J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2015 Oct;53(4):345-351. 10.4047/jkap.2015.53.4.345.
Axial wall thickness of zirconia abutment in anterior region
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea.
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. japeditor@kap.or.kr
- KMID: 2118807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2015.53.4.345
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proper axial thickness of zirconia abutment applied to implant in the anterior region.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
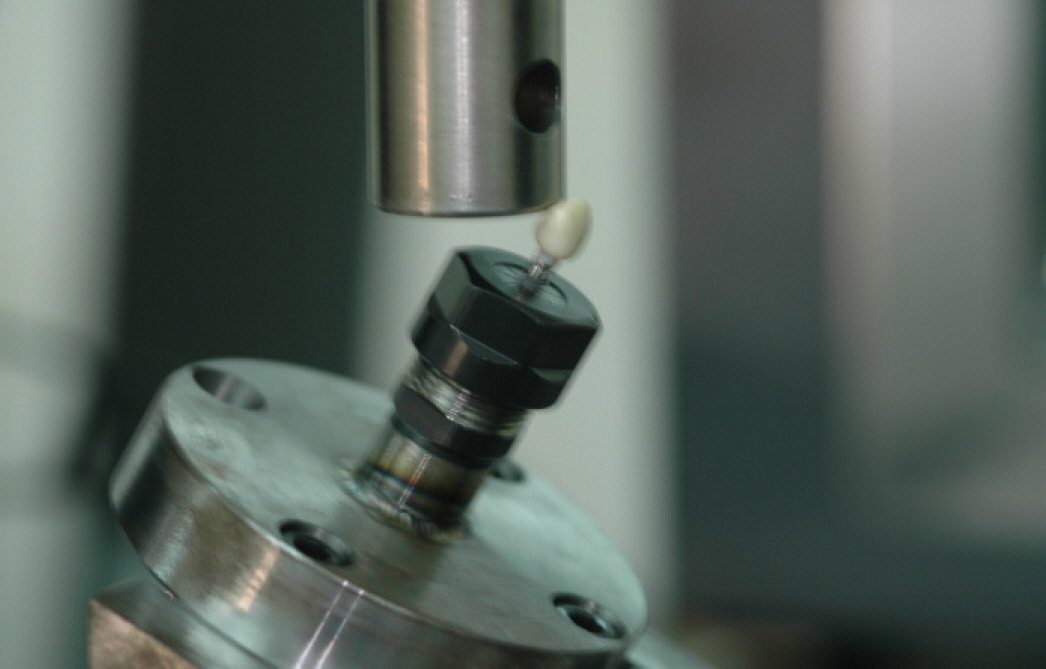
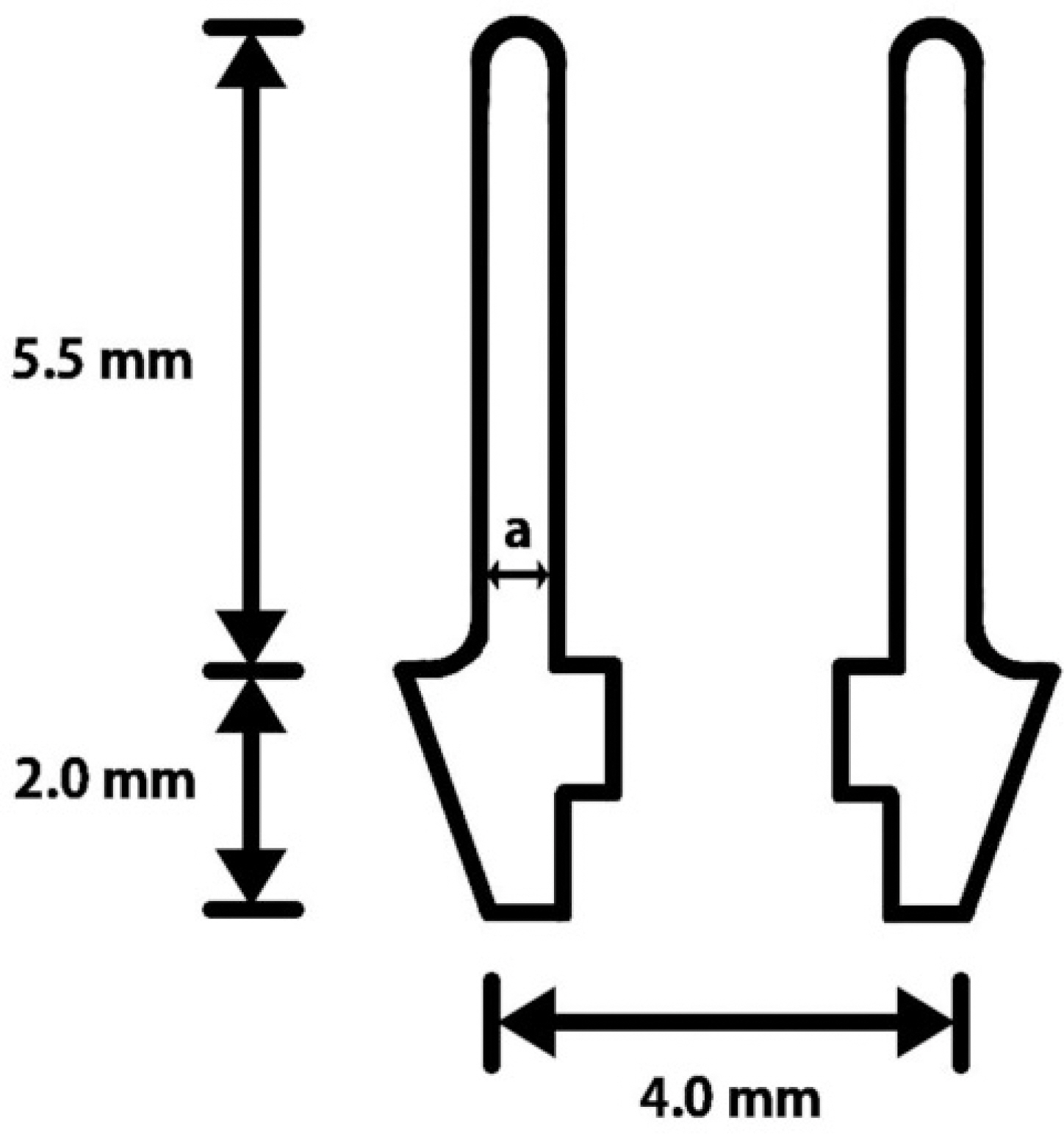
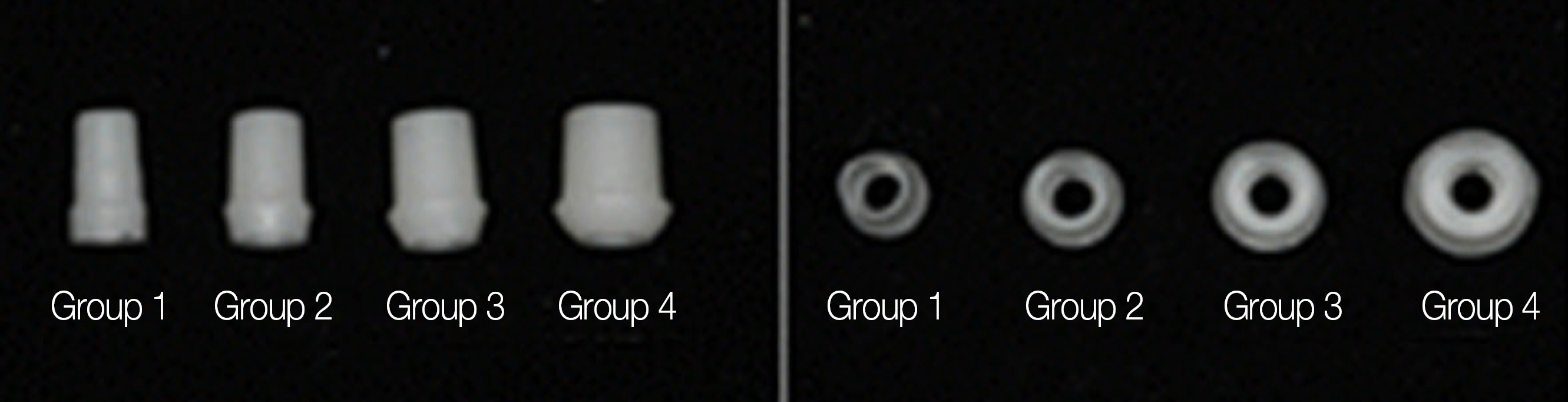
Zirconia abutments were prepared at different axial wall thickness by processing pre-sintered zirconia blocks via CAD/CAM to obtain equal specimens. The abutments were each produced with a thickness of 0.5 mm (Group 1), 0.8 mm (Group 2), 1.2 mm (Group 3), or 1.5 mm (Group 4). The implant used in this study was a external connection type one (US, Osstem, Pussan, Korea) product and the zirconia abutment was prepared via replication of a cemented abutment. The crowns were prepared via CAM/CAM with a thickness of 1.5 mm and were cemented to the abutments using RelyX(TM) UniCem cement. A universal testing machine was used to apply load at 30 degrees and measure fracture strength of the zirconia abutment.
