Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Sep;19(3):141-145. 10.6065/apem.2014.19.3.141.
Earlier re-evaluation may be possible in pediatric patients with eutopic congenital hypothyroidism requiring lower L-thyroxine doses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, St. Paul's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, St. Vincent's Hospital, Suwon, Korea. nicedoc@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2134081
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2014.19.3.141
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The incidence of congenital hypothyroidism (CH) has increased in several countries. Lower cut-off in screening programs have led to an increase in the proportion of transient hypothyroidism (TH) cases diagnosed, leading to debate on the associated clinical and economic impact. This study aimed to identify factors that would allow discrimination between TH and permanent CH (PH) in patients with a eutopic thyroid gland.
METHODS
Sixty-six patients with CH from 3 different hospitals were studied: 26 cases of TH, and 40 cases of PH. Laboratory findings and clinical parameters were analysed in 56 patients with eutopic thyroid gland.
RESULTS
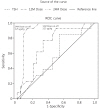
Initial serum thyroid stimulating hormone levels and L-thyroxine dose at 12 and 24 months of age were significantly higher in PH than TH patients with a eutopic thyroid gland. The area under the curve for the 12-month and 24-month dose for the prediction of TH in eutopic CH was 0.799 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.678-0.919; P<0.001) and 0.925 (95% CI, 0.837-1.000; P<0.001), respectively. The optimum 12-month and 24-month dose in predicting TH is 3.25 microg/kg (12-month: sensitivity, 87.1%; specificity, 68.0%; 24-month: sensitivity 93.5%, specificity 88%).
CONCLUSION
Infants with CH requiring lower L-thyroxine doses (<3.25 microg/kg) are likely to have TH, and thus might be re-evaluated at 12 months or 24 months rather than 3 years of age.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis Due to
Dual Oxidase Maturation Factor 2 Mutation as Non-Transient Status of Hypothyroidism
Jisu Lee, Sang-gyeom Kim, Arum Oh, Heon-Seok Han
Int J Thyroidol. 2022;15(1):54-59. doi: 10.11106/ijt.2022.15.1.54.Predictors of transient congenital hypothyroidism in children with eutopic thyroid gland
Il Soon Park, Jong Seo Yoon, Cheol Hwan So, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017;22(2):115-118. doi: 10.6065/apem.2017.22.2.115.
Reference
-
1. Leger J, Olivieri A, Donaldson M, Torresani T, Krude H, van Vliet G, et al. European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology consensus guidelines on screening, diagnosis, and management of congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:363–384. PMID: 24446653.
Article2. Deladoey J, Ruel J, Giguere Y, Van Vliet G. Is the incidence of congenital hypothyroidism really increasing? A 20-year retrospective population-based study in Québec. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:2422–2429. PMID: 21632812.
Article3. Sakka SD, Malamitsi-Puchner A, Loutradis D, Chrousos GP, Kanaka-Gantenbein C. Euthyroid hyperthyrotropinemia in children born after in vitro fertilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:1338–1341. PMID: 19190111.
Article4. Radetti G, Fanolla A, Pappalardo L, Gottardi E. Prematurity may be a risk factor for thyroid dysfunction in childhood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:155–159. PMID: 17032720.
Article5. Zoeller RT, Tan SW, Tyl RW. General background on the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2007; 37:11–53. PMID: 17364704.
Article6. Horn S, Heuer H. Thyroid hormone action during brain development: more questions than answers. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010; 315:19–26. PMID: 19765631.
Article7. Bhavani N. Transient congenital hypothyroidism. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 15(Suppl 2):S117–S120. PMID: 21966647.
Article8. Vermiglio F, Lo Presti VP, Scaffidi Argentina G, Finocchiaro MD, Gullo D, et al. Maternal hypothyroxinaemia during the first half of gestation in an iodine deficient area with endemic cretinism and related disorders. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1995; 42:409–415. PMID: 7750195.
Article9. Hashemipour M, Hovsepian S, Kelishadi R, Iranpour R, Hadian R, Haghighi S, et al. Permanent and transient congenital hypothyroidism in Isfahan-Iran. J Med Screen. 2009; 16:11–16. PMID: 19349525.
Article10. American Academy of Pediatrics. Rose SR. Section on Endocrinology and Committee on Genetics, American Thyroid Association. Brown RS. Public Health Committee, Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society. Foley T, et al. Update of newborn screening and therapy for congenital hypothyroidism. Pediatrics. 2006; 117:2290–2303. PMID: 16740880.
