New Korean reference for birth weight by gestational age and sex: data from the Korean Statistical Information Service (2008-2012)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ithwang83@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2134082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2014.19.3.146
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To construct new Korean reference curves for birth weight by sex and gestational age using contemporary Korean birth weight data and to compare them with the Lubchenco and the 2010 United States (US) intrauterine growth curves.
METHODS
Data of 2,336,727 newborns by the Korean Statistical Information Service (2008-2012) were used. Smoothed percentile curves were created by the Lambda Mu Sigma method using subsample of singleton. The new Korean reference curves were compared with the Lubchenco and the 2010 US intrauterine growth curves.
RESULTS
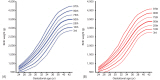
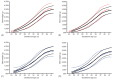
Reference of the 3rd, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 97th percentiles birth weight by gestational age were made using 2,249,804 (male, 1,159,070) singleton newborns with gestational age 23-43 weeks. Separate birth weight curves were constructed for male and female. The Korean reference curves are similar to the 2010 US intrauterine growth curves. However, the cutoff values for small for gestational age (<10th percentile) of the new Korean curves differed from those of the Lubchenco curves for each gestational age. The Lubchenco curves underestimated the percentage of infants who were born small for gestational age.
CONCLUSION
The new Korean reference curves for birth weight show a different pattern from the Lubchenco curves, which were made from white neonates more than 60 years ago. Further research on short-term and long-term health outcomes of small for gestational age babies based on the new Korean reference data is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 12 articles
-
Changes in the perinatal outcomes of twin pregnancies delivered at a tertiary referral center in Korea during a 24-year period from 1995 to 2018
Ji Young Hong, Hye Ran Lee, Yejin Kim, Yoo-Min Kim, Ji-Hee Sung, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-young Oh, Cheong-Rae Roh
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2020;63(3):251-260. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2020.63.3.251.Cerebral Palsy Rate of Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born at 36 Weeks of Gestation
Hyun Soo Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(10):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e77.Amino Acid-Based Formula in Premature Infants with Feeding Intolerance: Comparison of Fecal Calprotectin Level
Hyo-Jeong Jang, Jae Hyun Park, Chun Soo Kim, Sang Lak Lee, Won Mok Lee
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2018;21(3):189-195. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2018.21.3.189.Pregnancy Rates and Outcomes of HIV-Infected Women in Korea
Heun Choi, Moo Hyun Kim, Se Ju Lee, Eun Jin Kim, Woonji Lee, Wooyong Jeong, In Young Jung, Jin Young Ahn, Su Jin Jeong, Nam Su Ku, Ji Hyeon Baek, Young Hwa Choi, Hyo Youl Kim, June Myung Kim, Jun Yong Choi
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(47):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e296.Association between Birth Weight and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in <32 Weeks of Singleton Infants
Kee Hyun Cho, Jaewoo An, Heui Seung Jo, Kyu Hyung Lee
Perinatology. 2017;28(2):35-40. doi: 10.14734/PN.2017.28.2.35.Effects of Ponderal Index on Neonatal Mortality and Morbidities in Extremely Premature Infants
Jae Kyoon Hwang, Ha-Na Kang, Ja-Hye Ahn, Hyun Ju Lee, Hyun-Kyung Park, Chang-Ryul Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(24):e198. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e198.Small for gestational age and obesity: epidemiology and general risks
Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23(1):9-13. doi: 10.6065/apem.2018.23.1.9.Design of the long-term observational cohort study with recombinant human growth hormone in Korean children: LG Growth Study
Sochung Chung, Jae-Ho Yoo, Jin Ho Choi, Young-Jun Rhie, Hyun-Wook Chae, Jae Hyun Kim, Il Tae Hwang, Choong Ho Shin, Eun Young Kim, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23(1):43-50. doi: 10.6065/apem.2018.23.1.43.Insulin and glucagon levels of umbilical cord blood in appropriate for gestational age - preterm infants with or without postnatal hypoglycemia
Jae Hyun Park, Jin Gon Bae, Shin Kim, Chun Soo Kim, Sang Lak Lee, Heung Sik Kim
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2016;21(2):86-91. doi: 10.6065/apem.2016.21.2.86.Korean reference for full-term birth length by sex: data from the 4th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES-IV; 2007–2009)
Ji Hyun Kim, Jun Ah Lee, Dong Ho Kim, Jung Sub Lim
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;24(4):226-230. doi: 10.6065/apem.2019.24.4.226.Comparison of anthropometric, metabolic, and body compositional abnormalities in Korean children and adolescents born small, appropriate, and large for gestational age: a population-based study from KNHANES V (2010–2011)
Tae Kwan Lee, Yoo Mi Kim, Han Hyuk Lim
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024;29(1):29-37. doi: 10.6065/apem.2346044.022.Clinical Characteristics of Hypospadias and Its Association with Very Low Birth Weight Infants with Small for Gestational Age
Seon Nyo Kim, Seung Hyun Kim, Chan Kim, Hanna Kim, Jieun Hwang, Misun Yang, So Yoon Ahn, Se In Sung, Yun Sil Chang, Hyeseon Kim
Neonatal Med. 2024;31(2):17-23. doi: 10.5385/nm.2024.31.2.17.
Reference
-
1. Carlo WA. Prematurity and intrauterine growth restriction. In : Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 19th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders;2011. p. 555–564.2. Bae CW, Kim MH, Chun CS, Lee C, Moon SJ, Yoo BH, et al. Neonatal Statistics of Korea in 1996: collective results of live-births, neonatal mortality, and incidence of dischage against medical advice at 64 hospitals. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 1997; 4:153–169.3. Chernausek SD. Update: consequences of abnormal fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:689–695. PMID: 22238390.
Article4. Itabashi K, Mishina J, Tada H, Sakurai M, Nanri Y, Hirohata Y. Longitudinal follow-up of height up to five years of age in infants born preterm small for gestational age; comparison to full-term small for gestational age infants. Early Hum Dev. 2007; 83:327–333. PMID: 16930872.
Article5. Karlberg J, Albertsson-Wikland K. Growth in full-term small-for-gestational-age infants: from birth to final height. Pediatr Res. 1995; 38:733–739. PMID: 8552442.
Article6. Hernandez MI, Mericq V. Impact of being born small for gestational age on onset and progression of puberty. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 22:463–476. PMID: 18538286.
Article7. Ibanez L, Lopez-Bermejo A, Diaz M, Marcos MV, de Zegher F. Early metformin therapy (age 8-12 years) in girls with precocious pubarche to reduce hirsutism, androgen excess, and oligomenorrhea in adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:E1262–E1267. PMID: 21632811.9. Goldenberg RL, Cutter GR, Hoffman HJ, Foster JM, Nelson KG, Hauth JC. Intrauterine growth retardation: standards for diagnosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989; 161:271–277. PMID: 2669484.
Article10. Olsen IE, Groveman SA, Lawson ML, Clark RH, Zemel BS. New intrauterine growth curves based on United States data. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:e214–e224. PMID: 20100760.
Article11. Cole TJ, Williams AF, Wright CM. RCPCH Growth Chart Expert Group. Revised birth centiles for weight, length and head circumference in the UK-WHO growth charts. Ann Hum Biol. 2011; 38:7–11. PMID: 21175302.
Article12. Salihoglu O, Karatekin G, Uslu S, Can E, Baksu B, Nuhoglu A. New intrauterine growth percentiles: a hospital-based study in Istanbul, Turkey. J Pak Med Assoc. 2012; 62:1070–1074. PMID: 23866450.13. Sankilampi U, Hannila ML, Saari A, Gissler M, Dunkel L. New population-based references for birth weight, length, and head circumference in singletons and twins from 23 to 43 gestation weeks. Ann Med. 2013; 45:446–454. PMID: 23768051.
Article14. Kumar VS, Jeyaseelan L, Sebastian T, Regi A, Mathew J, Jose R. New birth weight reference standards customised to birth order and sex of babies from South India. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2013; 13:38. PMID: 23409828.
