Korean Circ J.
2014 May;44(3):184-188. 10.4070/kcj.2014.44.3.184.
Retrograde Distal Superficial Femoral Artery Approach in the Supine Position for Chronic Superficial Femoral Artery Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University Health System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cdhlyj@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2145480
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2014.44.3.184
Abstract
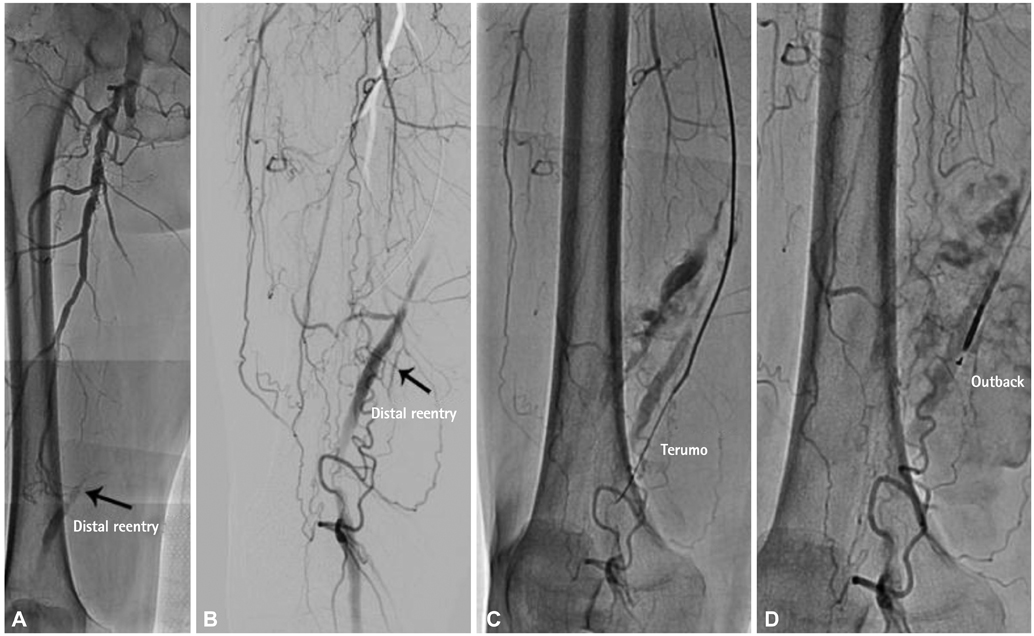
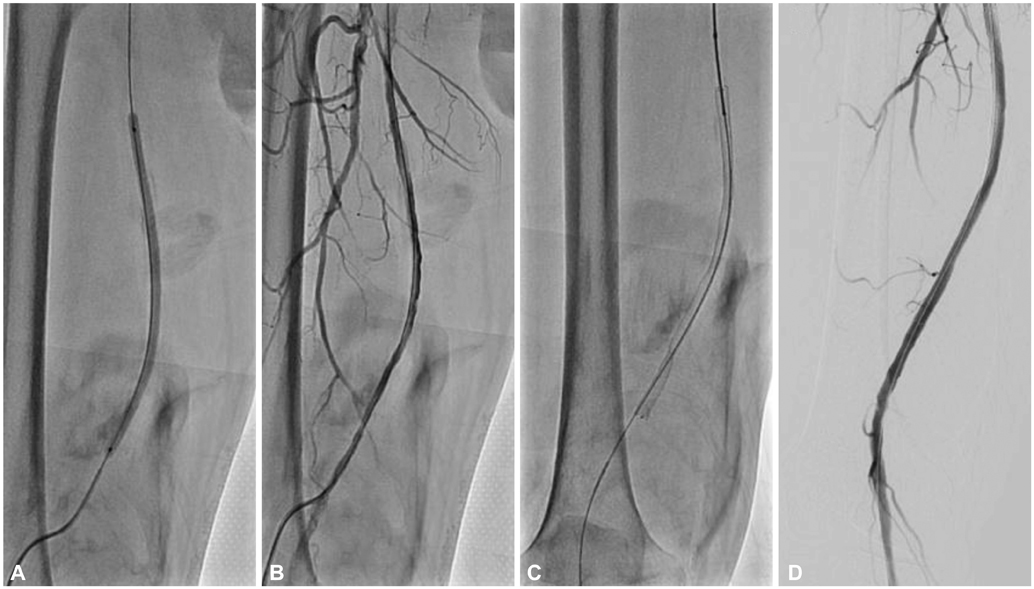
- Subintimal angioplasty is an effective method for the treatment of long superficial femoral artery (SFA) occlusions. One of the major limiting factors for the success of this procedure is the failure to re-enter the true lumen. The recently introduced luminal re-entry devices provide a high technical success rate, but failures can occur. In such cases, a retrograde popliteal approach can serve as a potential backup option. However, the need to reposition the patient remains a drawback. Here, we report a case of an 81-year-old male with a long SFA occlusion treated using a retrograde distal SFA approach in the supine position after the initial failure of antegrade angioplasty.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ko YG, Kim JS, Choi DH, Jang Y, Shim WH. Improved technical success and midterm patency with subintimal angioplasty compared to intraluminal angioplasty in long femoropopliteal occlusions. J Endovasc Ther. 2007; 14:374–381.2. Spinosa DJ, Leung DA, Harthun NL, et al. Simultaneous antegrade and retrograde access for subintimal recanalization of peripheral arterial occlusion. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1449–1454.3. Bolia A. Percutaneous intentional extraluminal (subintimal) recanalization of crural arteries. Eur J Radiol. 1998; 28:199–204.4. Hausegger KA, Georgieva B, Portugaller H, Tauss J, Stark G. The outback catheter: a new device for true lumen re-entry after dissection during recanalization of arterial occlusions. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004; 27:26–30.5. Casserly IP, Sachar R, Bajzer C, Yadav JS. Utility of IVUS-guided transaccess catheter in the treatment of long chronic total occlusion of the superficial femoral artery. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2004; 62:237–243.6. Tønnesen KH, Sager P, Karle A, Henriksen L, Jørgensen B. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of the superficial femoral artery by retrograde catheterization via the popliteal artery. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1988; 11:127–131.7. Zaitoun R, Iyer SS, Lewin RF, Dorros G. Percutaneous popliteal approach for angioplasty of superficial femoral artery occlusions. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1990; 21:154–158.8. Heenan SD, Vinnicombe SJ, Buckenham TM, Belli AM. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty by a retrograde subintimal transpopliteal approach. Clin Radiol. 1994; 49:824–827. discussion 827-8.9. Yilmaz S, Sindel T, Ceken K, Alimogğlu E, Lüleci E. Subintimal recanalization of long superficial femoral artery occlusions through the retrograde popliteal approach. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2001; 24:154–160.10. Noory E, Rastan A, Sixt S, et al. Arterial puncture closure using a clip device after transpopliteal retrograde approach for recanalization of the superficial femoral artery. J Endovasc Ther. 2008; 15:310–314.11. Trigaux JP, Van Beers B, De Wispelaere JF. Anatomic relationship between the popliteal artery and vein: a guide to accurate angiographic puncture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 157:1259–1262.12. Grimm J, Müller-Hülsbeck S, Jahnke T, Hilbert C, Brossmann J, Heller M. Randomized study to compare PTA alone versus PTA with Palmaz stent placement for femoropopliteal lesions. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12:935–942.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Retrograde Outback Catheter Through the Pedal Route in a Stumpless Long Superficial Femoral Artery Occlusion
- Successful Recanalization of a Long Superficial Femoral Artery Occlusion by Retrograde Subintimal Angioplasty After a Failed Antegrade Subintimal Approach
- Injury of the Superficial Femoral Artery Secondary to an Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Case Report
- Pseudoaneurysm of Superficial Femoral Artery Following Proximal Femoral Nail Fixation
- The Rupture of Distal Superficial Femoral Arterial Aneurysm on Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient