Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Mar;90(3):139-146. 10.4174/astr.2016.90.3.139.
Surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct invasion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hepatobiliary Surgery and Liver Transplantation, Department of Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. wanghj@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2155047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.90.3.139
Abstract
- PURPOSE
There is still some debate on surgical procedures for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with bile duct tumor thrombi (BDTT, Ueda type 3 or 4). What is adequate extent of liver resection for curative treatment? Is extrahepatic bile duct resection mandatory for cure? The aim of this study is to answer these questions.
METHODS
Between February 1994 and December 2012, 877 consecutive HCC patients underwent hepatic resection at Ajou University Hospital. Thirty HCC patients (3.4%) with BDTT (Ueda type 3 or 4) were retrospective reviewed in this study.
RESULTS
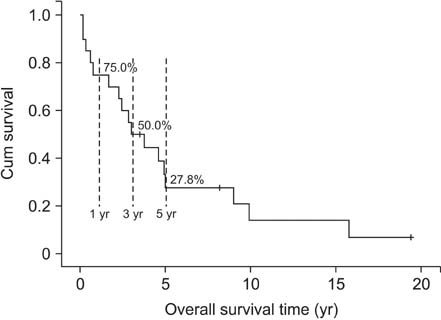
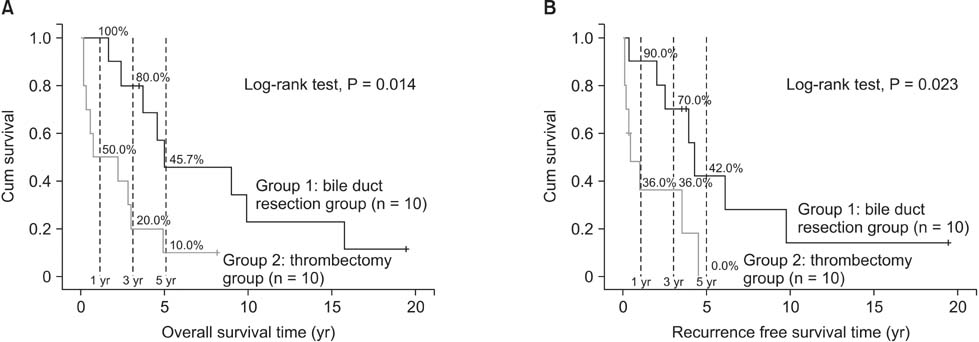
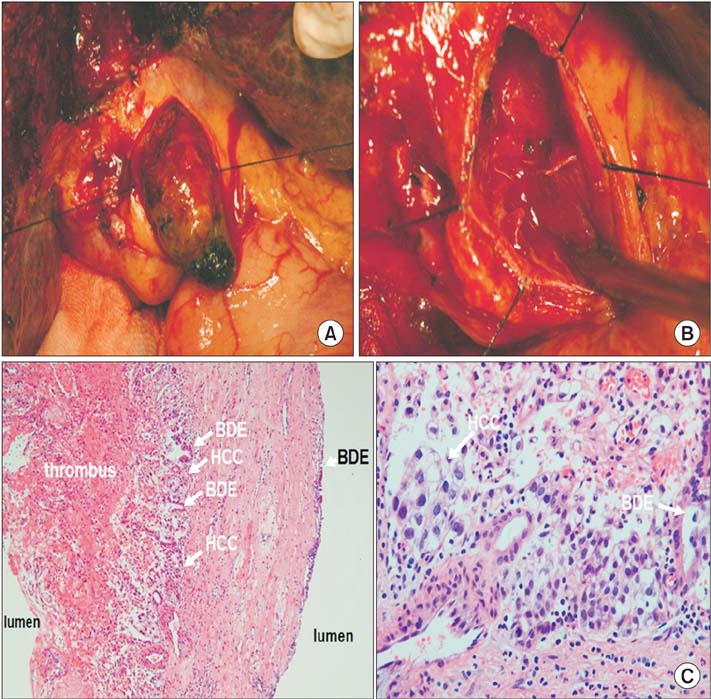
In total, 20 patients enrolled in this study were divided into 2 groups: patients who underwent hemihepatectomy with extrahepatic bile duct resection (group 1, n = 10) and with only removal of BDTT (group 2, n = 10). The 1-, 3- and 5-year overall survival rates were 75.0%, 50.0%, and 27.8%, respectively. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates of group 1 were 100.0%, 80.0%, and 45.7%, and those of group 2 were 50.0%, 20.0%, and 10.0%, respectively (P = 0.014). The 1-, 3-, and 5-year recurrences free survival rates of group 1 were 90.0%, 70.0%, and 42.0%, and those of group 2 were 36.0%, 36.0%, and 0%, respectively (P = 0.014). Thrombectomy and infiltrative growth type (Ig) were found as independent prognostic factors for recurrence free survival by multivariate analysis. Thrombectomy, Ig, and high indocyanine green retention rate at 15 minutes were found as independent prognostic factors for overall survival by multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
We suggest that the appropriate surgical procedure for icteric HCC patients should be comprised of ipsilateral hemihepatectomy with caudate lobectomy and extrahepatic bile duct resection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin TY. Tumor of the liver. In : Bockus HL, editor. Gastroenterology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1976. p. 522–533.2. Clark W, Schulz MD. Hepatoma, with invasion of cystic duct and metastasis to third lumbar vertebra. N Engl J Med. 1947; 237:673–676.3. Edmondson HA. Tumors of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts. Washington: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;1958.4. Creed DL, Fisher ER. Clot formation in the common duct; an unusual manifestation of primary hepatic carcinoma. AMA Arch Surg. 1956; 73:261–265.5. Tsuzuki T, Ogata Y, Iida S, Kasajima M, Takahashi S. Hepatoma with obstructive jaundice due to the migration of a tumor mass in the biliary tract: report of a successful resection. Surgery. 1979; 85:593–598.6. Lau WY, Leung JW, Li AK. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma presenting as obstructive jaundice. Am J Surg. 1990; 160:280–282.7. Ueda M, Takeuchi T, Takayasu T, Takahashi K, Okamoto S, Tanaka A, et al. Classification and surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with bile duct thrombi. Hepatogastroenterology. 1994; 41:349–354.8. Kojiro M, Kawabata K, Kawano Y, Shirai F, Takemoto N, Nakashima T. Hepatocellular carcinoma presenting as intrabile duct tumor growth: a clinicopathologic study of 24 cases. Cancer. 1982; 49:2144–2147.9. Liu Q, Chen J, Li H, Liang B, Zhang L, Hu T. Hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombi: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging features to histopathologic manifestations. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 76:103–109.10. Taguchi H, Ogino T, Miyata A, Munehisa T. Bile duct invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1983; 80:2259–2268.11. Wang HJ, Kim JH, Kim JH, Kim WH, Kim MW. Hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the bile duct. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999; 46:2495–2499.12. Shiomi M, Kamiya J, Nagino M, Uesaka K, Sano T, Hayakawa N, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary tumor thrombi: aggressive operative approach after appropriate preoperative management. Surgery. 2001; 129:692–698.13. Huang JF, Wang LY, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Hsieh MY, Chuang WL, et al. Incidence and clinical outcome of icteric type hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17:190–195.14. Satoh S, Ikai I, Honda G, Okabe H, Takeyama O, Yamamoto Y, et al. Clinicopathologic evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct thrombi. Surgery. 2000; 128:779–783.15. Peng SY, Wang JW, Liu YB, Cai XJ, Deng GL, Xu B, et al. Surgical intervention for obstructive jaundice due to biliary tumor thrombus in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2004; 28:43–46.16. Mok KT, Chang HT, Liu SI, Jou NW, Tsai CC, Wang BW. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary tumor thrombi. Int Surg. 1996; 81:284–288.17. Moon DB, Hwang S, Wang HJ, Yun SS, Kim KS, Lee YJ, et al. Surgical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus: a Korean multicenter study. World J Surg. 2013; 37:443–451.18. Ha TY, Hwang S, Moon DB, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Song GW, et al. Long-term survival analysis of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus. Transplant Proc. 2014; 46:774–777.19. Lee KW, Park JW, Park JB, Kim SJ, Choi SH, Heo JS, et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct thrombi. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:2093–2094.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bile Duct Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- CT feature of bile duct invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Percutaneous placement of self-expandable metallic stents in patients with obstructive jaundice due to hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bile duct invasion can be an independent prognostic factor in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- Common Bile Duct Obstruction Caused by Tumor Thrombus after Trans-arterial Chemoembolization in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient