J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2011 Dec;37(6):457-463. 10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.6.457.
Soft tissue changes of upper lip and nose following posterosuperior rotation of the maxilla by Le Fort I osteotomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jupark@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- KMID: 2136981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.6.457
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
This study evaluate the soft tissue changes to the upper lip and nose after Le Fort I maxillary posterosuperior rotational movement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
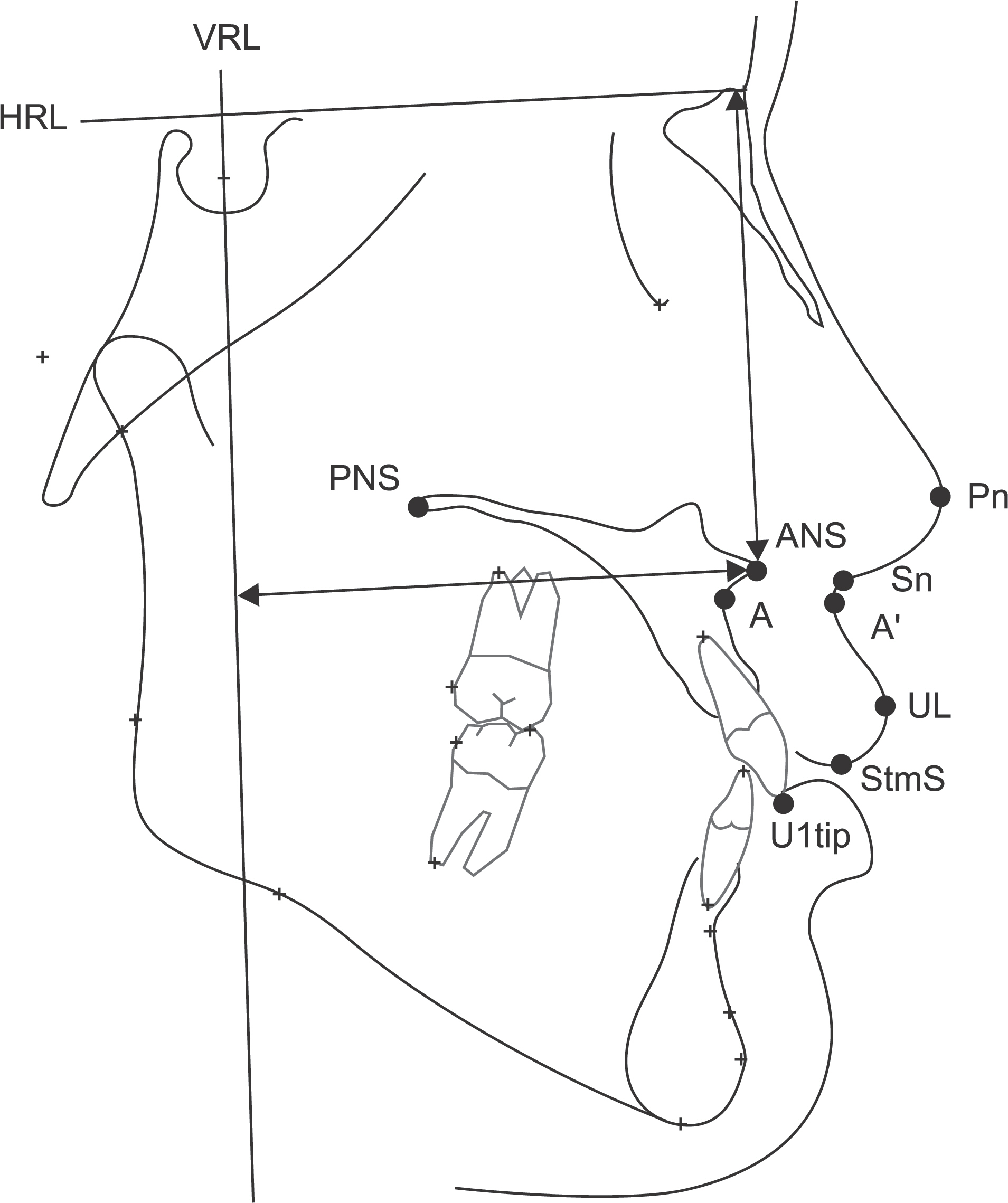
Twenty Skeletal class III patients, who had undergone bimaxillary surgery with a maxillary Le Fort I osteotomy and bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy, were included in the study. The surgical plan for maxilla was posterosuperior rotational movement, with the rotation center in the anterior nasal spine (ANS) of maxilla. Soft and hard tissue changes were measured by evaluating the lateral cephalograms obtained prior to surgery and at least 6 months after surgery. For cephalometric analysis, four hard tissue landmarks ANS, posterior nasal spine [PNS], A point, U1 tip), and five soft tissue landmarks (pronasale [Pn], subnasale [Sn], A' Point, upper lip [UL], stomion superius [StmS]) were marked. A paired t test, Pearson's correlation analysis and linear regression analysis were used to evaluate the soft and hard tissue changes and assess the correlation. A P value <0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
The U1 tip moved 2.52+/-1.54 mm posteriorly in the horizontal plane (P<0.05). Among the soft tissue landmarks, Pn moved 0.97+/-1.1 mm downward (P<0.05), UL moved 1.98+/-1.58 mm posteriorly (P<0.05) and 1.18+/-1.85 mm inferiorly (P<0.05), and StmS moved 1.68+/-1.48 mm posteriorly (P<0.05) and 1.06+/-1.29 mm inferiorly (P<0.05). The ratios of horizontal soft tissue movement to the hard tissue were 1:0.47 for the A point and A' point, and 1:0.74 for the U1 tip and UL. Vertically, the movement ratio between the A point and A' point was 1:0.38, between U1 tip and UL was 1:0.83, and between U1 tip and StmS was 1:0.79.
CONCLUSION
Posterosuperior rotational movement of the maxilla in Le Fort I osteotomy results in posterior and inferior movement of UL. In addition, nasolabial angle was increased. Nasal tip and base of the nose showed a tendency to move downward and showed significant horizontal movement. The soft tissue changes in the upper lip and nasal area are believed to be induced by posterior movement at the UL area.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. von Langenbeck B. Beiträge zur osteoplastik – Die osteoplastische resektion des oberkiefers. Göschen A, editor. Deutsche Klinik. Berlin: Reimer;1859.2. Cheever DW. Nasopharyngeal polypus, attached to the basilar process of occipital and body of the sphenoid bone successfully removed by a section, displacement, and subsequent replacement and reunion of the superior maxillary bone. Boston Med Surg J. 1867; 8:162.3. Wassmund M. Frakturen und Luxationen des Gesichtsschädels. Leipzig: Meusser;1927.4. Axhausen G. Technik und Ergebnisse der Lippenplastiked. Leipzig: Thieme;1941.5. Schuchardt K. Ein Beitrag zur chirurgischen Kieferorthopädie unter Berücksichtigung ihrer Bedeutung für die Behandlung angeborener und erworbener Kieferdeformitäten bei Soldaten. Dtsch Zahn Mund Kieferheil. 1942; 9:73–89.6. Obwegeser H. [Surgery of the maxilla for the correction of prognathism]. SSO Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnheilkd. 1965; 75:365–74.7. Proffit WR, Turvey TA, Phillips C. The hierarchy of stability and predictability in orthognathic surgery with rigid fixation: an update and extension. Head Face Med. 2007; 30:3–21.
Article8. Baek SH, Kim K, Choi JY. Evaluation of treatment modality for skeletal Class III malocclusion with labioversed upper incisors and/or protrusive maxilla: surgical movement and stability of rotational maxillary setback procedure. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20:2049–54.9. Betts NJ, Edwards SP. Soft tissue changes associated with orthognathic surgery. Perterson's Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery. Vol.II:2nd ed.Hamilton: BC Decker;2004. p. 1221–46.
Article10. Dann JJ 3rd, Fonseca RJ, Bell WH. Soft tissue changes associated with total maxillary advancement: a preliminary study. J Oral Surg. 1976; 34:19–23.11. Schendel SA, Eisenfeld JH, Bell WH, Epker BN. Superior repositioning of the maxilla: stability and soft tissue osseous relations. Am J Orthod. 1976; 70:663–74.
Article12. Burstone CJ, James RB, Legan H, Murphy GA, Norton LA. Cephalometrics for orthognathic surgery. J Oral Surg. 1978; 36:269–77.13. Legan HL, Burstone CJ. Soft tissue cephalometric analysis for orthognathic surgery. J Oral Surg. 1980; 38:744–51.14. Radney LJ, Jacobs JD. Soft-tissue changes associated with surgical total maxillary intrusion. Am J Orthod. 1981; 80:191–212.
Article15. Mansour S, Burstone C, Legan H. An evaluation of soft-tissue changes resulting from Le Fort I maxillary surgery. Am J Orthod. 1983; 84:37–47.
Article16. O'Ryan F, Carlotti A. Nasal anatomy and maxillary surgery. III. Surgical techniques for correction of nasal deformities in patients undergoing maxillary surgery. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1989; 4:157–74.17. O'Ryan F, Schendel S. Nasal anatomy and maxillary surgery. II. Unfavorable nasolabial esthetics following the Le Fort I osteotomy. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1989; 4:75–84.18. O'Ryan F, Schendel S. Nasal anatomy and maxillary surgery. I. Esthetic and anatomic principles. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1989; 4:27–37.19. Stella JP, Streater MR, Epker BN, Sinn DP. Predictability of upper lip soft tissue changes with maxillary advancement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989; 47:697–703.
Article20. Betts NJ, Fonseca RJ. Soft tissue changes associated with orthognathic surgery. Bell WH, editor. Modern practice in orthognathic and reconstructive surgery, Volume III. Philadelphia: Saunders;1992. p. 2171–209.
Article21. Jensen AC, Sinclair PM, Wolford LM. Soft tissue changes associated with double jaw surgery. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992; 101:266–75.
Article22. Hack GA, de Mol van Otterloo JJ, Nanda R. Long-term stability and prediction of soft tissue changes after LeFort I surgery. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993; 104:544–55.
Article23. Enacar A, Taner T, Toroğlu S. Analysis of soft tissue profile changes associated with mandibular setback and double-jaw surgeries. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1999; 14:27–35.24. Park JO, Lee SC. A clinicostatistical study of soft tissue changes of upper lip & nose following Le Fort I maxillary movement. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 22:310–8.25. Mommaerts MY, Lippens F, Abeloos JV, Neyt LF. Nasal profile changes after maxillary impaction and advancement surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 58:470–5.
Article26. Koh CH, Chew MT. Predictability of soft tissue profile changes following bimaxillary surgery in skeletal class III Chinese patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62:1505–9.
Article27. Chew MT. Soft and hard tissue changes after bimaxillary surgery in Chinese Class III patients. Angle Orthod. 2005; 75:959–63.28. Jeong MH, Choi JH, Kim BH, Kim SG, Nahm DS. Soft tissue changes after double jaw rotation surgery in skeletal class III malocclusion. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 32:559–65.29. Chew MT, Sandham A, Wong HB. Evaluation of the linearity of soft- to hard-tissue movement after orthognathic surgery. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008; 134:665–70.
Article30. Chung C, Lee Y, Park KH, Park SH, Park YC, Kim KH. Nasal changes after surgical correction of skeletal Class III malocclusion in Koreans. Angle Orthod. 2008; 78:427–32.
Article31. Joss CU, Thüer UW. Stability of the hard and soft tissue profile after mandibular advancement in sagittal split osteotomies: a longitudinal and longterm follow-up study. Eur J Orthod. 2008; 30:16–23.
Article32. Joss CU, Vassalli IM, Thuer UW. Stability of soft tissue profile after mandibular setback in sagittal split osteotomies: a longitudinal and longterm follow-up study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:1610–6.
Article33. Park JU, Hwang YS. Evaluation of the soft and hard tissue changes after anterior segmental osteotomy on the maxilla and mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:98–103.
Article34. Marsan G, Cura N, Emekli U. Soft and hard tissue changes after bimaxillary surgery in Turkish female Class III patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009; 37:8–17.35. Schouman T, Baralle MM, Ferri J. Facial morphology changes after total maxillary setback osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:1504–11.
Article36. Jacobson R, Sarver DM. The predictability of maxillary repositioning in LeFort I orthognathic surgery. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002; 122:142–54.
Article37. Semaan S, Goonewardene MS. Accuracy of a LeFort I maxillary osteotomy. Angle Orthod. 2005; 75:964–73.38. Robinson SW, Speidel TM, Isaacson RJ, Worms FW. Soft tissue profile change produced by reduction of mandibular prognathism. Angle Orthod. 1972; 42:227–35.39. Hershey HG, Smith LH. Soft-tissue profile change associated with surgical correction of the prognathic mandible. Am J Orthod. 1974; 65:483–502.
Article40. Lee JJ. Maxillary osteotomies: Le Fort I Osteotomy. Turvey TA, editor. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Vol. III. 2nd ed.St. Louis: Saunders;2009. p. 172–91.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A clinico-statistical study of soft tissue changes of upper lip & nose following Le Fort I maxillary movement
- Stability And Soft Tissue Changes Following Advancement Le Fort I Osteotomy In The Cleft Lip And Palate Patients
- A study on long-term soft tissue changes after superior repositioning of the maxilla
- The soft tissue changes of the nasolabial region after maxillary le fort i advancement osteotomy
- The amount of soft tissue change to hard tissue movement following le fort ii osteotomy