Electrolyte Blood Press.
2015 Dec;13(2):58-61. 10.5049/EBP.2015.13.2.58.
Spinning-induced Rhabdomyolysis: Eleven Case Reports and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. dhyang@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2152088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2015.13.2.58
Abstract
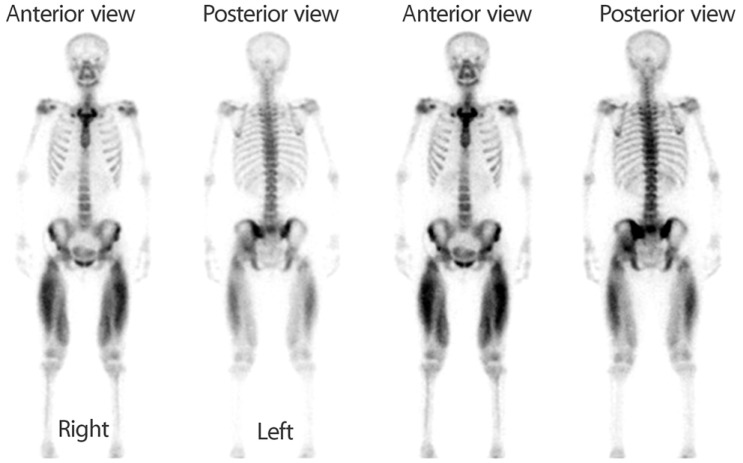
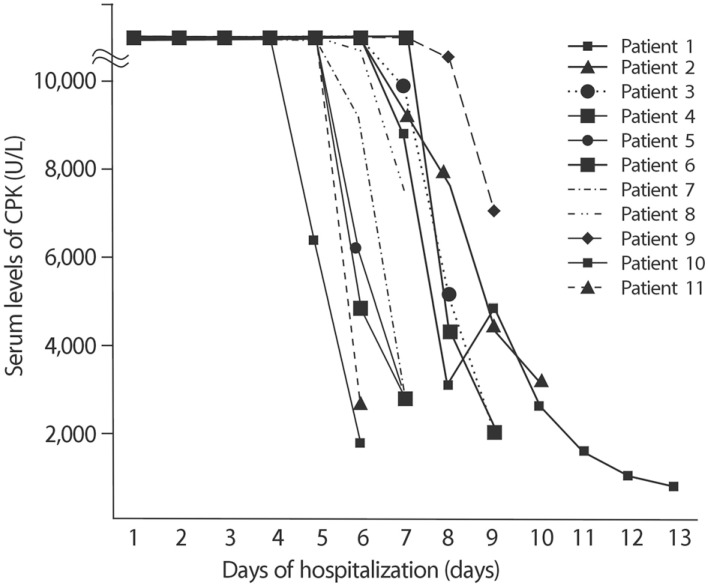
- Non-traumatic exertional rhabdomyolysis (exRML) occurs in individuals with normal muscles when the energy supplied to the muscle is insufficient. Here, we report 11 cases of spinning-induced rhabdomyolysis and review related literature. Spinning is a kind of indoor bicycle sport. The 11 patients who were diagnosed with exRML and admitted to CHA Bundang Medical Center were female and their ages ranged from 15 to 46 years. Two to three days prior to the presentation, the patients had attended a spinning class for the first time. All the patients had been otherwise healthy without any known medical illnesses. They were successfully treated without any complications, except mild non-symptomatic hypocalcemia. However, in the literature, severe complications such as compartment syndrome or acute kidney injury had been reported in relation to exRML including spinning-induced rhabdomyolysis. This spinning exercise needs prior guidelines and specific warnings to prevent exertional rhabdomyolysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Melli G, Chaudhry V, Cornblath DR. Rhabdomyolysis: an evaluation of 475 hospitalized patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84:377–385. PMID: 16267412.2. Giannoglou GD, Chatzizisis YS, Misirli G. The syndrome of rhabdomyolysis: Pathophysiology and diagnosis. Eur J Intern Med. 2007; 18:90–100. PMID: 17338959.
Article3. Kim J, Lee J, Kim S, Ryu HY, Cha KS, Sung DJ. Exerciseinduced rhabdomyolysis mechanisms and prevention: A literature review. J Sport Health Sci. 2015; 1–11.
Article4. DeFilippis EM, Kleiman DA, Derman PB, DiFelice GS, Eachempati SR. [Primary care] Spinning-induced rhabdomyolysis and the risk of compartment syndrome and acute kidney injury: Two cases and a Review of the Literature. Sports Health. 2014; 6:333–335. PMID: 24982706.5. Walter C, Tannander AB. Complete idiot's guide to fitness. 1st ed. New York: Alpha Books;2000. p. 148–149.6. Bagley WH, Yang H, Shah KH. Rhabdomyolysis. Intern Emerg Med. 2007; 2:210–218. PMID: 17909702.
Article7. Young IM, Thomson K. Spinning-induced rhabdomyolysis: a case report. Eur J Emerg Med. 2004; 11:358–359. PMID: 15542997.
Article8. Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012; 380:756–766. PMID: 22617274.
Article9. Petejova N, Martinek A. Acute kidney injury due to rhabdomyolysis and renal replacement therapy: a critical review. Crit Care. 2014; 18:224. PMID: 25043142.
Article10. Heyne N, Guthoff M, Krieger J, Haap M, Häring HU. High cut-off renal replacement therapy for removal of myoglobin in severe rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury: a case series. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012; 121:c159–c164. PMID: 23327834.
Article11. Amyot SL, Leblanc M, Thibeault Y, Geadah D, Cardinal J. Myoglobin clearance and removal during continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Intensive Care Med. 1999; 25:1169–1172. PMID: 10551978.
Article