Ann Dermatol.
2012 Feb;24(1):74-76. 10.5021/ad.2012.24.1.74.
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Clinically Mimicking Necrobiosis Lipoidica in a Patient with Systemic Sarcoidosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan. allheart@dermatol.med.kyushu-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2156860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.1.74
Abstract
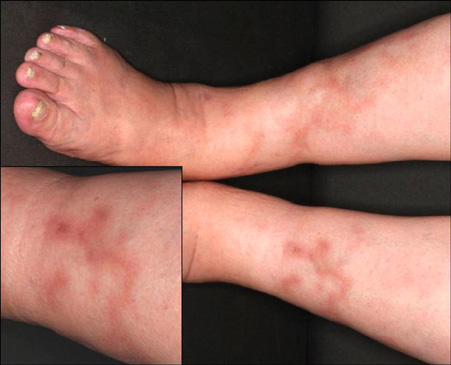
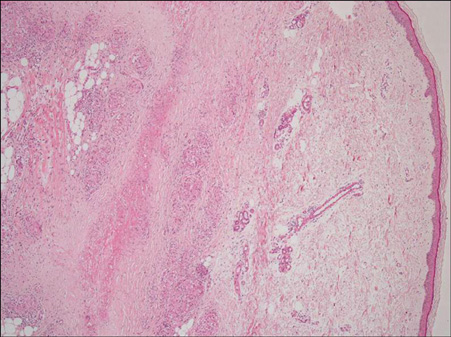
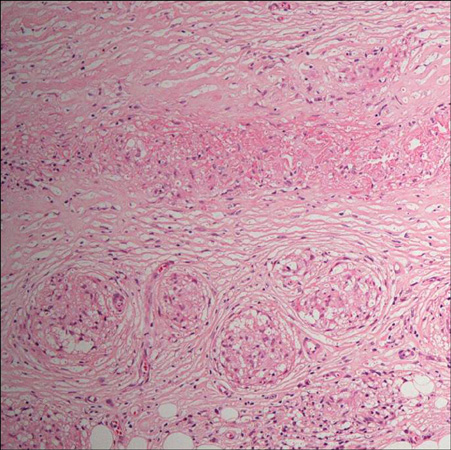
- A 70-year-old woman with an 8-year history of systemic sarcoidosis developed round, red-brown eruptions, with central atrophic lesions on her lower legs. The features of the biopsy specimen resembled those of necrobiosis lipoidica (NL), but although necrobiosis was present there were well-formed non-necrotizing granulomas in the dermis. The histological diagnosis was cutaneous sarcoidosis. Systemic sarcoidosis presenting with NL has rarely been reported. The histological features of cutaneous sarcoidosis sometimes mimic those of other granulomatous diseases, including NL and granuloma annulare, which are difficult to distinguish. We discuss the novel association between sarcoidosis and other granulomatous diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Phillip M, Eduardo C, Scott G. Michel H, editor. Necrobiosis lipoidica. Pathology of the skin with clinical correlations. 2005. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: ELSEVIER MOSBY;305–310.2. Harrison P, Shuster S. Granuloma annulare and sarcoidosis. Br J Dermatol. 1979. 100:231.3. Gudmundsen K, Smith O, Dervan P, Powell FC. Necrobiosis lipoidica and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1991. 16:287–291.
Article4. Monk BE, Du Vivier AW. Necrobiosis lipoidica and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1987. 12:294–295.
Article5. Igawa K, Maruyama R, Satoh T, Yokozeki H, Katayama I, Nishioka K. Necrobiosis lipoidica-like skin lesions in systemic sarcoidosis. J Dermatol. 1998. 25:653–656.
Article6. Ngo BT, Hayes KD, DiMiao DJ, Srinivasan SK, Huerter CJ, Rendell MS. Manifestations of cutaneous diabetic microangiopathy. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005. 6:225–237.
Article7. Putkonen T, Virkkunen M, Wager O. Joint involvement in sarcoidosis with special reference to the coexistence of sarcoidosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1965. 11:53–61.
Article8. Fries W, Grassi SA, Leone L, Giacomin D, Galeazzi F, Naccarato R, et al. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and sarcoidosis. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995. 30:1221–1223.
Article9. Macaron NC, Cohen C, Chen SC, Arbiser JL. gli-1 Oncogene is highly expressed in granulomatous skin disorders, including sarcoidosis, granuloma annulare, and necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum. Arch Dermatol. 2005. 141:259–262.
Article10. Mehregan AH, Pinkus H. Necrobiosis lipoidica with sarcoid reaction. A case report. Arch Dermatol. 1961. 83:143–145.11. Ball NJ, Kho GT, Martinka M. The histologic spectrum of cutaneous sarcoidosis: a study of twenty-eight cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2004. 31:160–168.
Article