J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Feb;74(2):105-113. 10.3348/jksr.2016.74.2.105.
Effect of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty on the Stenosis of Autogenous Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. ho7ok7@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Vascular Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Seonam University College of Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2152602
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.2.105
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) on stenosis of autogenous radiocephalic arteriovenous fistula (RCF) for hemodialysis and to determine the factors influencing patency.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective study included 136 patients referred for PTA of RCF stenosis between March 2005 and July 2014. The technical success rate, complications, and patency rate were evaluated. The following factors were analyzed as they might influence patency: age, gender, site and duration of arteriovenous fistula, underlying disease, body mass index, hypercholesterolemia, smoking, peripheral artery or coronary artery occlusive disease, stenosis length/grade, cutting balloon, and balloon size.
RESULTS
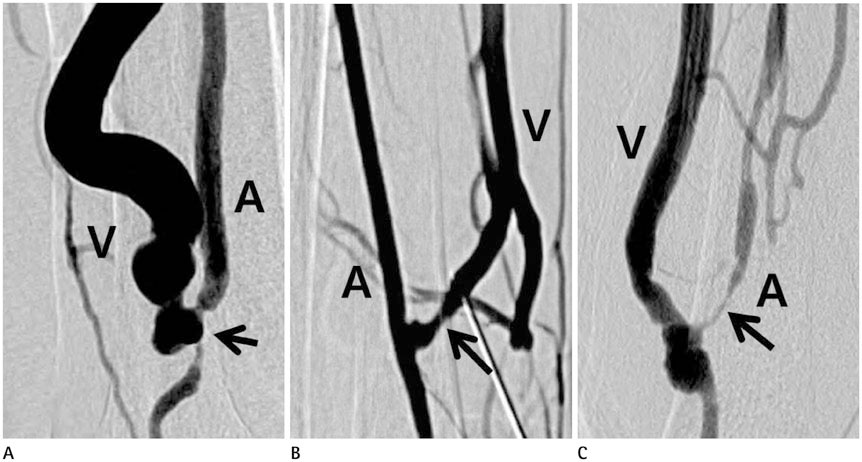
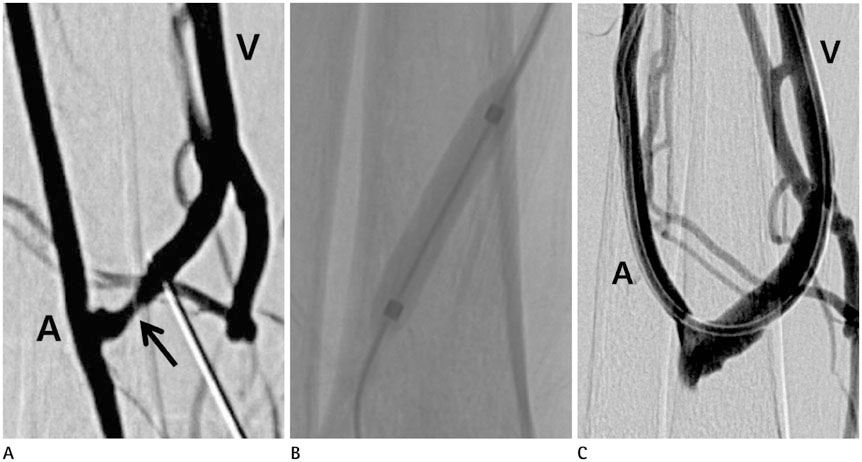
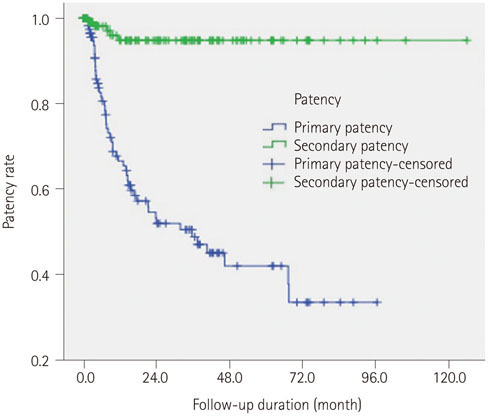
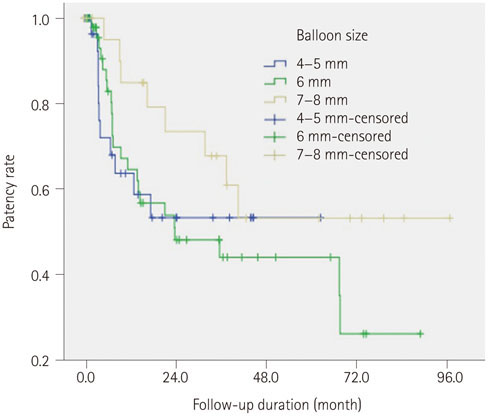
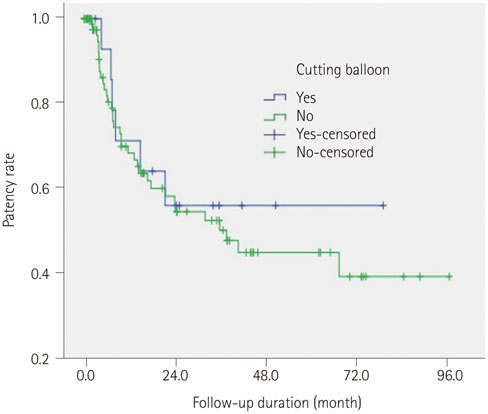
The initial technical success rate was 91.9% (125/136). Complications included vessel rupture (n = 2) and vessel dissection (n = 2). The patency rates at 6, 12, 24, and 48 months after PTA were 81.9, 67.1, 52.7, and 42.3%, respectively. The patency rate was higher in cases with longer (> 3 cm) stenosis (p = 0.04). Use of cutting balloon and larger size of balloon catheter made the patency longer, but this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.637, 0.258).
CONCLUSION
PTA is a safe and effective way to manage stenosis in RCF. The length of stenosis was the only factor which affected the patency rate in this study.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effectiveness and Influencing Factors of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty for Stenosis of Transposed Brachiobasilic Arteriovenous Fistula
Dahye Shin, Yong Jae Kim, Seung Boo Yang, Jae Myeong Lee, Woong Hee Lee, Dong Erk Goo
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2019;80(3):477-489. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2019.80.3.477.
Reference
-
1. Berkoben M, Schwab SJ. Maintenance of permanent hemodialysis vascular access patency. ANNA J. 1995; 22:17–24.2. Porile JL, Richter M. Preservation of vascular access. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993; 4:997–1003.3. Fan PY, Schwab SJ. Vascular access: concepts for the 1990s. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992; 3:1–11.4. Turmel-Rodrigues L, Pengloan J, Baudin S, Testou D, Abaza M, Dahdah G, et al. Treatment of stenosis and thrombosis in haemodialysis fistulas and grafts by interventional radiology. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000; 15:2029–2036.5. Manninen HI, Kaukanen ET, Ikäheimo R, Karhapää P, Lahtinen T, Matsi P, et al. Brachial arterial access: endovascular treatment of failing Brescia-Cimino hemodialysis fistulas--initial success and long-term results. Radiology. 2001; 218:711–718.6. Kim YO, Yoon SA, Kim YS, Kim MK, Oh HJ, Ku YM, et al. Early dysfunction of radiocephalic arteriovenous fistula: primary and secondary patency rate of percutaneous angioplasty. Korean J Nephrol. 2003; 22:414–419.7. Long B, Brichart N, Lermusiaux P, Turmel-Rodrigues L, Artru B, Boutin JM, et al. Management of perianastomotic stenosis of direct wrist autogenous radial-cephalic arteriovenous accesses for dialysis. J Vasc Surg. 2011; 53:108–114.8. Heye S, Maleux G, Vaninbroukx J, Claes K, Kuypers D, Oyen R. Factors influencing technical success and outcome of percutaneous balloon angioplasty in de novo native hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulas. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:2298–2303.9. Choi CS, Goo DE, Kim KS, Kim HH, Kim DH, Choi DL, et al. Effect of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in insufficiency of arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999; 40:1105–1111.10. Jung YS, Kim MD, Shin HS, Jung GS, Yoo CH, Kim HK, et al. The effect of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty on hemodialysis shunt insufficiency. Korean J Nephrol. 2002; 21:276–284.11. Kariya S, Tanigawa N, Kojima H, Komemushi A, Shomura Y, Shiraishi T, et al. Primary patency with cutting and conventional balloon angioplasty for different types of hemodialysis access stenosis. Radiology. 2007; 243:578–587.12. Beathard GA, Arnold P, Jackson J, Litchfield T. Physician Operators Forum of RMS Lifeline. Aggressive treatment of early fistula failure. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:1487–1494.13. Gray RJ, Sacks D, Martin LG, Trerotola SO. Society of Interventional Radiology Technology Assessment Committee. Reporting standards for percutaneous interventions in dialysis access. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14(9 Pt 2):S433–S442.14. Lay JP, Ashleigh RJ, Tranconi L, Ackrill P, Al-Khaffaf H. Result of angioplasty of brescia-cimino haemodialysis fistulae: medium-term follow-up. Clin Radiol. 1998; 53:608–611.15. Vascular Access 2006 Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006; 48:Suppl 1. S176–S247.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of an Immature Autogenous Arteriovenous Fistula with Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty
- Successful Treatment of Resistant Arteriovenous Fistula Stenosis by Cutting Balloon Angioplasty
- Early Dysfunction of Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula: Primary and Secondary Patency Rate of Percutaneous Angioplasty
- A case of arteriovenous fistula with drainage into the coronary sinus during the percutaneous tranluminal coronary angioplasty of chronic total occlusion of circumflex coronary artery
- Intervention of the Dysfunctional and Thrombosed Autogenous Vascular Access