Commissioning Experience of Tri-Cobalt-60 MRI-guided Radiation Therapy System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. madangin@gmail.com
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Center for Convergence Research on Robotics, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Interdisciplinary Program in Radiation Applied Life Science, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2151751
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.193
Abstract
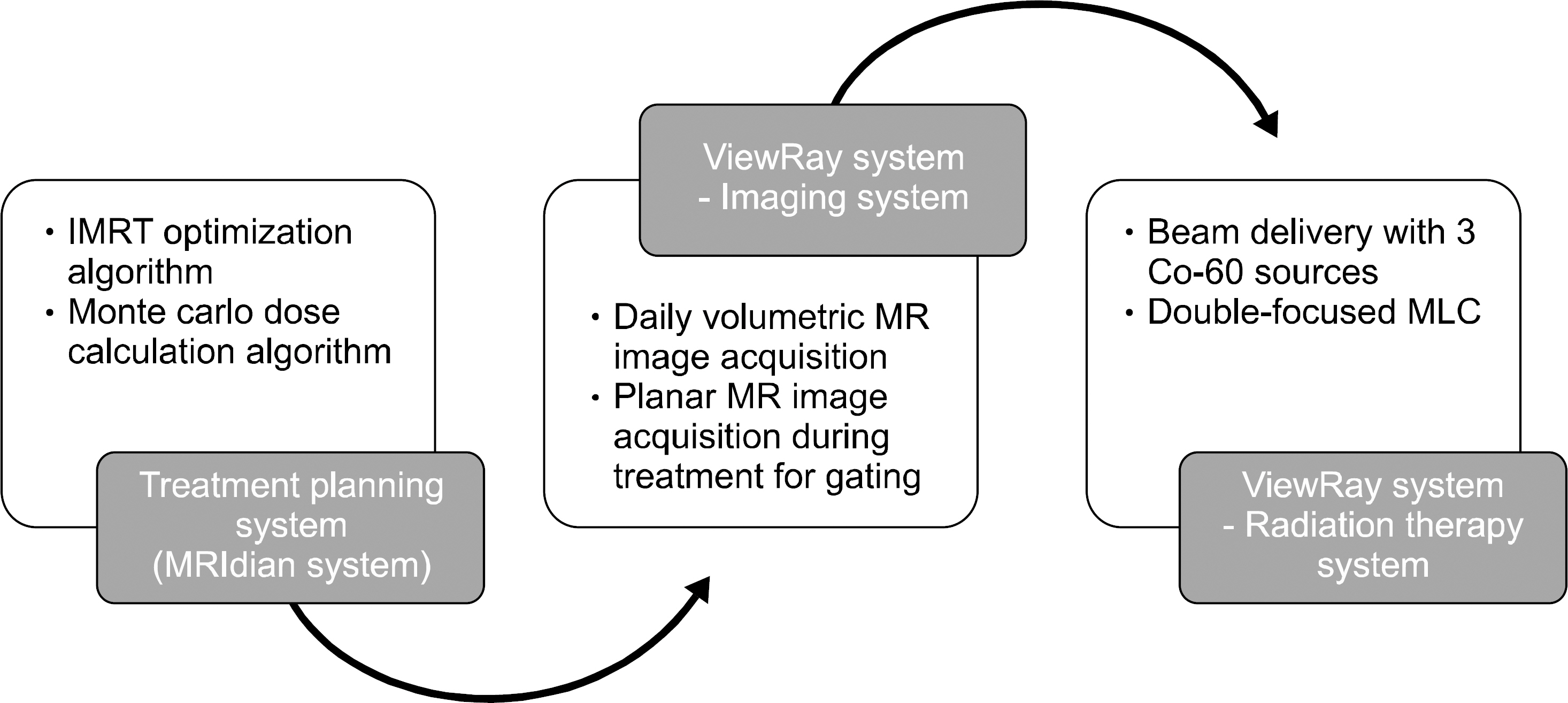
- The aim of this study is to present commissioning results of the ViewRay system. We verified safety functions of the ViewRay system. For imaging system, we acquired signal to noise ratio (SNR) and image uniformity. In addition, we checked spatial integrity of the image. Couch movement accuracy and coincidence of isocenters (radiation therapy system, imaging system and virtual isocneter) was verified. Accuracy of MLC positioing was checked. We performed reference dosimetry according to American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) Task Group 51 (TG-51) in water phantom for head 1 and 3. The deviations between measurements and calculation of percent depth dose (PDD) and output factor were evaluated. Finally, we performed gamma evaluations with a total of 8 IMRT plans as an end-to-end (E2E) test of the system. Every safety system of ViewRay operated properly. The values of SNR and Uniformity met the tolerance level. Every point within 10 cm and 17.5 cm radii about the isocenter showed deviations less than 1 mm and 2 mm, respectively. The average couch movement errors in transverse (x), longitudinal (y) and vertical (z) directions were 0.2 mm, 0.1 mm and 0.2 mm, respectively. The deviations between radiation isocenter and virtual isocenter in x, y and z directions were 0 mm, 0 mm and 0.3 mm, respectively. Those between virtual isocenter and imaging isocenter were 0.6 mm, 0.5 mm and 0.2 mm, respectively. The average MLC positioning errors were less than 0.6 mm. The deviations of output, PDDs between mesured vs. BJR supplement 25, PDDs between measured and calculated and output factors of each head were less than 0.5%, 1%, 1% and 2%, respectively. For E2E test, average gamma passing rate with 3%/3 mm criterion was 99.9%+/-0.1%.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Low Magnetic Field MRI Visibility of Rubber-Based Markers
Jeong Ho Kim, Seongmoon Jung, Jung-in Kim
Prog Med Phys. 2019;30(4):89-93. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2019.30.4.89.Treatment Plan Delivery Accuracy of the ViewRay System in Two-Headed Mode
Jong Min Park, So-Yeon Park, Hong-Gyun Wu, Jung-in Kim
Prog Med Phys. 2016;27(3):169-174. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.3.169.Implementation of AAPM's TG-51 Protocol on Co-60 MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy System
Jin Dong Cho, Jong Min Park, Chang Heon Choi, Jung-in Kim, Hong-Gyun Wu, So-Yeon Park
Prog Med Phys. 2017;28(4):190-196. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2017.28.4.190.Efficient Verification of X-ray Target Replacement for the C-series High Energy Linear Accelerator
