Ann Dermatol.
2009 Nov;21(4):419-422. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.4.419.
A Case of Erythroplasia of Queyrat Treated with Imiquimod 5% Cream and Excision
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khcho@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2156511
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.4.419
Abstract
- Imiquimod is a new immunomodulating agent with antitumor and antiviral properties that has been shown to be clinically effective in various kinds of skin diseases, including precancerous dermatoses. Erythroplasia of Queyrat is a carcinoma in situ that mainly occurs on the glans penis. There are several non-invasive treatment options for erythroplasia of Queyrat such as photodynamic therapy, cryosurgery and applying various kinds of topical agents. We now report a case of typical erythroplasia of Queyrat on glans penis associated with human papillomavirus type 16 infection that was treated by imiquimod 5% cream and the subsequent excision of an imiquimod-resistant penile lesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
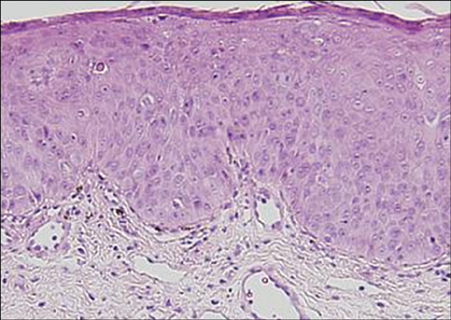
Figure
Reference
-
1. Graham JH, Helwig EB. Erythroplasia of Queyrat. A clinicopathologic and histochemical study. Cancer. 1973. 32:1396–1414.
Article2. Mikhail GR. Cancers, precancers, and pseudocancers on the male genitalia. A review of clinical appearances, histopathology, and management. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1980. 6:1027–1035.
Article3. Peterka ES, Lynch FW, Goltz RW. An association between Bowen's disease and internal cancer. Arch Dermatol. 1961. 84:623–629.
Article4. Kao GF. Carcinoma arising in Bowen's disease. Arch Dermatol. 1986. 122:1124–1126.
Article5. Wieland U, Jurk S, Weissenborn S, Krieg T, Pfister H, Ritzkowsky A. Erythroplasia of Queyrat: coinfection with cutaneous carcinogenic human papillomavirus type 8 and genital papillomaviruses in a carcinoma in situ. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 115:396–401.
Article6. Meyer T, Arndt R, Christophers E, Nindl I, Stockfleth E. Importance of human papillomaviruses for the development of skin cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 2001. 25:533–547.7. Stables GI, Stringer MR, Robinson DJ, Ash DV. Erythroplasia of Queyrat treated by topical aminolaevulinic acid photodynamic therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1999. 140:514–517.
Article8. Perry CM, Lamb HM. Topical imiquimod: a review of its use in genital warts. Drugs. 1999. 58:375–390.9. Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Sanjo H, Hoshino K, et al. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2002. 3:196–200.
Article10. Miller RL, Gerster JF, Owens ML, Slade HB, Tomai MA. Imiquimod applied topically: a novel immune response modifier and new class of drug. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1999. 21:1–14.
Article11. Arlette JP. Treatment of Bowen's disease and erythroplasia of Queyrat. Br J Dermatol. 2003. 149:Suppl 66. 43–49.
Article12. Micali G, Nasca MR, De Pasquale R. Erythroplasia of Queyrat treated with imiquimod 5% cream. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:901–903.
Article13. van Seters M, Fons G, van Beurden M. Imiquimod in the treatment of multifocal vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia 2/3. Results of a pilot study. J Reprod Med. 2002. 47:701–705.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Erythroplasia of Queyrat Treated with Topical 5% 5-Fluorouracil Cream
- Treatment of Erythroplasia of Queyrat with Topical 5 % 5 - Fluorouracil Cream under Occlusion
- Erythroplasia of Queyrat Involving the Distal Glans Penis Surrounding the Urethral Meatus
- Treatment of Keratoacanthoma with 5% Imiquimod Cream
- A Case of Verrucous Carcinoma Treated by 5% Imiquimod Cream