Cancer Res Treat.
2015 Apr;47(2):329-333. 10.4143/crt.2013.145.
Reversible Cerebellar Ataxia Related to Extrapontine Myelinolysis without Hyponatremia after Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. sgkimpatheny@gmail.com
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2132813
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.145
Abstract
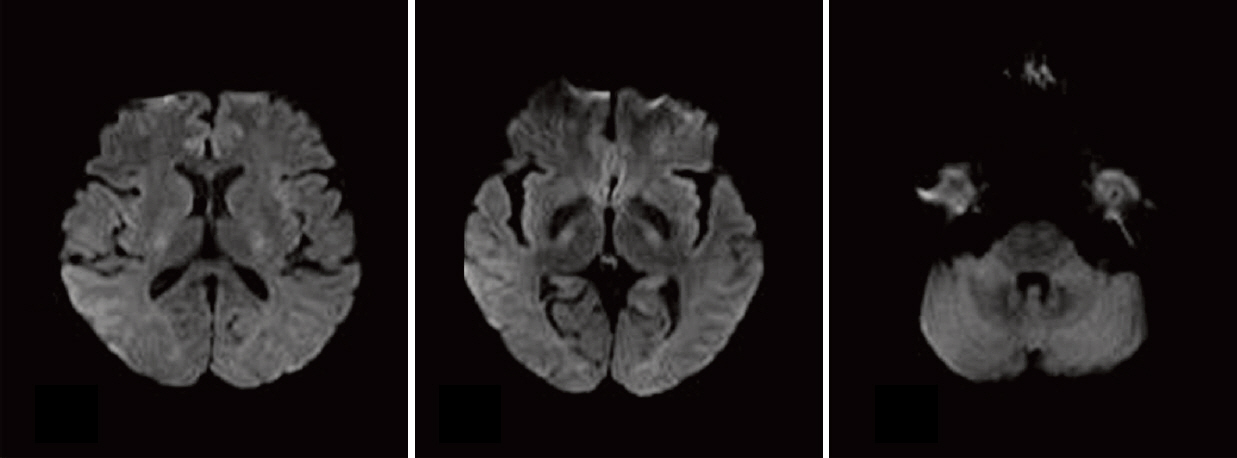
- A 60-year-old woman presented with cerebellar signs including dysarthria and ataxia, after intravenous infusion of cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Several blood tests showed mild neutropenia, normocytic normochromic anemia, but no evidence of a marked hyponatremia. Brain magnetic resonance imaging with diffusion-weighted sequences showed hyper-intense signal abnormalities in the extrapontine region, sparing the basis pontis. Here, we report on the case of a patient with reversible cerebellar ataxia related to extrapontine myelinolysis without hyponatremia after treatment with cisplatin-based chemotherapy for cholangiocarcinoma and discuss the literature on cerebellar ataxia in patients who underwent recent chemotherapy for malignancy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL. Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959; 81:154–72.2. Martin RJ. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: the osmotic demyelination syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75 Suppl 3:iii22–8.
Article3. King JD, Rosner MH. Osmotic demyelination syndrome. Am J Med Sci. 2010; 339:561–7.
Article4. Dolciotti C, Nuti A, Cipriani G, Borelli P, Baldacci F, Logi C, et al. Cerebellar ataxia with complete clinical recovery and resolution of MRI lesions related to central pontine myelinolysis: case report and literature review. Case Rep Neurol. 2010; 2:157–62.
Article5. Ho VB, Fitz CR, Yoder CC, Geyer CA. Resolving MR features in osmotic myelinolysis (central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993; 14:163–7.6. Forster A, Nolte I, Wenz H, Al-Zghloul M, Kerl HU, Brockmann C, et al. Value of diffusion-weighted imaging in central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Neuroradiology. 2013; 55:49–56.
Article7. Steller U, Koschorek F, Strenge H. Cerebellar ataxia with recovery related to central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol. 1988; 235:379–81.
Article8. Weissman JD, Weissman BM. Pontine myelinolysis and delayed encephalopathy following the rapid correction of acute hyponatremia. Arch Neurol. 1989; 46:926–7.
Article9. Garzon T, Mellibovsky L, Roquer J, Perich X, Diez-Perez A. Ataxic form of central pontine myelinolysis. Lancet Neurol. 2002; 1:517–8.
Article10. Kim J, Song T, Park S, Choi IS. Cerebellar peduncular myelinolysis in a patient receiving hemodialysis. J Neurol Sci. 2007; 253:66–8.
Article11. Yau TK, Yiu HY, Lee WM. Central pontine myelinolysis: report of two occurrences after cisplatin-containing chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 1993; 5:395–6.
Article12. Patel SV, Parish DC, Patel RM, Grimsley EW. Resolution of MRI findings in central pontine myelinosis associated with hypokalemia. Am J Med Sci. 2007; 334:490–2.
Article13. Bahr M, Sommer N, Petersen D, Wietholter H, Dichgans J. Central pontine myelinolysis associated with low potassium levels in alcoholism. J Neurol. 1990; 237:275–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Central Pontine Myelinolysis Presenting With Cerebellar Ataxia
- Neuropsychological Findings of Extrapontine Myelinolysis without Central Pontine Myelinolysis: Initial and Follow-up Evaluation
- Central Pontine and Extrapontine Myelinolysis in a Patient with Traumatic Brain Injury Following Not Rapid Correction of Hyponatremia: A Case Report
- Central Pontine and EXtrapontine Myelinolysis
- Asymptomatic Extrapontine Myelinolysis in Diabetic Woman