Jin Dong Cho, Minsoo Chun, Jaeman Son, Hyun Joon An, Jeongmin Yoon, Chang Heon Choi, Jung-in Kim, Jong Min Park, Jin Sung Kim
Prog Med Phys. 2018;29(3):92-100. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2018.29.3.92.
Reference
-
References
1. Stam MK, van Vulpen M, Barendrecht MM, et al. Kidney motion during free breathing and breath hold for MR-guided radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 58(7):2235–2245. 2013.
Article2. Seierstad T, Hole KH, Saelen E, et al. MR-guided simultaneous integrated boost in preoperative radiotherapy of locally advanced rectal cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 93(2):279–284. 2009.
Article3. Mutic S, Dempsey JF. The ViewRay system: magnetic resonance-guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24(3):196–199. 2014.
Article4. Wooten HO, Green O, Yang M, et al. Quality of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Treatment Plans Using a Co-60 Magnetic Resonance Image Guidance Radiation Therapy System. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 92(4):771–778. 2015.5. Wooten HO, Rodriguez V, Green O, et al. Benchmark IMRT evaluation of a Co-60 MRI-guided radiation therapy system. Radiother Oncol. 114(3):402–405. 2015.
Article6. Kishan AU, Cao M, Wang PC, et al. Feasibility of magnetic resonance imaging-guided liver stereotactic body radiation therapy: A comparison between modulated tri-cobalt-60 teletherapy and linear accelerator-based intensity modulated radiation therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol. 5(5):330–337. 2015.
Article7. Rajiv L, Gopi K, Sathish K. Acceptance Test Procedure for MRIdian System. ViewRay Inc., Cleveland, OH (. 2015.8. Attix FH. Introduction to radiological physics and radiation dosimetry. 1st ed., Wiley, New York, NY (. 1986.9. Day M, EGA A. Central axis depth dose data for use in radiotherapy: A survey of depth doses and related data measured in water or equivalent media. Brit J Radiol Suppl. 17:1–147. 1983.10. Ezzell GA, Burmeister JW, Dogan N, et al. IMRT commissioning: multiple institution planning and dosimetry comparisons, a report from AAPM Task Group 119. Med Phys. 36(11):5359–5373. 2009.
Article11. Almond PR, Biggs PJ, Coursey BM, et al. AAPM's TG-51 protocol for clinical reference dosimetry of high-energy photon and electron beams. Med Phys. 26(9):1847–1870. 1999.
Article12. Klein EE, Hanley J, Bayouth J, et al. Task Group 142 report: quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med Phys. 36(9):4197–4212. 2009.13. Kutcher GJ, Coia L, Gillin M, et al. Comprehensive QA for radiation oncology: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 40. Med Phys. 21(4):581–618. 1994.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Commissioning and Validation of a Dedicated Scanning Nozzle at Samsung Proton Therapy Center
- Effect of 5-fluorouracil on carcinoma of the bladder
- Study on the Reduction of Electron Contamination with A Cobalt-60 Gamma Ray
- Evaluation of Treatment Plan Quality between Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiotherapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- Practical Considerations in Preparing an Institutional Procedure of Image Guided Radiation Therapy