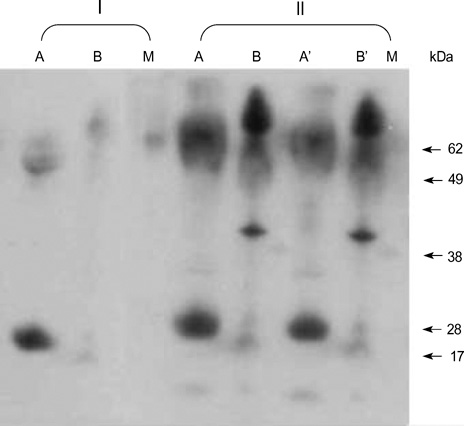
- We report a case of hypersensitivity pneumonitis in a 30-yr-old female housewife caused by Penicillium species found in her home environment. The patient was diagnosed according to history, chest radiograph, spirometry, high-resolution chest CT, and transbronchial lung biopsy. To identify the causative agent, cultured aeromolds were collected by the open-plate method. From the main fungi cultured, fungal antigens were prepared, and immunoblot analysis with the patient's serum and each fungal antigen was performed. A fungal colonies were isolated from the patient's home. Immunoblotting analysis with the patient's sera demonstrated a IgG-binding fractions to Penicillium species extract, while binding was not noted with control subject. This study indicates that the patient had hypersensitivity pneumonitis on exposure to Penicillium species in her home environment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Erkinjuntti-Pekkanen R, Rytkonen H, Kokkarinen JI, Tukiainen HO, Partanen K, Terho EO. Long-term risk of emphysema in patients with farmer's lung and matched control farmers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:662–665.
Article2. Lee MW, Jung WJ, Lee JA, Lee JH, Choe KH, Kim MK. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by oyster mushroom spores. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 18:84–89.3. Kim YY. Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1993. 40:1–5.
Article4. Do YK, Kim YJ, Kang HJ, Yu KS, Yun HJ, Jun JH, Lee BK, Song DY. A case of hypersensitivity pneumonitis by Alternaria as a suspected etiology. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2003. 54:338–345.5. Park JW, Hong CS, Jee YK, Park JS, Lee KY, Kim KY, Jun Y, Hwang YJ, Oh HT, Lyu S. A case of hypersensitivity pneumonitis with positive precipitin antibody to Trichosporon cutaneum. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 19:969–973.6. Moreno-Ancillo A, Vicente J, Gomez L, Martin Barroso JA, Barranco P, Cabanas R, Lopez-Serrano MC. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis related to a covered and heated swimming pool environment. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. 114:205–206.
Article7. Yoo CG, Kim YW, Han SK, Nakagawa K, Suga M, Nishiura Y, Ando M, Shim YS. Summer-type hypersensitivity pneumonitis outside Japan: a case report and the state of the art. Respirology. 1997. 2:75–77.
Article8. Park HS, Jung KS, Kim SO, Kim SJ. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by Penicillium expansum in a home environment. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994. 24:383–385.9. Lee SK, Kim SS, Nahm DH, Park HS, Oh YJ, Park KJ, Kim SO, Kim SJ. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by Fusarium napiforme in a home environment. Allergy. 2000. 55:1190–1193.10. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970. 227:680–685.
Article11. Tsang VC, Peralta JM, Simons AR. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983. 92:377–391.12. Belin L. Clinical and immunological data on "wood trimmer's disease" in Sweden. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1980. 107:169–176.13. van Assendelft AH, Raitio M, Turkia V. Fuel chip-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by Penicillium species. Chest. 1985. 87:394–396.14. Campbell JA, Kryda MJ, Treuhaft MW, Marx JJ Jr, Roberts RC. Cheese worker's hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983. 127:495–496.15. Solley GO, Hyatt RE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by Penicillium species. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980. 65:65–70.16. Patel AM, Ryu JH, Reed CE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts and future questions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 108:661–670.
Article17. Zwick H, Popp W, Braun O, Wanke T, Wagner C. Personal spore sampling and indirect immunofluorescent test for exploration of hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to mould spores. Allergy. 1991. 46:277–283.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Caused by Fungi in a Home Environment
- The first case of summer-type hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Korea
- Two Species of Endophytic Penicillium from Pinus rigida in Korea
- Detection of Extracellular Enzyme Activity in Penicillium using Chromogenic Media
- Re-Identification on Korean Penicillium Sequences in GenBank Collected by Software GenMine