J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2015 Dec;22(4):153-159. 10.4184/jkss.2015.22.4.153.
Relationship of the Pre-operative Condition of Paravertebral Muscle with Post-operative Functional Disability in Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea. husucabi@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2150542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2015.22.4.153
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study on the outcomes of surgical treatment for degenerative lumbar spinal disease.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the pre-operative paravertebral muscle condition as a predictive factor in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal disease who undergo surgery. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Previous studies have reported that the atrophy of the paravertebral muscle is associated with chronic low back pain. However, few studies have reported on the relationship of the pre-operative paravertebral muscle status with the postoperative functional disability scale.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this study, we reviewed the history of 20 patients with degenerative lumbar spinal disease treated by decompression and posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior instrumentation between 2010 and 2011. The evaluation included the paravertebral muscle volume, fat infiltration on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), preoperative lumbar lordosis, levels operated on, and the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI). Further, the inter-relationship of the pre-operative paravertebral muscle status, lumbar lordosis, and levels operated on with the post-operative ODI was analyzed.
RESULTS
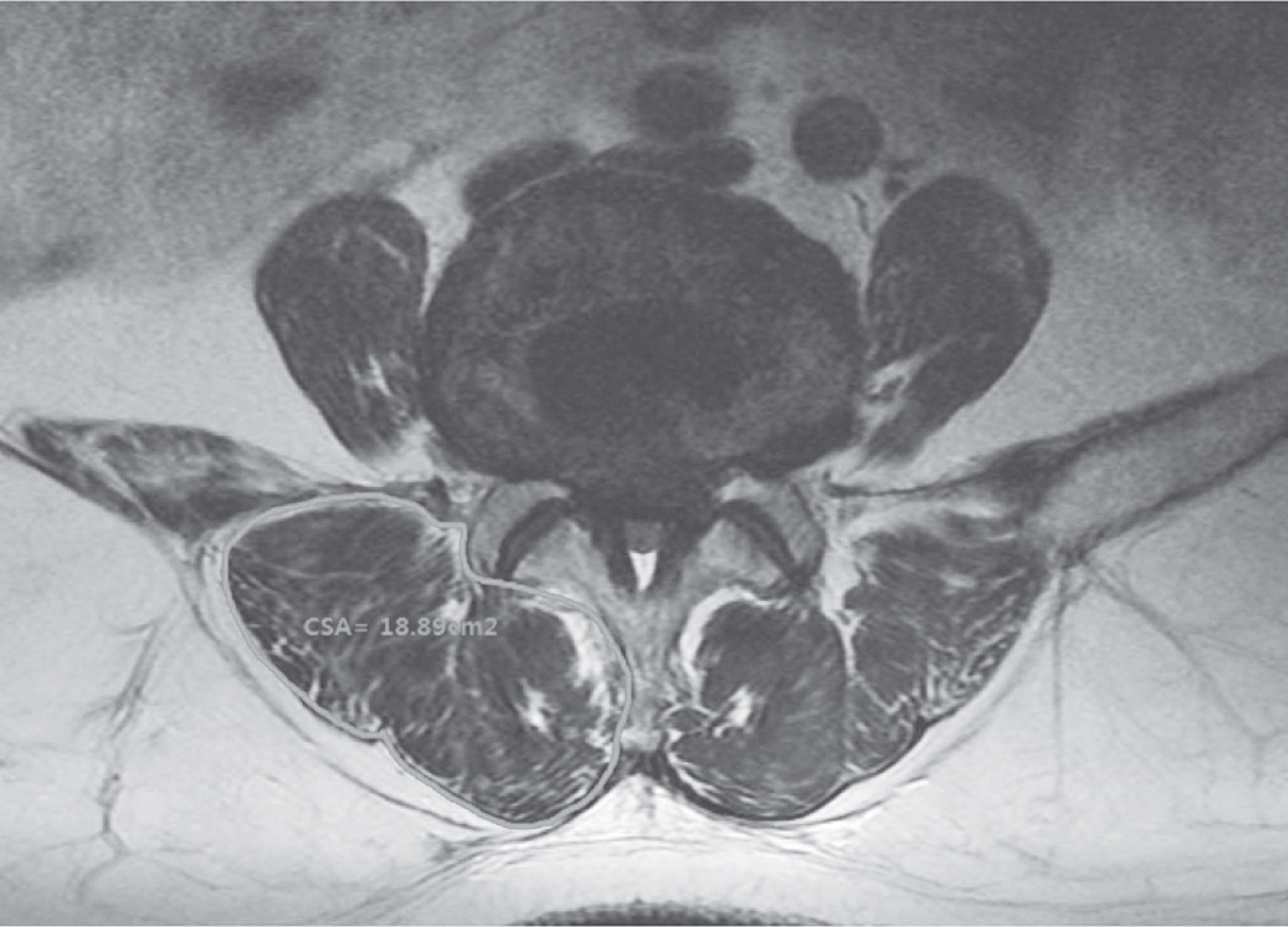
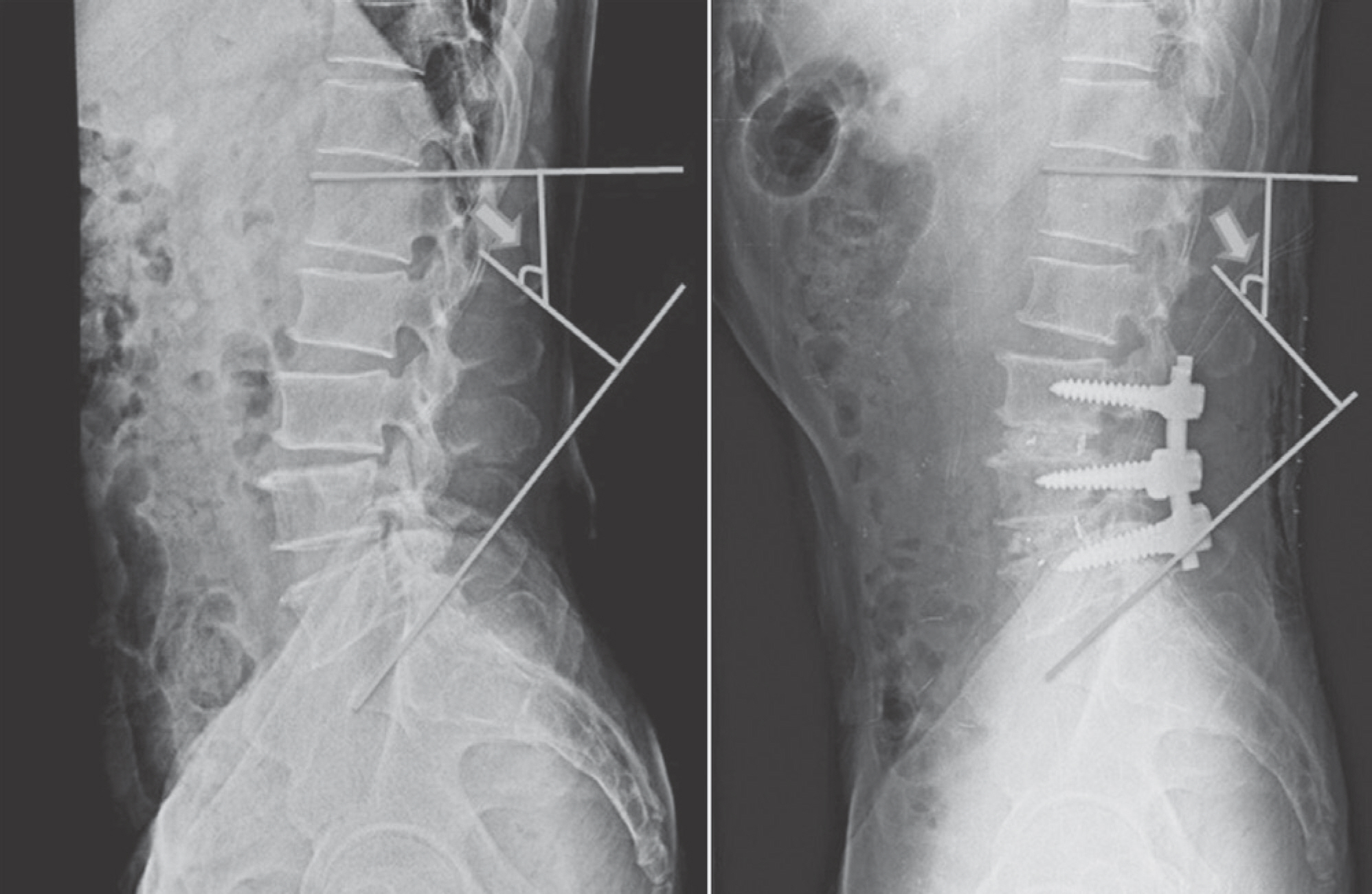
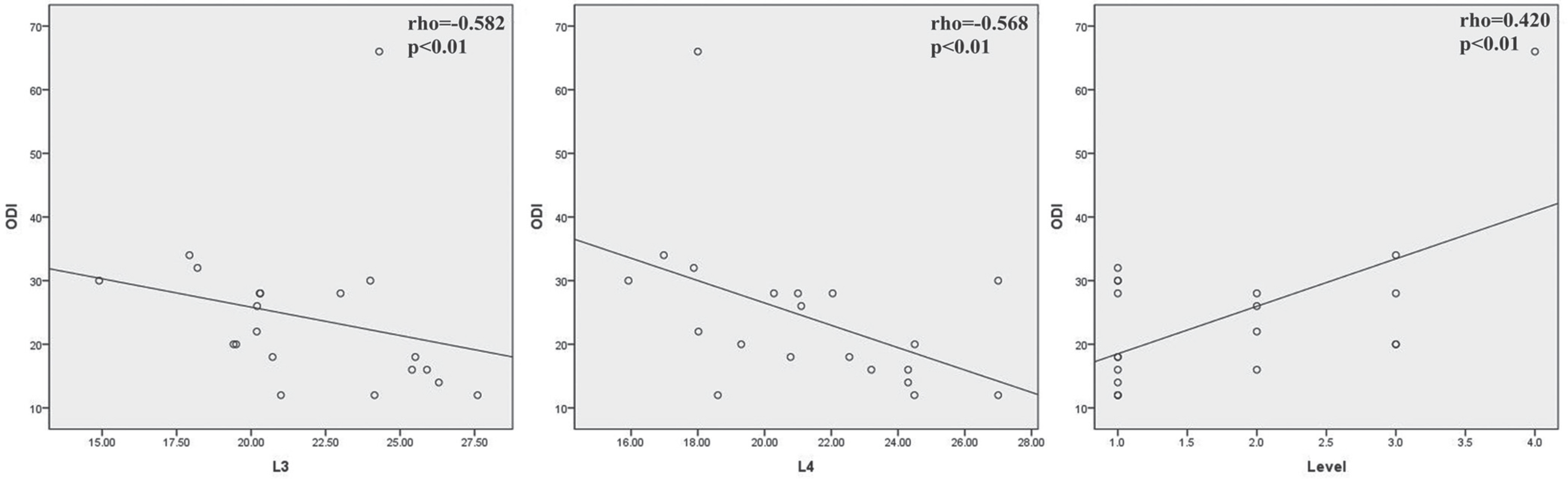
The mean cross-sectional area (CSA) of the paravertebral muscle at the L3-4 and L4-5 levels was 21.9+/-3.4 cm2 and 21.4+/-3.3 cm2, respectively. The mean pre- and post-operative lumbar lordotic angle was 41.0+/-17.5degrees, and 42.3+/-11.1degrees, respectively. The lumbar lordotic angle and the levels operated on were not correlated with the post-operative ODI. However, the CSA of the paravertebral muscle at the L3-4 (r=-0.582, p<0.01) and L4-5 (r=-0.568, p<0.01) levels showed a negative correlation with the post-operative ODI. The levels operated on showed a positive correlation with the post-operative ODI (r=0.420, p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
The mean CSA of the paravertebral muscle and the levels operated on in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal disease have a significant correlation with the post-operative clinical outcome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nasca RJ. Surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12(8):809–16.
Article2. Mofidi A, O'Connor D, El-Abed K, et al. Functional outcome study of patients after surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: effects of concomitant pathology. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002; 15(5):377–83.
Article3. Katz JN, Stucki G, Lipson SJ, et al. Predictors of surgical outcome in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24(21):2229.
Article4. Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, et al. Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: attempted meta-analysis of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992; 17(1):1–8.5. Ng LC, Tafazal S, Sell P. The effect of duration of symptoms on standard outcome measures in the surgical treatment of spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16(2):199–206.
Article6. Herno A, Airaksinen O, Saari T, et al. The effect of prior back surgery on surgical outcome in patients operated on for lumbar spinal stenosis A matched-pair study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138(4):357–63.
Article7. Lee HI, Song J, Lee HS, et al. Association between crosssectional areas of lumbar muscles on magnetic resonance imaging and chronicity of low back pain. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35(6):852–9.
Article8. Ploumis A, Michailidis N, Christodoulou P, et al. Ipsilateral atrophy of paraspinal and psoas muscle in unilateral back pain patients with monosegmental degenerative disc disease. Br J Radiol. 2011; 84(1004):709–13.
Article9. Kang CH, Shin MJ, Kim SM, et al. MRI of paraspinal muscles in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients and control patients with chronic low back pain. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62(5):479–86.
Article10. Hu ZJ, He J, Zhao FD, et al. An assessment of the intra-and inter-reliability of the lumbar paraspinal muscle parameters using CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(13):E868–74.11. Hides J, Gilmore C, Stanton W, et al. Multifidus size and symmetry among chronic LBP and healthy asymptomatic subjects. Man Ther. 2008; 13(1):43–9.
Article12. Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, et al. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionaire. Physiotherapy. 1980; 66(8):271–3.13. Kader DF, Wardlaw D, Smith FW. Correlation between the MRI changes in the lumbar multifidus muscles and leg pain. Clin Radiol. 2000; 55(2):145–9.
Article14. Kjaer P, Bendix T, Sorensen JS, et al. Are MRI-defined fat infiltrations in the multifidus muscles associated with low back pain? BMC Med. 2007; 5:2.
Article15. Parkkola R, Rytö koski U, Kormano M. Magnetic resonance imaging of the discs and trunk muscles in patients with chronic low back pain and healthy control subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18(7):830–6.
Article16. Herron LD, Mangelsdorf C. Lumbar spinal stenosis: results of surgical treatment. J Spinal Disord. 1991; 4(1):26–33.17. Keorochana G, Laohacharoensombat W, Wajanavisit W, et al. Functional outcome after decompression and instrumented arthrodesis in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: factors influencing unsuccessful outcome change. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011; 94(12):1487–94.18. Airaksinen O, Herno A, Turunen V, et al. Surgical outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22(19):2278–82.
Article19. Paalanne N, Niinimä ki J, Karppinen J, et al. Assessment of association between low back pain and paraspinal muscle atrophy using opposed-phase magnetic resonance imaging: a population-based study among young adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(23):1961–8.20. Kamaz M, Kiresi D, Oguz H, et al. CT measurement of trunk muscle areas in patients with chronic low back pain. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2007; 13(3):144–8.21. Park SI, Lee WY, Kim HS, et al. Quantitative correlations of trunk muscles in young and middle-aged men with chronic low back pain by magnetic resonance imaging. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31(1):1–6.22. Bae JH, Na JK, Yu JY, et al. Atrophy of multifidus muscle on low back pain patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25(4):684–91.23. Fan S, Hu Z, Zhao F, et al. Multifidus muscle changes and clinical effects of one-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion: minimally invasive procedure versus conventional open approach. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(2):316–24.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Complex Regional Pain Syndrome a Cause of Post-Operative Syndrome in the Lumbar Spine?: A Case Report
- Differences in Biomechanical Factors for Fusion Transition Syndrome of Lumbar Spine between Pedicle Screw Fixation and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Groups
- Operative Risk Assessment of Degenerative Spinal Disorder Comparing with Total Hip Replacement
- Efficacy of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion using PEEK Cage and Pedicle Screw Stabilization in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disorders: Minimum 3 Years Follow up Results
- Outcomes and Complications of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion as a Surgical Option in Elderly Patients (Over 70 Years Old) with Degenerative Spinal Disease