Article11. Hong SY, Chung HR, Lee SY, Shin CH, Yang SW. Factors distinguishing between transient and permanent hypothyroidism in patients diagnosed as congenital hypothyroidism by newborn screening. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2005; 10:154–160.12. Unuvar T, Demir K, Abaci A, Buyukgebiz A, Bober E. The role of initial clinical and laboratory findings in infants with hyperthyrotropinemia to predict transient or permanent hypothyroidism. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013; 5:170–173. PMID: 24072085.13. Zung A, Tenenbaum-Rakover Y, Barkan S, Hanukoglu A, Hershkovitz E, Pinhas-Hamiel O, et al. Neonatal hyperthyrotropinemia: population characteristics, diagnosis, management and outcome after cessation of therapy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010; 72:264–271. PMID: 19473184.14. Skordis N, Toumba M, Savva SC, Erakleous E, Topouzi M, Vogazianos M, et al. High prevalence of congenital hypothyroidism in the Greek Cypriot population: results of the neonatal screening program 1990-2000. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 18:453–461. PMID: 15921174.15. Kohler B, Schnabel D, Biebermann H, Gruters A. Transient congenital hypothyroidism and hyperthyrotropinemia: normal thyroid function and physical development at the ages of 6-14 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996; 81:1563–1567. PMID: 8636368.16. Rabbiosi S, Vigone MC, Cortinovis F, Zamproni I, Fugazzola L, Persani L, et al. Congenital hypothyroidism with eutopic thyroid gland: analysis of clinical and biochemical features at diagnosis and after re-evaluation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:1395–1402. PMID: 23426615.
Article17. Lim HK, Kim KH, Kim SH, No HY, Kim CJ, Woo YJ, et al. Predictors of transient hypothyroidism in neonatal screening test. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2006; 11:50–56.18. Ghasemi M, Hashemipour M, Hovsepian S, Heiydari K, Sajadi A, Hadian R, et al. Prevalence of transient congenital hypothyroidism in central part of Iran. J Res Med Sci. 2013; 18:699–703. PMID: 24379847.19. Unuvar T, Demir K, Abacı A, Atas A, Buyukgebiz A, Bober E. Monitoring and prognostic evaluation of patients with congenital hypothyroidism treated in a pediatric endocrinology unit. Turk J Pediatr. 2013; 55:384–390. PMID: 24292031.20. Lim G, Lee YK, Han HS. Early discontinuation of thyroxine therapy is possible in most very low-birthweight infants with hypothyroidism detected by screening. Acta Paediatr. 2014; 103:e123–e129. PMID: 24117608.
Article21. Srinivasan R, Harigopal S, Turner S, Cheetham T. Permanent and transient congenital hypothyroidism in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2012; 101:e179–e182. PMID: 22107264.
Article22. Chung HR, Shin CH, Yang SW, Choi CW, Kim BI, Kim EK, et al. High incidence of thyroid dysfunction in preterm infants. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:627–631. PMID: 19654943.
Article23. Chee YY, Wong KY, Low L. Review of primary hypothyroidism in very low birthweight infants in a perinatal centre in Hong Kong. J Paediatr Child Health. 2011; 47:824–831. PMID: 21435074.
Article24. Bijarnia S, Wilcken B, Wiley VC. Newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism in very-low-birth-weight babies: the need for a second test. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011; 34:827–833. PMID: 21331666.
Article25. Eugster EA, LeMay D, Zerin JM, Pescovitz OH. Definitive diagnosis in children with congenital hypothyroidism. J Pediatr. 2004; 144:643–647. PMID: 15127002.
Article26. Parazzini C, Baldoli C, Scotti G, Triulzi F. Terminal zones of myelination: MR evaluation of children aged 20-40 months. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1669–1673. PMID: 12427621.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predictors of transient congenital hypothyroidism in children with eutopic thyroid gland
- A Case of Thyroxine Binding Globulin Deficiency with Hypothyroidism
- Two Cases with Prolonged TSH Elevation in Congenital Hypothyroidism
- A case of congenital goiter with congenital hypothyroidism due to organification defect
- Factors Distinguishing between Transient and Permanent Hypothyroidism in Patients Diagnosed as Congenital Hypothyroidism by Newborn Screening