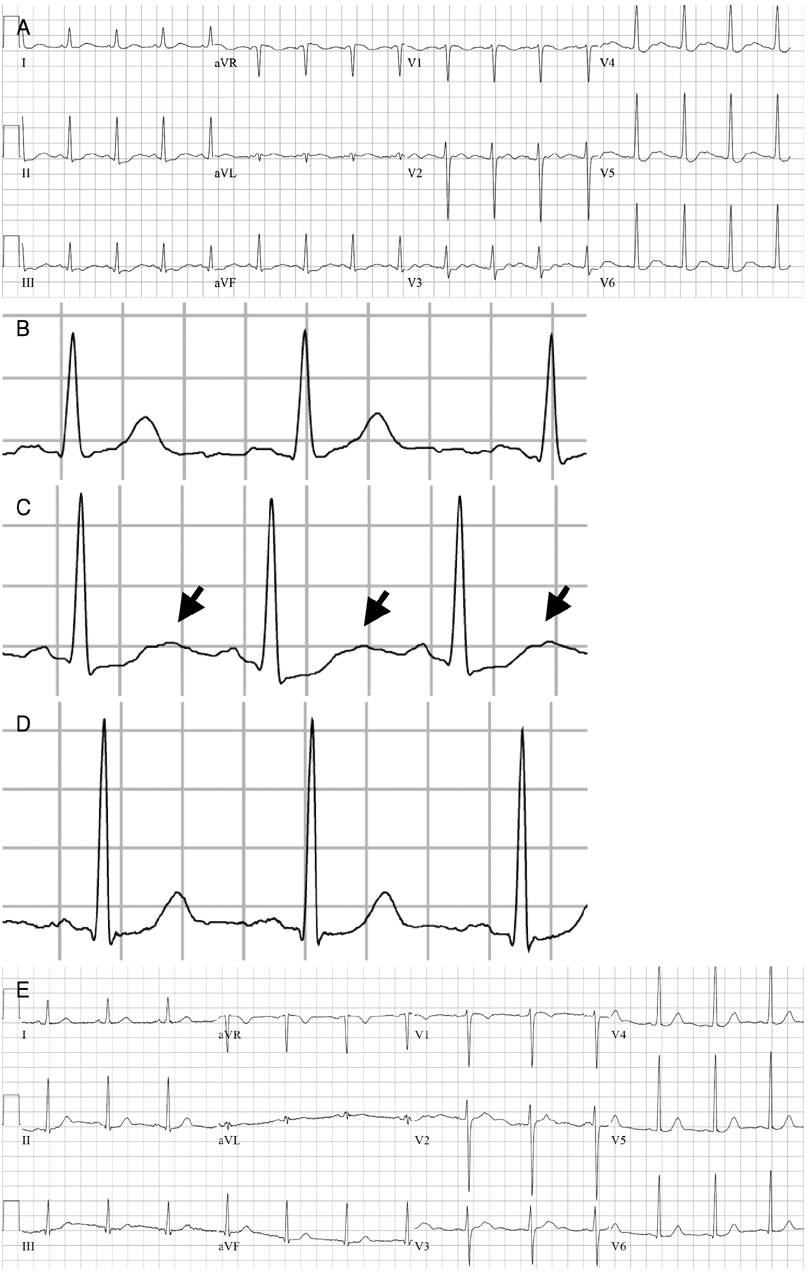
Korean Circ J.
2009 Jul;39(7):295-296. 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.7.295.
Ritodrine-Induced Hypokalemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Kyunghee University East-West Neo Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. issohn@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2145567
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2009.39.7.295
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gyetvai K, Hannah ME, Hodnett ED, Ohlsson A. Tocolytics for preterm labor: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 94:869–877.2. Caldwell G, Scougall I, Boddy K, Toft AD. Fasting hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia after ritodrine therapy for premature labor. Obstet Gynecol. 1987. 70:478–480.3. Braden GL, von Oeyen PT, Germain MJ, Watson DJ, Haag BL. Ritodrine- and terbutaline-induced hypokalemia in preterm labor: mechanisms and consequences. Kidney Int. 1997. 51:1867–1875.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hyperkalemia after Cessation of Ritodrine in a Parturient during Cesarean Section: A case report
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Comparative trial of combination therapy of indomethacin and ritodrine versus single therapy of ritodrine for the premature labor
- The effect of intravenous ritodrine hydrochloride on premature labor
- A comparison of ritodrine and magnesium sulfate for the suppression of preterm labor