Clin Endosc.
2015 May;48(3):228-233. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.228.
Risk Factors for Dieulafoy Lesions in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. porrtos@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2148571
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.228
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The purpose of this study is to verify the risk factors associated with Dieulafoy lesion formation in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
METHODS
A case-control study was performed by reviewing the electronic medical records of 42 patients who were admitted to a tertiary medical center in the Daejeon region for Dieulafoy lesions from September 2008 to October 2013, and the records of 132 patients who were admitted during the same period and who underwent endoscopic examination for reasons other than bleeding. We analyzed clinical and endoscopic findings retrospectively, and searched for risk factors associated with Dieulafoy lesion formation.
RESULTS
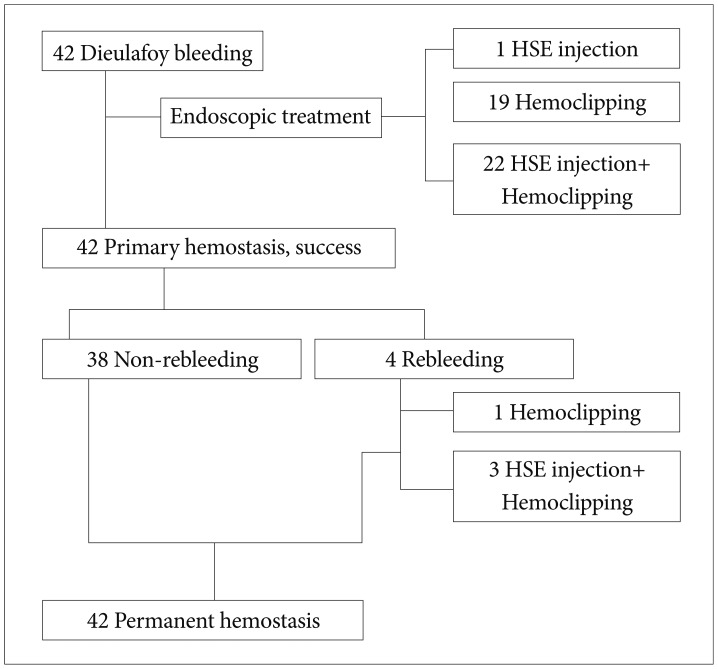
All 42 patients diagnosed with Dieulafoy lesion had accompanying bleeding, and the location of the bleeding was proximal in 25 patients (59.5%), the middle portion in seven patients (16.7%), and distal in 10 patients (23.8%). Antiplatelet agents (p=0.022) and alcohol (p=0.001) use showed statistically significant differences between the two groups. The odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) of the two factors were 2.802 (1.263 to 6.217) and 3.938 (1.629 to 9.521), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that antiplatelet agents and alcohol consumption were risk factors associated with Dieulafoy lesion formation in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stark ME, Gostout CJ, Balm RK. Clinical features and endoscopic management of Dieulafoy's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:545–550. PMID: 1397908.
Article2. Strong RW. Dieulafoy's disease: a distinct clinical entity. Aust N Z J Surg. 1984; 54:337–339. PMID: 6333234.3. Chaer RA, Helton WS. Dieulafoy's disease. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 196:290–296. PMID: 12595057.
Article4. Marangoni G, Cresswell AB, Faraj W, Shaikh H, Bowles MJ. An uncommon cause of life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding: 2 synchronous Dieulafoy lesions. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:441–443. PMID: 19231553.
Article5. Lara LF, Sreenarasimhaiah J, Tang SJ, Afonso BB, Rockey DC. Dieulafoy lesions of the GI tract: localization and therapeutic outcomes. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:3436–3441. PMID: 20848205.
Article6. Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Bartelsman JF, Schipper ME, Tytgat GN. Recurrent massive haematemesis from Dieulafoy vascular malformations: a review of 101 cases. Gut. 1986; 27:213–222. PMID: 3485070.7. Lee YT, Walmsley RS, Leong RW, Sung JJ. Dieulafoy's lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:236–243. PMID: 12872092.
Article8. Kasapidis P, Georgopoulos P, Delis V, Balatsos V, Konstantinidis A, Skandalis N. Endoscopic management and long-term follow-up of Dieulafoy's lesions in the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:527–531. PMID: 11923766.
Article9. Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Méndez Jerez PV, et al. Endoscopic management of Dieulafoy lesions of the stomach: a case study of 26 patients. Endoscopy. 1997; 29:834–839. PMID: 9476766.
Article10. Schmulewitz N, Baillie J. Dieulafoy lesions: a review of 6 years of experience at a tertiary referral center. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1688–1694. PMID: 11419815.
Article11. Chung IK, Kim EJ, Lee MS, et al. Bleeding Dieulafoy's lesions and the choice of endoscopic method: comparing the hemostatic efficacy of mechanical and injection methods. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:721–724. PMID: 11115902.
Article12. al-Mishlab T, Amin AM, Ellul JP. Dieulafoy's lesion: an obscure cause of GI bleeding. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1999; 44:222–225. PMID: 10453143.13. Anireddy D, Timberlake G, Seibert D. Dieulafoy's lesion of the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:604. PMID: 8365632.
Article14. Pollack R, Lipsky H, Goldberg RI. Duodenal Dieulafoy's lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:820–822. PMID: 8293911.
Article15. Alshumrani G, Almuaikeel M. Angiographic findings and endovascular embolization in Dieulafoy disease: a case report and literature review. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006; 12:151–154. PMID: 16972222.16. Katsinelos P, Pilpilidis I, Paroutoglou G, et al. Dieulafoy-like lesion of the colon presenting with massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:346. PMID: 15106623.17. Dulic-Lakovic E, Dulic M, Hubner D, et al. Bleeding Dieulafoy lesions of the small bowel: a systematic study on the epidemiology and efficacy of enteroscopic treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:573–580. PMID: 21802676.
Article18. Yoshikumi Y, Mashima H, Suzuki J, et al. A case of rectal Dieulafoy's ulcer and successful endoscopic band ligation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006; 20:287–290. PMID: 16609760.
Article19. Nunoo-Mensah JW, Alkari B, Murphy GJ, Watson AJ. Rectal Dieulafoy lesions. J Am Coll Surg. 2008; 206:388–389. PMID: 18222397.
Article20. Firat O, Karaköse Y, Calis¸kan C, Makay O, Ozütemiz O, Korkut MA. Dieulafoy's lesion of the anal canal: report of a case. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2007; 18:265–267. PMID: 18080926.21. Baxter M, Aly EH. Dieulafoy's lesion: current trends in diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:548–554. PMID: 20883603.
Article22. Baettig B, Haecki W, Lammer F, Jost R. Dieulafoy's disease: endoscopic treatment and follow up. Gut. 1993; 34:1418–1421. PMID: 8244112.
Article23. Skok P. Endoscopic hemostasis in exulceratio simplex-Dieulafoy's disease hemorrhage: a review of 25 cases. Endoscopy. 1998; 30:590–594. PMID: 9826135.24. Pointner R, Schwab G, Königsrainer A, Dietze O. Endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988; 94:563–566. PMID: 3257449.
Article25. Lin HJ, Lee FY, Tsai YT, Lee SD, Lee CH, Kang WM. Therapeutic endoscopy for Dieulafoy's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989; 11:507–510. PMID: 2794429.
Article26. Asaki S, Sato H, Nishimura T, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of Dieulafoy's ulcer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1988; 154:135–141. PMID: 3289138.
Article27. Sone Y, Kumada T, Toyoda H, Hisanaga Y, Kiriyama S, Tanikawa M. Endoscopic management and follow up of Dieulafoy lesion in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:449–453. PMID: 15844024.
Article28. Romãozinho JM, Pontes JM, Lérias C, Ferreira M, Freitas D. Dieulafoy's lesion: management and long-term outcome. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:416–420. PMID: 15100950.
Article29. Norton ID, Petersen BT, Sorbi D, Balm RK, Alexander GL, Gostout CJ. Management and long-term prognosis of Dieulafoy lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:762–767. PMID: 10570333.
Article30. Yamaguchi Y, Yamato T, Katsumi N, et al. Short-term and long-term benefits of endoscopic hemoclip application for Dieulafoy's lesion in the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:653–656. PMID: 12709692.
Article31. Nikolaidis N, Zezos P, Giouleme O, et al. Endoscopic band ligation of Dieulafoy-like lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:754–760. PMID: 11558028.
Article32. Dy NM, Gostout CJ, Balm RK. Bleeding from the endoscopically-identified Dieulafoy lesion of the proximal small intestine and colon. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995; 90:108–111. PMID: 7801908.33. Iacopini F, Petruzziello L, Marchese M, et al. Hemostasis of Dieulafoy's lesions by argon plasma coagulation (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:20–26. PMID: 17591469.
Article34. Lee EA, Kim JB, Kim BS, et al. Morphological effect of chronic alcohol drinking upon the gastric mucosa of rats. Korean J Anat. 2000; 33:519–527.35. Ding YJ, Zhao L, Liu J, Luo HS. Clinical and endoscopic analysis of gastric Dieulafoy's lesion. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:631–635. PMID: 20128034.
Article36. Laine L. Multipolar electrocoagulation in the treatment of active upper gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage. A prospective controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987; 316:1613–1617. PMID: 3295547.37. Park CH, Joo YE, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ. A prospective, randomized trial of endoscopic band ligation versus endoscopic hemoclip placement for bleeding gastric Dieulafoy's lesions. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:677–681. PMID: 15280971.
Article38. Park CH, Sohn YH, Lee WS, et al. The usefulness of endoscopic hemoclipping for bleeding Dieulafoy lesions. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:388–392. PMID: 12701008.
Article39. Alis H, Oner OZ, Kalayci MU, et al. Is endoscopic band ligation superior to injection therapy for Dieulafoy lesion? Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:1465–1469. PMID: 19125307.
Article40. Cui J, Huang LY, Liu YX, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic therapy for gastrointestinal bleeding from Dieulafoy's lesion. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:1368–1372. PMID: 21455339.
Article41. Cheng CL, Liu NJ, Lee CS, et al. Endoscopic management of Dieulafoy lesions in acute nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dig Dis Sci. 2004; 49:1139–1144. PMID: 15387335.
Article42. Yilmaz M, Ozütemiz O, Karasu Z, et al. Endoscopic injection therapy of bleeding Dieulafoy lesion of the stomach. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005; 52:1622–1625. PMID: 16201129.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Death due to Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Associated with Dieulafoy's Lesion
- A Case of Dieulafoy's Lesion in Duodenal Bulb
- A Case of a Jejunal Dieulafoy's Lesion Mimicking a Submucosal Tumor
- A Case of Dieulafoy's Lesion with Pseudoaneurysm in the Sigmoid Colon
- Life-threatening Gastrointestinal Bleeding from a Dieulafoy’s Lesion in the Duodenum: A Case Report