Ann Dermatol.
2008 Sep;20(3):153-156. 10.5021/ad.2008.20.3.153.
Combined Mastocytoma-hemangioma in a Patient with Urticaria Pigmentosa
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Anyang, Korea. kkj51818@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2156384
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2008.20.3.153
Abstract
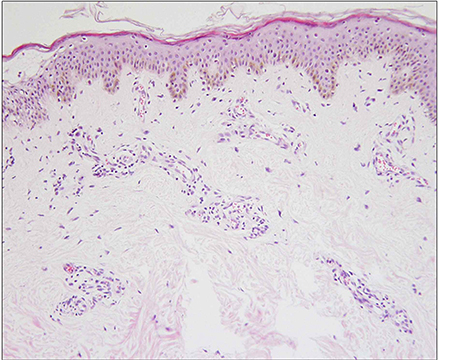
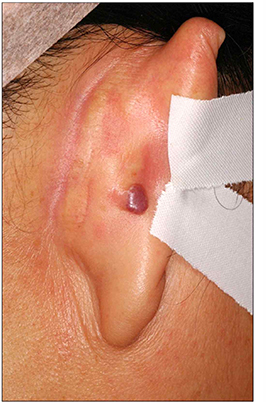
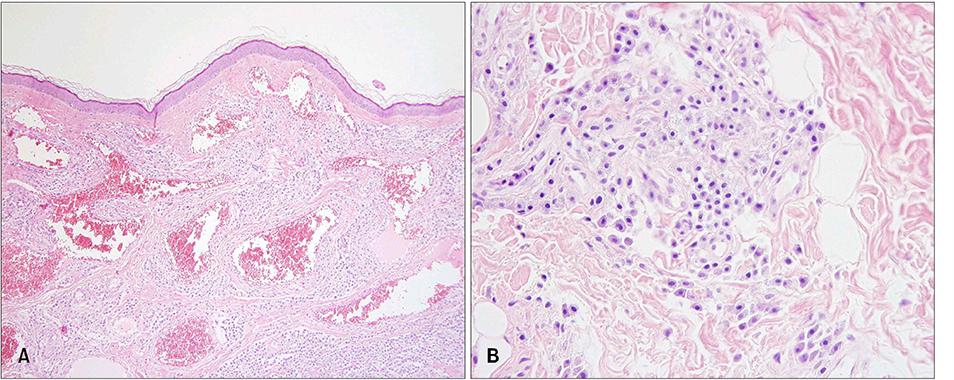
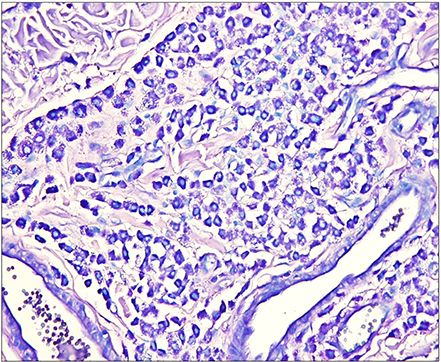
- A patient with long-standing urticaria pigmentosa presented with a pea-sized reddish to purplish papule on the posterior part of the right ear. Histopathologic examination revealed numerous dilated vascular structures in the upper dermis and mast cell infiltrations throughout the whole dermis, consistent with combined mastocytoma-hemangioma. The mast cells were strongly positive with Giemsa stain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chu DH, Haake AR, Holbrook K, Loomis CA. The structure and development of skin. In : Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 6th ed. New York: McGrow-Hill;2003. p. 58–87.2. Folkman J. Regulation of angiogenesis: a new function of heparin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985; 34:905–909.
Article3. Gordon JR, Galli SJ. Release of both preformed and newly synthesized tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)/cachectin by mouse mast cells stimulated via the FcεRI. A mechanism for the sustained action of mast cell-derived TNF-α during IgE-dependent biological responses. J Exp Med. 1991; 174:103–107.
Article4. Gordon JR, Galli SJ. Promotion of mouse fibroblast collagen gene expression by mast cells stimulated via the FcεRI. Role for mast cell-derived transforming growth factor β and tumor necrosis factor α. J Exp Med. 1994; 180:2027–2037.
Article5. Boesiger BJ, Tsai M, Maurer M, Uamaguchi M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, et al. Mast cell can secrete vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial cell growth factor and exhibit enhanced release after immunoglobulin E-dependent upregulation of Fcε receptor I expression. J Exp Med. 1998; 188:1135–1145.
Article6. Pasyk KA, Grabb WC, Cherry GW. Ultrastructure of mast cells in growing and involuting stages of hemangiomas. Hum Pathol. 1983; 14:174–181.
Article7. Glowacki J, Mulliken JB. Mast cells in hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Pediatrics. 1982; 70:48–51.
Article8. Inamadar AC, Palit A. Cutaneous mastocytosis: report of six cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006; 72:50–53.
Article9. Okun MR, Bhawan J. Combined melanocytomamastocytoma in a case of nodular mastocytosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979; 1:338–347.
Article10. Wood C, Sina B, Webster CG, Kurgansky D, Drachenberg CB, Reedy EA. Fibrous mastocytoma in a patient with generalized cutaneous mastocytosis. J Cutan Pathol. 1992; 19:128–133.
Article11. Shea CR, Prieto VG. Mast cells in angiolipomas and hemangimas of human skin: are they important for angiogenesis? J Cutan Pathol. 1994; 21:247–251.
Article12. Taylor S, Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982; 297:307–312.
Article13. Azizkhan RG, Azizkhan JC, Zetter BR, Folkman J. Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1980; 152:931–944.
Article14. Shing Y, Folkman J, Sullivan R, Butterfield C, Murray J, Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984; 223:1296–1299.
Article15. Qu Z, Liebler JM, Powers MR, Galey T, Ahmadi P, Huang XN, et al. Mast cells are a major source of basic fibroblast growth factor in chronic inflammation and cutaneous hemangioma. Am J Pathol. 1995; 147:564–573.