J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2015 Mar;23(1):52-53. 10.4250/jcu.2015.23.1.52.
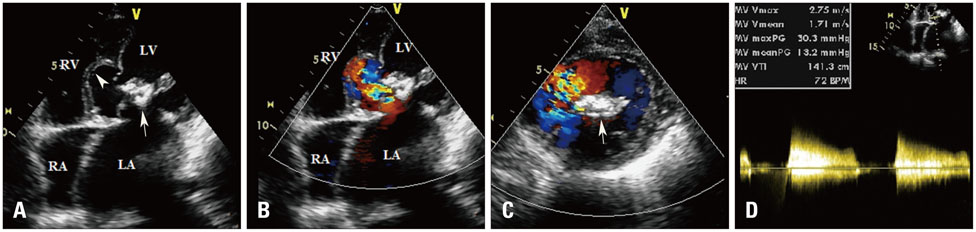
Basal Interventricular Septal Aneurysm in Rheumatic Mitral Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, King George's Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. dr.rajivkharwar@gmail.com
- KMID: 2135409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2015.23.1.52
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mohan JC, Kumar P. Cross-sectional echocardiographic diagnosis of a congenital aneurysm of the muscular interventricular septum. Int J Cardiol. 1992; 35:415–416.2. Kasprzak JD, Borkowski M, Rogowski W, Drozdz J, Krzemin´ska-Pakula M. A congenital complex including muscular interventricular septal aneurysm in an adult: case report and review of literature. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2002; 18:25–30.3. Mohan JC, Nath LR. Aneurysmal deformity of the basal interventricular septum secondary to impinging turbulent transprosthetic eccentric flow jets. Indian Heart J. 2005; 57:258–260.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Thrombus within an Interventricular Membranous Septal Aneurysm Leading to Cerebral Infarction: A Case Report
- A Giant Left Atrium in Rheumatic Mitral Stenosis
- Noninvasive Evaluation of Rheumatic Tricuspid Stenosis with Doppler and 2 Dimensional Echocardiography
- Rheumatic Carditis Associated with Mitral Stenosis
- Congenital Giant Aneurysm of Pulmonary Artery-Associated with Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis : A Case Report