Ann Dermatol.
2011 Oct;23(Suppl 2):S258-S260. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S2.S258.
Steatocystoma Multiplex Confined to the Scalp with Concurrent Alopecia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. btyouth@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Dermatology, Maryknoll Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2156804
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S2.S258
Abstract
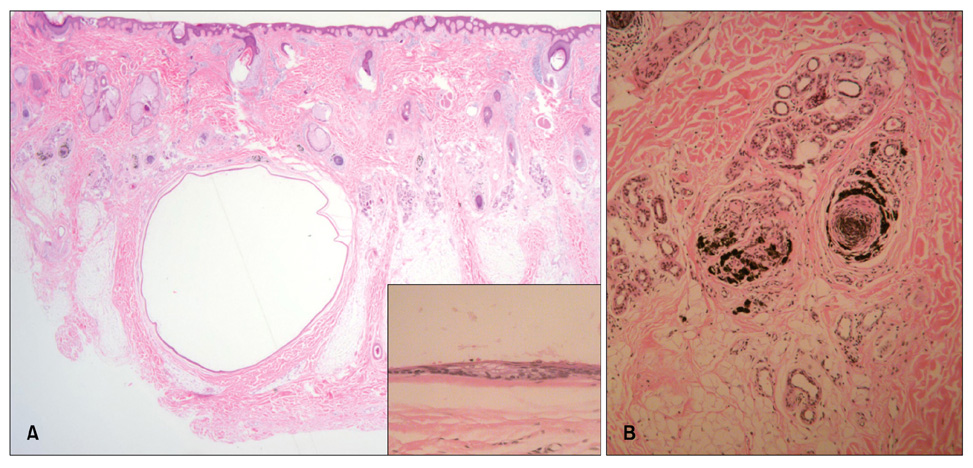
- Steatocystoma multiplex (SM) is an uncommon disorder of the pilosebaceous unit characterized by the development of numerous sebum-containing dermal cysts which rarely involves the scalp. Here, we report a case of a 50-year-old man with multiple cystic nodules and alopecic patches on his scalp. On histopathological examination, the folded cyst was found to be lined by stratified squamous epithelium, while flattened sebaceous gland cells were identified in the cystic wall. Pigment casts were present in the hair papillae and perifollicular regions, suggesting trichotillomania as a possible cause of the observed alopecia. This case appears to represent an unusual clinical manifestation of SM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim CH, Kim DH, Jeon JS, Kang SG, Kim DW, Cho MK. A case of zosteriform Kaposi's sarcoma after prednisolon treatment. Korean J Dermatol. 2009. 47:583–587.2. Plewig G, Wolff HH, Braun-Falco O. Steatocystomamultiplex: anatomic reevaluation, electron microscopy, and autoradiography. Arch Dermatol Res. 1982. 272:363–380.
Article3. Kim MB, Jang HS, Oh CK, Kwon KS. Clinical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical study of steatocystoma multiplex. Korean J Dermatol. 1999. 37:1769–1776.4. Jeong SY, Kim JH, Seo SH, Son SW, Kim IH. Giant steatocystoma multiplex limited to the scalp. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009. 34:e318–e319.
Article5. Lee YJ, Lee SH, Ahn SK. Sebocystomatosis: a clinical variant of steatocystoma multiplex. Int J Dermatol. 1996. 35:734–735.
Article6. Lim SH, Ha JH, Chae KO, Park HJ, Baek SC, Byun DG. A case of eruptive steatocystoma multiplex on the scalp. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:1664–1667.7. Marley WM, Buntin DM, Chesney TM. Steatocystoma multiplex limited to the scalp. Arch Dermatol. 1981. 117:673–674.
Article8. Su WP, Chun SI, Hammond DE, Gordon H. Pachyonychia congenita: a clinical study of 12 cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 1990. 7:33–38.
Article9. Lee HW, Oh SH, Chang SE, Choi JH, Moon KC, Koh JK. A case of steatocystoma multiplex: successful treatment with mini-incisions. Ann Dermatol. 2005. 17:35–37.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Steatocystoma Multiplex Limited to the Scalp
- A Case of Eruptive Steatocystoma Multiplex on the Scalp
- A Case of Steatocystoma Multiplex: Successful Treatment with Mini-incisions
- A Case of Steatocystoma Simplex Involving the Scalp
- A Case of Eruptive Vellus Hair Cyst Combined With Steatocystoma Multiplex