Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Mar;90(3):147-156. 10.4174/astr.2016.90.3.147.
Intraoperative radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in 112 patients with cirrhosis: a surgeon's view
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Pusan, Korea. yhkim1@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Pusan, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Pusan, Korea.
- KMID: 2155048
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.90.3.147
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This retrospective study was an investigation of overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and prognostic factors affecting OS and DFS in cirrhotic patients who received intraoperative radiofrequency ablation (IORFA).
METHODS
Between April 2009 and November 2013, 112 patients (94 men, 84%; 18 women, 16%) underwent IORFA for 185 cases of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC). Repeat IORFA was done in 9 patients during the same period (total of 121 treatments).
RESULTS
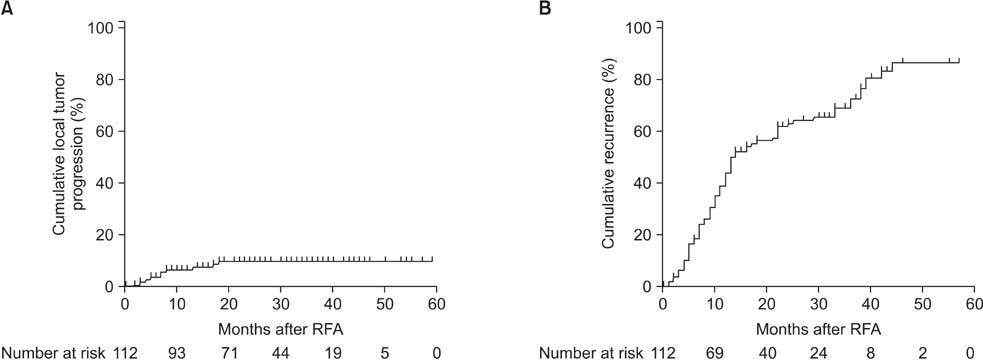
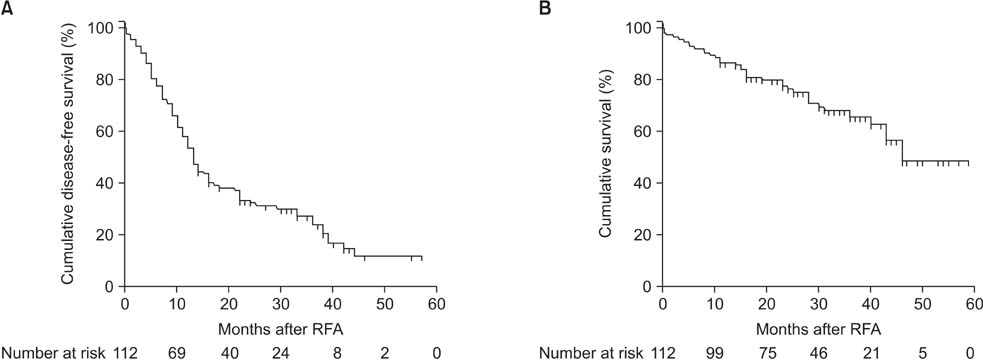
All patients were followed-up for at least 12 months (mean follow-up, 32 months). Surgical resection combined with IORFA was performed in 20 patients. The technical effectiveness at 1 week was 91.78% (111 of 121). Readmission was 9.1% (11 of 121) and the most common cause was ventral hernia. Procedure-related mortality was 2.7% (3 of 112) and continued fatal biliary leakage was 1.8% (2 of 112). Local recurrence developed in 10 patients (8.9%). Most recurrence was intrahepatic. Cumulative survival was assessed in 33 patients who received IORFA as primary treatment (naive patients) and 79 non-naive patients. The cumulative DFS and OS rate at l and 3 years was 54% and 24%, and 87% and 66%, respectively. Moderate ascites (P = 0.001), tumor located segment I (P = 0.001), portal vein thrombosis (P = 0.001) had poor survival were significant factors by multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
IORFA alone or in combination with surgical resection extends the spectrum of liver surgery. A fundamental understanding of RFA, additional comorbidities, and postablation complication are necessary to maximize the safety and efficacy of IORFA for treating HCC with cirrhosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Raut CP, Izzo F, Marra P, Ellis LM, Vauthey JN, Cremona F, et al. Significant long-term survival after radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005; 12:616–628.2. El-Gendi A, El-Shafei M, Abdel-Aziz F, Bedewy E. Intraoperative ablation for small HCC not amenable for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in Child A cirrhotic patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013; 17:712–718.3. Nishikawa H, Inuzuka T, Takeda H, Nakajima J, Matsuda F, Sakamoto A, et al. Comparison of percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation and surgical resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. BMC Gastroenterology. 2011; 11:143.4. Ribeiro MA Jr, Rodrigues JJ, Habr-Gama A, Chaib E, D'Ipolitto G, Fonseca AZ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of primary and metastatic liver tumors: 4 years experience. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:1170–1175.5. Kim YS, Rhim H, Lim HK, Choi D, Lee WJ, Jeon TY, et al. Intraoperative radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results in a large series. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:1862–1870.6. Elias D, Goharin A, El Otmany A, Taieb J, Duvillard P, Lasser P, et al. Usefulness of intraoperative radiofrequency thermoablation of liver tumours associated or not with hepatectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000; 26:763–769.7. Cheung TT, Ng KK, Chok KS, Chan SC, Poon RT, Lo CM, et al. Combined resection and radiofrequency ablation for multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma: prognosis and outcomes. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:3056–3062.8. Eisele RM, Zhukowa J, Chopra S, Schmidt SC, Neumann U, Pratschke J, et al. Results of liver resection in combination with radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010; 36:269–274.9. Choi D, Lim HK, Joh JW, Kim SJ, Kim MJ, Rhim H, et al. Combined hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation for multifocal hepatocellular carcinomas: long-term follow-up results and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007; 14:3510–3518.10. Pawlik TM, Izzo F, Cohen DS, Morris JS, Curley SA. Combined resection and radiofrequency ablation for advanced hepatic malignancies: results in 172 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003; 10:1059–1069.11. Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Franchini C, Pina CD, Lera J, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2005; 234:961–967.12. Gao ZH, Bai DS, Jiang GQ, Jin SJ. Review of preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2015; 7:40–43.13. Khan MR, Poon RT, Ng KK, Chan AC, Yuen J, Tung H, et al. Comparison of percutaneous and surgical approaches for radiofrequency ablation of small and medium hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2007; 142:1136–1143.14. Machi J, Uchida S, Sumida K, Limm WM, Hundahl SA, Oishi AJ, et al. Ultrasound-guided radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors: percutaneous, laparoscopic, and open surgical approaches. J Gastrointest Surg. 2001; 5:477–489.15. Lee SD, Han HS, Cho JY, Yoon YS, Hwang DW, Jung K, et al. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 83:36–42.16. Sakoda M, Ueno S, Iino S, Minami K, Ando K, Kawasaki Y, et al. Endoscopic versus open radiofrequency ablation for treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2013; 37:597–601.17. Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008; 47:82–89.18. Shen SQ, Xiang JJ, Xiong CL, Wu SM, Zhu SS. Intraoperative radiofrequency thermal ablation combined with portal vein infusion chemotherapy and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable HCC. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005; 52:1403–1407.19. Minami Y, Kawasaki T, Kudo M, Haji S, Shiraishi O, Kawabe T, et al. Treatment of large and/or multiple hepatic malignancies: open surgical approaches of radiofrequency ablation. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:2358–2360.20. Ueno S, Sakoda M, Kubo F, Hiwatashi K, Tateno T, Baba Y, et al. Surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinomas within the Milan criteria. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009; 16:359–366.21. Tateishi R, Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Koike Y, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer. 2005; 103:1201–1209.22. Tepel J, Hinz S, Klomp HJ, Kapischke M, Kremer B. Intraoperative radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for irresectable liver malignancies. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004; 30:551–555.23. de Baere T, Risse O, Kuoch V, Dromain C, Sengel C, Smayra T, et al. Adverse events during radiofrequency treatment of 582 hepatic tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:695–700.24. Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, Nicolas Vauthey J, Vallone P. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 2000; 232:381–391.25. Masuzaki R, Shiina S, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Goto E, Sugioka Y, et al. Utility of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with Sonazoid in radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26:759–764.26. Ikeda K, Osaki Y, Nakanishi H, Nasu A, Kawamura Y, Jyoko K, et al. Recent progress in radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2014; 87:Suppl 1. 73–77.27. Rhim H, Dodd GD 3rd, Chintapalli KN, Wood BJ, Dupuy DE, Hvizda JL, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: lessons learned from complications. Radiographics. 2004; 24:41–52.28. Xiao WK, Chen D, Hu AB, Peng BG, Guo YZ, Fu SJ, et al. Radiofrequency-assisted versus clamp-crush liver resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Res. 2014; 187:471–483.29. Kim HO, Kim SK, Son BH, Yoo CH, Hong HP, Cho YK, et al. Intraoperative radiofrequency ablation with or without tumorectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in locations difficult for a percutaneous approach. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2009; 8:591–596.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas