Clin Endosc.
2012 Sep;45(3):245-247.
Estimation by Gross Findings in Early Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. harley1333@hanmail.net
Abstract
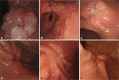
- Endoscopic resection has been accepted as both minimally invasive and curative treatment modality for early gastric cancer (EGC). The widely accepted indication of endoscopic resection for EGC is small sized, differentiated mucosal cancer in which the risk of lymph node metastasis is negligible. Tumor size can be measured by conventional endoscopy, and chromoendoscopy, magnifying endoscopy, narrow band imaging, autofluorescence imaging can also be helpful for accurate estimation of tumor size. Pretreatment tumor histology can be assessed with endoscopic biopsy, and also be measured by confocal endomicroscopy (so called "virtual biopsy"). Although endoscopic ultrasonography may be helpful for the assessment of tumor depth in EGC, the accurate assessment of tumor depth can be performed by the typical findings in the conventional endoscopy, by which treatment modality can be decided according to the depth of tumor invasion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, et al. Therapeutic outcomes in 1,000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1228–1235. PMID: 19249769.
Article2. Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study. Gut. 2009; 58:331–336. PMID: 19001058.
Article3. Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, et al. Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer. 2000; 3:219–225. PMID: 11984739.
Article4. Yamao T, Shirao K, Ono H, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis from intramucosal gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1996; 77:602–606. PMID: 8616749.
Article5. Botet JF, Lightdale CJ, Zauber AG, et al. Preoperative staging of gastric cancer: comparison of endoscopic US and dynamic CT. Radiology. 1991; 181:426–432. PMID: 1924784.
Article6. Pfau PR, Perlman SB, Stanko P, et al. The role and clinical value of EUS in a multimodality esophageal carcinoma staging program with CT and positron emission tomography. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:377–384. PMID: 17321235.
Article7. Kwee RM, Kwee TC. The accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography in differentiating mucosal from deeper gastric cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:1801–1809. PMID: 18564110.
Article8. Yanai H, Noguchi T, Mizumachi S, et al. A blind comparison of the effectiveness of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in staging early gastric cancer. Gut. 1999; 44:361–365. PMID: 10026321.
Article9. Yanai H, Matsumoto Y, Harada T, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in early gastric cancer: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 46:212–216. PMID: 9378206.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Screening of gastric cancer
- Endoscopic Resection of Undifferentiated Early Gastric Cancer
- Guidelines for Pathologic Study of Gastric Cancer
- Endoscopic Findings and Its Diagnostic Accuracy in Gastric Cancer Confirmed by Surgery
- Study on the Gastric Cancer Initially Diagnosed as Benign Gastric Ulcer during Endoscopic Follow-up