Korean J Urol.
2006 Oct;47(10):1065-1068. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.10.1065.
Alteration in Renal Function for Patients with Ileal Conduit and Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. uroking@naver.com
- KMID: 2139806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.10.1065
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We performed this study to evaluate the alterations in renal function for patients with ileal conduit and ileal orthotopic neobladder
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1999 to June 2004, 48 patients who had undergone radical cystectomy with urinary diversion were included in our study. The patients were divided into two groups according to the types of urinary diversion. One group consisted of 29 patients with ileal conduit and the other group consisted of 19 patients with ileal W neobladder. The mean age of the ileal conduit group and the ileal W neobladder group were 65.6+/-9.9 years and 60.8+/-8.3 years, respectively. The preoperative and postoperative blood urea nitrogen/creatinine (BUN/Cr) levels, postoperative complications and postoperative GFR, as measured by (99m)Tc-DTPA scans, were compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
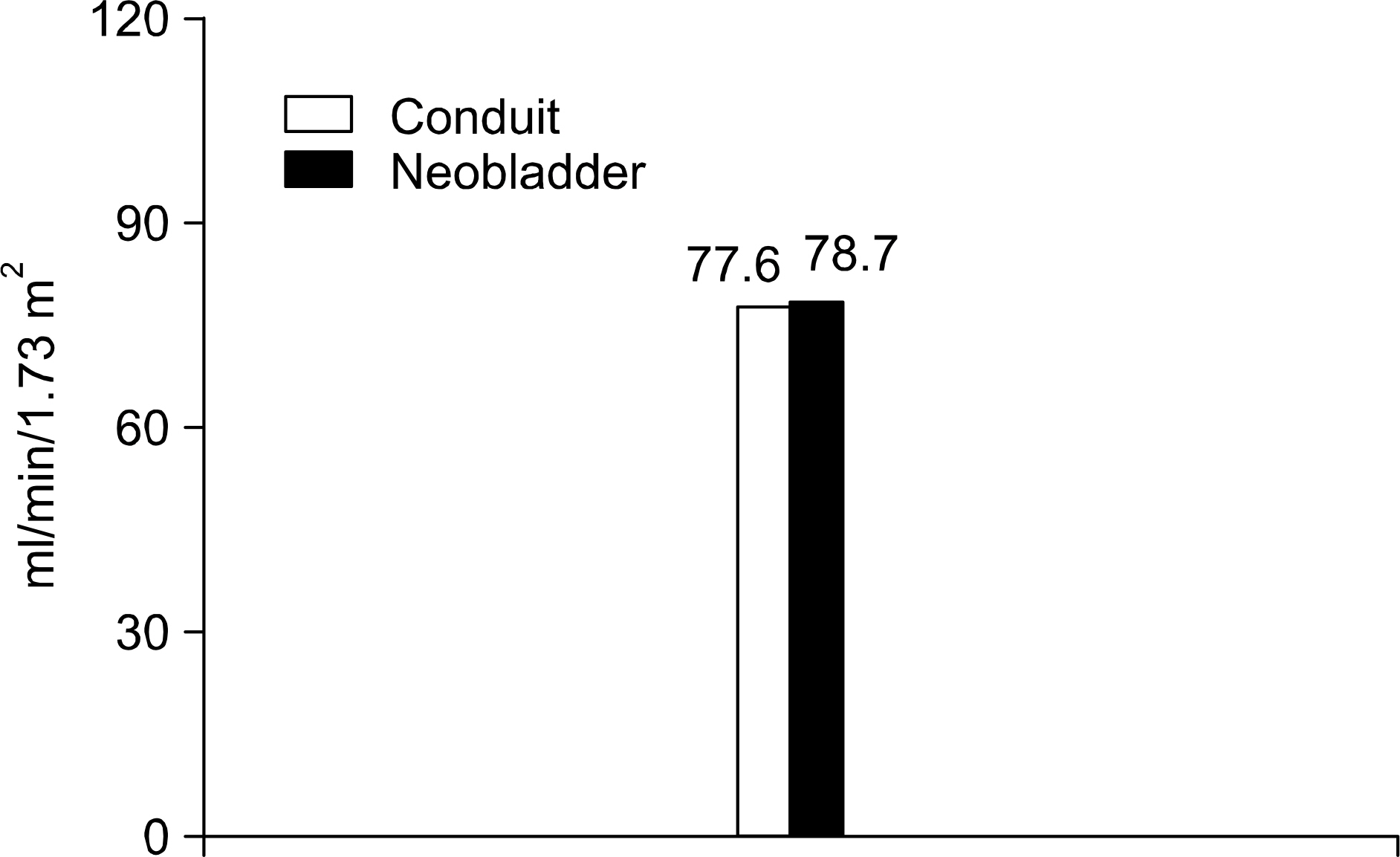
For the postoperative complications, stricture at the ureterovesical anastomosis site occurred in 1.7% (1/58 renal units) of the ileal conduit group and in 10.5% (4/38 renal units) of the ileal W neobladder group. Acute pyelonephritis occurred in 5.2% (3/58 renal units) of the ileal conduit group and in 5.3% (2/38 renal units) of the ileal W neobladder group. The pre- and postoperative serum BUN/Cr levels were 20.8/1.3 and 24.8/1.6, respectively, in the ileal conduit group, and 17.2/1.1 and 18.8/1.2, respectively, in the ileal W neobladder group. There were no statistical significant differences between the pre- and postoperative changes of the serum BUN/Cr levels for both groups. The GFR, as measured by (99m)Tc-DTPA scans, were 77.6 and 78.7ml/ min/1.73m2 in the ileal conduit group and the ileal W neobladder group, respectively. There were no statistical significant differences between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
There were no significant differences in renal function between the ileal conduit and ileal W neobladder.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Impact of Vesico-ureteral Reflux on Renal Function after a Radical Cystectomy: a Comparison of Refluxing and Antirefluxing Orthotopic Bladder Substitutes
Gyeong Eun Min, Cheryn Song, Hanjong Ahn
Korean J Urol. 2007;48(9):933-937. doi: 10.4111/kju.2007.48.9.933.
Reference
-
1.Gonzalez EC., Liedana TJ., Roncales BA., Martinez BJ., Gil SM., Rioja SL. Radical cystectomy for the treatment of infiltrating bladder carcinoma. Analysis of 15 years. Arch Esp Urol. 1991. 44:395–402.2.Madersbacher S., Schmidt J., Eberle JM., Thoeny HC., Burkhard F., Hochreiter W, et al. Long-term outcome of ileal conduit diversion. J Urol. 2003. 169:985–90.
Article3.Kim SW., Oh JM., Lee JY., Cho YH., Yoon MS. The ileal W-neobladder: early experience in 13 patients. Korean J Urol. 1999. 35:381–6.4.Abol-Enein H., Ghoneim MA. A novel uretero-ileal reimplantation technique: the serous lined extramural tunnel. A preliminary report. J Urol. 1994. 151:1193–7.
Article5.Bricker EM. Bladder substitution after pelvic evisceration. Surg Clin North Am. 1950. 30:1511–21.
Article6.Pitts WJ Jr., Muecke EC. A 20-year experience with ileal conduits: the fate of the kidneys. J Urol. 1979. 122:154–7.7.Kock NG., Nilson AE., Norlen LJ., Sundin T., Trasi H. Urinary diversion via a continent ileum reservior. Clinical experience. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1978. 49((Suppl):):23–31.8.Skinner DG., Boyd SD., Lieskovsky G. Clinical experience with the Kock continent ileal reservoir for urinary diversion. J Urol. 1984. 132:1101–7.
Article9.Marshall FF. Creation of ileocolic bladder after cystectomy. J Urol. 1988. 139:1264–8.10.Hautmann RE., Egghart G., Frohneberg D., Miller K. The ileal neobladder. J Urol. 1988. 139:39–42.
Article11.Kam BK., Shin YH., Park YK., Yoon DH., Jang ED., Kim MS, et al. Clinical usefulness of GFR measurement using Tc-99m DTPA renal scan in kidney transplantation patients. Korean J Nephrol. 1999. 18:168–74.12.Kristjansson A., Bajc M., Wallim L., Willner J., Mansson W. Renal function up to 16 years after conduit (refluxing or antireflux anastomosis) or continent urinary diversion. 2. Renal scarring and location of bacteriuria. Br J Urol. 1995. 76:546–50.13.Stein JP., Skinner DG. Application of the T-mechanism to an orthotopic (T-pouch neobladder: a new era of urinary diversion. World J Urol. 2000. 18:315–23.
Article14.Pantuck AJ., Han KR., Perrotti M., Weiss RE., Cummings KB. Ureteroenteric anastomosis in continent urinary diversion: long-term results and complications of direct versus nonre-fluxing techniques. J Urol. 2000. 163:450–5.
Article15.Hautmann RE. Urinary diversion: ileal conduit to neobladder. J Urol. 2003. 169:834–42.
Article16.Minervini A., Boni G., Salinitri G., Mariani G., Minervini R. Evaluation of renal function and upper urinary tract morphology in the ileal orthotopic neobladder with no antireflux mechanism. J Urol. 2005. 173:144–7.
Article17.Constantinides C., Manousakas T., Chrisofos M., Giannopoulos A. Orthotopic bladder substitution after radical cystectomy: 5 years of experience with a novel personal modification of the ileal S pouch. J Urol. 2001. 166:532–7.
Article18.Studer UE., Danuser H., Merz VW., Springer JP., Zingg EJ. Experience in 100 patients with an ileal low pressure bladder substitute combined with an afferent tubular isoperistaltic segment. J Urol. 1995. 154:49–56.
Article19.Hautmann RE., Miller K., Steiner U., Wenderoth U. The ileal neobladder: 6 years of experience with more than 200 patients. J Urol. 1993. 150:40–5.
Article20.Casanova GA., Springer JP., Gerber E., Studer UE. Functional and clinical aspects of ileal low pressure bladder substitutes. Br J Urol. 1993. 72:728–35.21.Abol-Enein H., Ghoneim MA. Functional results of orhtotopic ileal neobladder with serous-lined extramural ureteral reimplantation: experience with 450 patients. J Urol. 2001. 165:1427–32.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Quality of Life in Different Type of Urinary Diversion after Radical Cystectomy
- Comparison of the Complications and Urodynamic Parameters for Orthotopic Bladder Substitution with using Ileocolic or Ileal Segments after Radical Cystectomy
- Body Image Following Radical Cystectomy and Ileal Neobladder or Conduit in Korean Patients
- Safety of Adjuvant Chemotherapy after Orthotopic Bladder Substitution: Comparison to Ileal Conduit
- Delayed Spontaneous Rupture of an Orthotopic Ileal Neobladder