Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):208-214. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.208.
Effect of Low Magnetic Field on Dose Distribution in the Partial-Breast Irradiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. leodavinci@naver.com
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Center for Convergence Research on Robotics, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Interdisciplinary Program in Radiation Applied Life Science, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2151753
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.208
Abstract
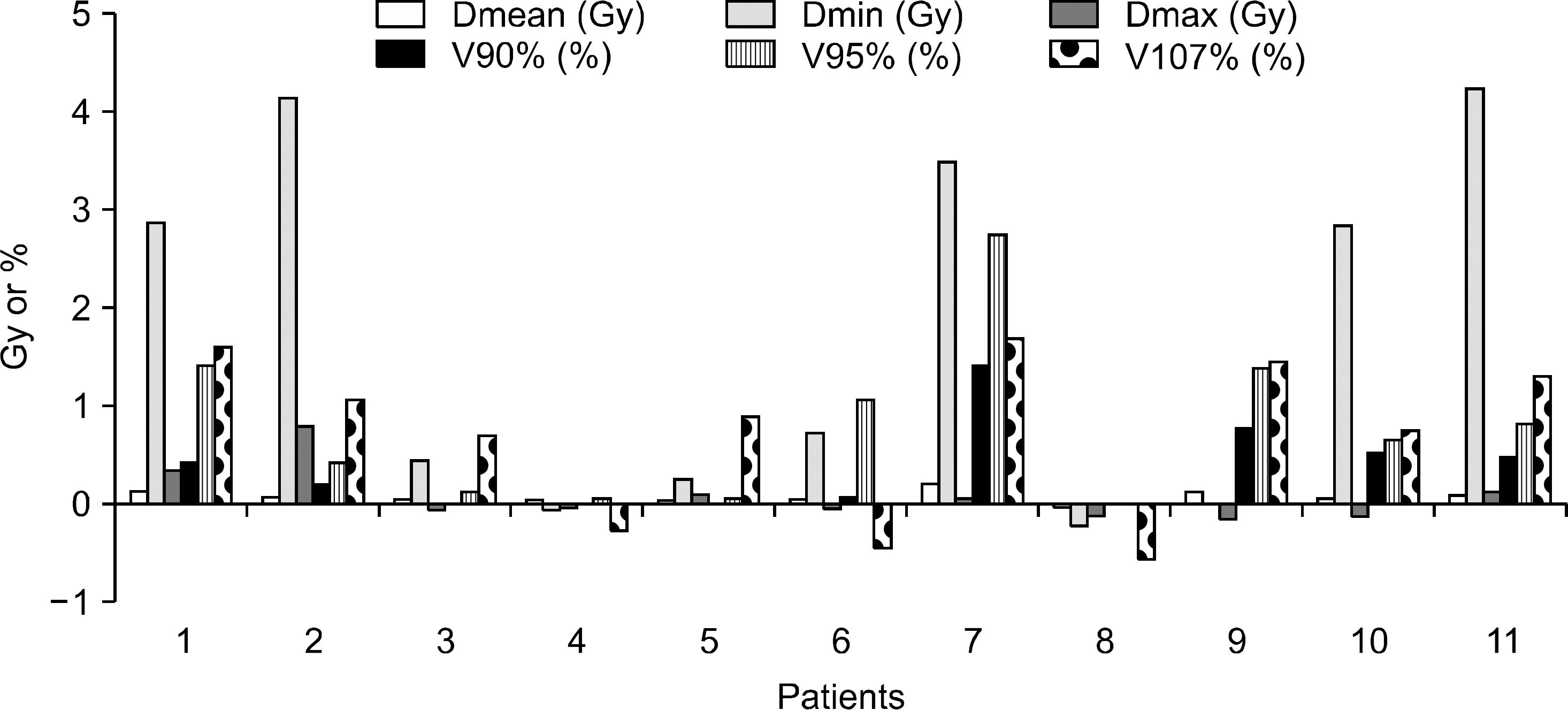
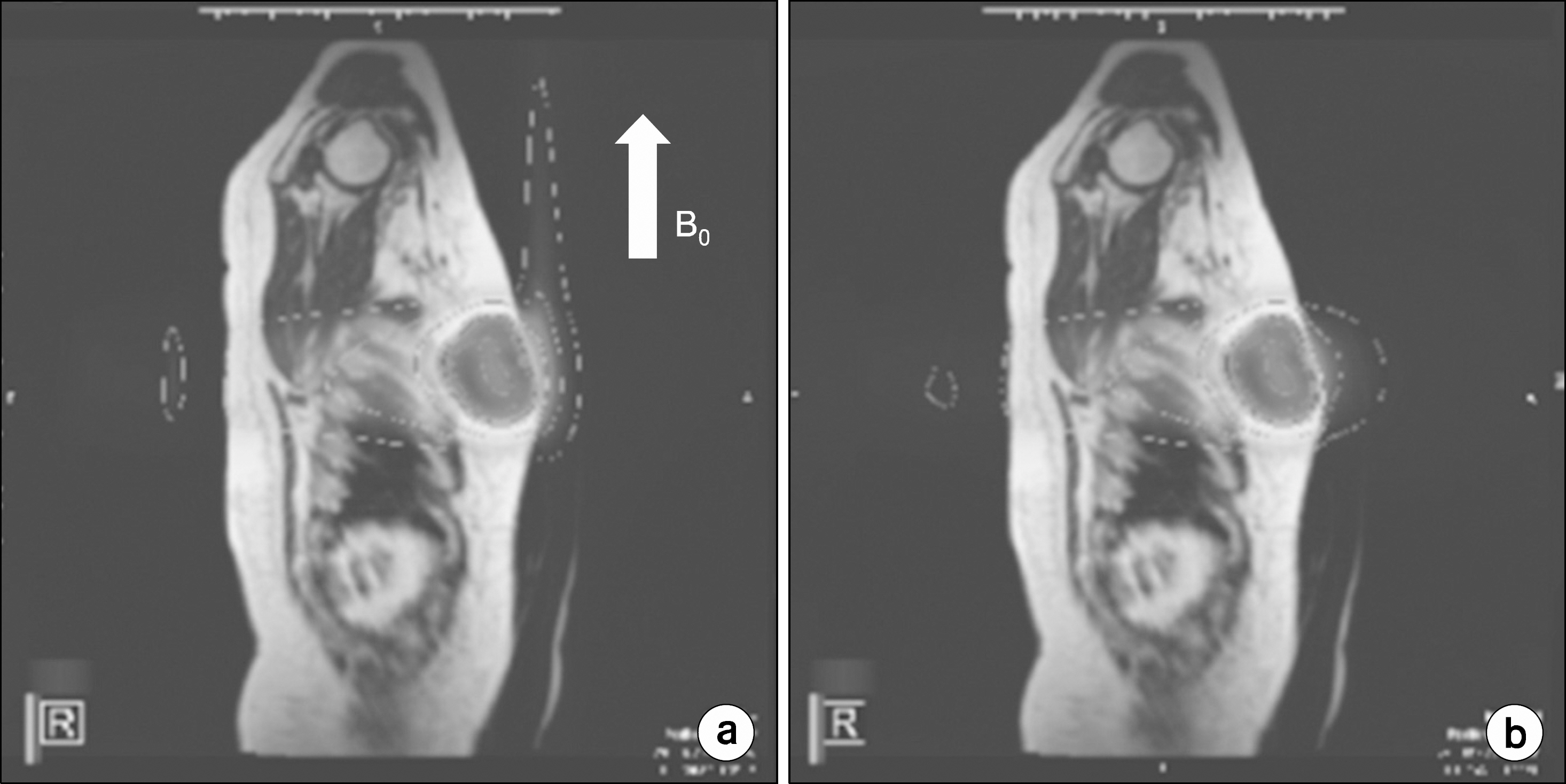
- The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of low magnetic field on dose distribution in the partial-breast irradiation (PBI). Eleven patients with an invasive early-stage breast carcinoma were treated prospectively with PBI using 38.5 Gy delivered in 10 fractions using the ViewRay(R) system. For each of the treatment plans, dose distribution was calculated with magnetic field and without magnetic field, and the difference between dose and volume for each organ were evaluated. For planning target volume (PTV), the analysis included the point minimum (Dmin), maximum, mean dose (Dmean) and volume receiving at least 90% (V90%), 95% (V95%) and 107% (V107%) of the prescribed dose, respectively. For organs at risk (OARs), the ipsilateral lung was analyzed with Dmean and the volume receiving 20 Gy (V20 Gy), and the contralateral lung was analyzed with only Dmean. The heart was analyzed with Dmean, Dmax, and V20 Gy, and both inner and outer shells were analyzed with the point Dmin, Dmax and Dmean, respectively. For PTV, the effect of low magnetic field on dose distribution showed a difference of up to 2% for volume change and 4 Gy for dose. In OARs analysis, the significant effect of the magnetic field was not observed. Despite small deviation values, the average difference of mean dose values showed significant difference (p<0.001), but there was no difference of point minimum dose values in both sehll structures. The largest deviation for the average difference of Dmax in the outer shell structure was 5.0+/-10.5 Gy (p=0.148). The effect of low magnetic field of 0.35 T on dose deposition by a Co-60 beam was not significantly observed within the body for PBI IMRT plans. The dose deposition was only appreciable outside the body, where a dose build-up due to contaminated electrons generated in the treatment head and scattered electrons formed near the body surface.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Low Magnetic Field on Dose Distribution in the SABR Plans for Liver Cancer
Jaeman Son, Minsoo Chun, Hyun Joon An, Seong-Hee Kang, Eui Kyu Chie, Jeongmin Yoon, Chang Heon Choi, Jong Min Park, Jung-in Kim
Prog Med Phys. 2018;29(2):47-52. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2018.29.2.47.
Reference
-
References
1. Beitsch PD, Shaitelman SF, Vicini FA. Accelerated partial breast irradiation. J Surg Oncol. 103(4):362–368. 2011.
Article2. Alvarez C. Accelerated partial breast irradiation. J Am Coll Surg. 209(6):795–796. 2009.
Article3. McIntosh A, Read PW, Khandelwal SR, et al. Evaluation of coplanar partial left breast irradiation using tomotherapy-based topotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 71(2):603–610. 2008.
Article4. Kozak KR, Smith BL, Adams J, et al. Accelerated partial-breast irradiation using proton beams: initial clinical experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 66(3):691–698. 2006.
Article5. Wilder RB, Curcio LD, Khanijou RK, et al. A Contura catheter offers dosimetric advantages over a MammoSite catheter that increase the applicability of accelerated partial breast irradiation. Brachytherapy. 8(4):373–378. 2009.
Article6. Weed DW, Edmundson GK, Vicini FA, et al. Accelerated partial breast irradiation: a dosimetric comparison of three different techniques. Brachytherapy. 4(2):121–129. 2005.
Article7. Stewart AJ, Khan AJ, Devlin PM. Partial breast irradiation: a review of techniques and indications. Br J Radiol. 83(989):369–378. 2010.
Article8. Mydin AR, Gaffney H, Bergman A, et al. Does a three-field electron/minitangent photon technique offer dosimetric advantages to a multifield, photon-only technique for accelerated partial breast irradiation? Am J Clin Oncol. 33(4):336–340. 2010.
Article9. Bourgier C, Taghian A, Marsiglia H. Three-field electron/minitangent photon technique offer dosimetric advantages to a multifield, photon-only technique for accelerated partial breast irradiation if well implemented. Am J Clin Oncol. 34(6):648. 2011.
Article10. Vera R, Trombetta M, Mukhopadhyay ND, et al. Long-term cosmesis and toxicity following 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy in the delivery of accelerated partial breast irradiation. Pract Radiat Oncol. 4(3):147–152. 2014.
Article11. Galland-Girodet S, Pashtan I, MacDonald SM, et al. Long-term cosmetic outcomes and toxicities of proton beam therapy compared with photon-based 3-dimensional conformal accelerated partial-breast irradiation: a phase 1 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 90(3):493–500. 2014.
Article12. Mutic S, Dempsey JF. The ViewRay system: magnetic resonance-guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24(3):196–199. 2014.
Article13. Rubinstein AE, Liao Z, Melancon AD, et al. Technical Note: A Monte Carlo study of magnetic-field-induced radiation dose effects in mice. Med Phys. 42(9):5510–5516. 2015.
Article14. Burke B, Ghila A, Fallone BG, et al. Radiation induced current in the RF coils of integrated linac-MR systems: the effect of buildup and magnetic field. Med Phys. 39(8):5004–5014. 2012.
Article15. Kirkby C, Stanescu T, Fallone BG. Magnetic field effects on the energy deposition spectra of MV photon radiation. Phys Med Biol. 54(2):243–257. 2009.
Article16. Wen Z, Pelc NJ, Nelson WR, et al. Study of increased radiation when an x-ray tube is placed in a strong magnetic field. Med Phys. 34(2):408–418. 2007.
Article17. Shen CS. adiation problems in a strong magnetic field. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 257:44–55. 1975.18. Al-Basheer AK, Sjoden GE, Ghita M. Electron Dose Kernels to Account for Secondary article Transport in Deterministic Simulations. Nucl Technol. 168(3):906–918. 2009.19. Kim JO, Kim JK. ose equivalent per unit fluence near the surface of the ICRU phantom by including the secondary electron transport for photons. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 83(3):211–219. 1999.20. Raaijmakers AJE, Raaymakers BW, Lagendijk JJW. Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotherapy accelerator: dose increase at tissue-air interfaces in a lateral magnetic field due to returning electrons. Phys Med Biol. 50(7):1363–1376. 2005.
Article21. Esmaeeli AD, Pouladian M, Monfared AS, et al. Effect of uniform magnetic field on dose distribution in the breast radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Res. 12(2):151–160. 2014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Virtual Wedge versus Physical Wedge Affecting on Dose Distribution of Treated Breast and Adjacent Normal Tissue for Tangential Breast Irradiation
- A Study on Dose Distribution using Virtual Wedge in Breast Cancer
- Effect of Low Magnetic Field on Dose Distribution in the SABR Plans for Liver Cancer
- The Dose Distribution of Arc therapy for High Energy Electron
- Dosimetric Characteristics of Dynamic Wedge Techinique