Article15. Itabashi K, Miura F, Uehara R, Nakamura Y. New Japanese neonatal anthropometric charts for gestational age at birth. Pediatr Int. 2014; 3. 12. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ped.12331.16. Korean Statistical Information Service [Internet]. Daejeon: KOSIS;cited 2014 Aug 20. Available from: http://kosis.kr/.17. Tukey JW. Exploratory data analysis. Don Mills, CA: Addison-Wesley;1977.18. Cole TJ, Green PJ. Smoothing reference centile curves: the LMS method and penalized likelihood. Stat Med. 1992; 11:1305–1319. PMID: 1518992.
Article19. Clayton PE, Cianfarani S, Czernichow P, Johannsson G, Rapaport R, Rogol A. Management of the child born small for gestational age through to adulthood: a consensus statement of the International Societies of Pediatric Endocrinology and the Growth Hormone Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:804–810. PMID: 17200164.
Article20. Boguszewski MC, Mericq V, Bergada I, Damiani D, Belgorosky A, Gunczler P, et al. Latin American consensus: children born small for gestational age. BMC Pediatr. 2011; 11:66. PMID: 21771322.
Article21. Ranke MB, Lindberg A. KIGS International Board. Prediction models for short children born small for gestational age (SGA) covering the total growth phase. Analyses based on data from KIGS (Pfizer International Growth Database). BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2011; 11:38. PMID: 21627853.
Article22. Albertsson-Wikland K, Karlberg J. Natural growth in children born small for gestational age with and without catch-up growth. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994; 399:64–70. PMID: 7949620.23. Ibanez L, Lopez-Bermejo A, Diaz M, Jaramillo A, Marin S, de Zegher F. Growth hormone therapy in short children born small for gestational age: effects on abdominal fat partitioning and circulating follistatin and high-molecular weight adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:2234–2239. PMID: 20332245.24. Christensen T, Fidler C, Bentley A, Djurhuus C. The cost-effectiveness of somatropin treatment for short children born small for gestational age (SGA) and children with growth hormone deficiency (GHD) in Sweden. J Med Econ. 2010; 13:168–178. PMID: 20136580.
Article25. Bell J, Parker KL, Swinford RD, Hoffman AR, Maneatis T, Lippe B. Long-term safety of recombinant human growth hormone in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:167–177. PMID: 19906787.
Article26. de Zegher F, Lopez-Bermejo A, Ibanez L. Adipose tissue expandability and the early origins of PCOS. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 20:418–423. PMID: 19796964.
Article27. Wang X, Guyer B, Paige DM. Differences in gestational agespecific birthweight among Chinese, Japanese and white Americans. Int J Epidemiol. 1994; 23:119–128. PMID: 8194906.
Article28. Shiono PH, Rauh VA, Park M, Lederman SA, Zuskar D. Ethnic differences in birthweight: the role of lifestyle and other factors. Am J Public Health. 1997; 87:787–793. PMID: 9184507.
Article29. Madan A, Holland S, Humbert JE, Benitz WE. Racial differences in birth weight of term infants in a northern California population. J Perinatol. 2002; 22:230–235. PMID: 11948387.
Article30. Lee SI, Khang YH, Lee MS. Women's attitudes toward mode of delivery in South Korea: a society with high cesarean section rates. Birth. 2004; 31:108–116. PMID: 15153130.
Article31. Uehara R, Miura F, Itabashi K, Fujimura M, Nakamura Y. Distribution of birth weight for gestational age in Japanese infants delivered by cesarean section. J Epidemiol. 2011; 21:217–222. PMID: 21478642.
Article32. Maternal anthropometry and pregnancy outcomes. A WHO Collaborative Study. Bull World Health Organ. 1995; 73(Suppl):1–98.33. Lee JJ. Birth weight for gestational age patterns by sex, plurality, and parity in Korean population. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:732–739.
Article34. Lubchenco LO, Hansman C, Dressler M, Boyd E. Intrauterine growth as estimated from liveborn birth-weight data at 24 to 42 weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 1963; 32:793–800. PMID: 14075621.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percentile Distributions of Birth Weight according to Gestational Ages in Korea (2010-2012)
- Birth weight for gestational age patterns by sex, plurality, and parity in Korean population
- Estimation of Fetal Growth by Measurement of Birth Weight for Gestational Age in Newborn
- Birth Weight Reference for Triples in Korea
- Recent Trends in the Incidence of Multiple Births and Its Consequences on Perinatal Problems in Korea