RESULTS
Fracture strength of the abutments for Group 1, Group 2, Group 3, and Group 4 were 236.00 +/- 67.55 N, 599.00 +/- 15.80 N, 588.20 +/- 33.18 N, and 97.83 +/- 98.13 N, respectively. Group 1 showed a significantly lower value, as compared to the other groups (independent Mann-Whitney U-test. P<.05). No significant differences were detected among Group 2, Group 3, and Group 4 (independent Mann-Whitney U-test. P>.05).
CONCLUSION
Zirconia abutment requires optimal thickness for fracture resistance. Within the limitation of this study, > 0.8 mm thickness is recommended for zirconia abutment in anterior implants.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Glantz PO, Lindhe J. The mucosal attachment at different abutments. An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 1998; 25:721–7.2. Andersson B, Schä rer P, Simion M, Bergströ m C. Ceramic implant abutments used for short-span fixed partial dentures: a prospective 2-year multicenter study. Int J Prosthodont. 1999; 12:318–24.3. Welander M, Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T. The mucosal barrier at implant abutments of different materials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:635–41.
Article4. Andersson B, Glauser R, Maglione M, Taylor A. Ceramic implant abutments for short-span FPDs: a prospective 5-year multicenter study. Int J Prosthodont. 2003; 16:640–6.5. Aramouni P, Zebouni E, Tashkandi E, Dib S, Salameh Z, Almas K. Fracture resistance and failure location of zirconium and metal-lic implant abutments. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008; 9:41–8.6. Att W, Kurun S, Gerds T, Strub JR. Fracture resistance of single-tooth implant-supported all-ceramic restorations: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2006; 95:111–6.
Article7. Yildirim M, Edelhoff D, Hanisch O, Spiekermann H. Ceramic abutments–a new era in achieving optimal esthetics in implant dentistry. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2000; 20:81–91.8. Bressan E1, Paniz G, Lops D, Corazza B, Romeo E, Favero G. Influence of abutment material on the gingival color of implant-supported all-ceramic restorations: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:631–7.
Article9. Prestipino V, Ingber A. Esthetic high-strength implant abutments. Part I. J Esthet Dent. 1993; 5:29–36.10. Rasperini G, Maglione M, Cocconcelli P, Simion M. In vivo early plaque formation on pure titanium and ceramic abutments: a comparative microbiological and SEM analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998; 9:357–64.
Article11. Prestipino V, Ingber A. Esthetic high-strength implant abutments. Part II. J Esthet Dent. 1993; 5:63–8.
Article12. Glauser R, Sailer I, Wohlwend A, Studer S, Schibli M, Schä rer P. Experimental zirconia abutments for implant-supported sin-gle-tooth restorations in esthetically demanding regions: 4-year results of a prospective clinical study. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17:285–90.13. Reich S1, Petschelt A, Lohbauer U. The effect of finish line preparation and layer thickness on the failure load and fractography of ZrO2 copings. J Prosthet Dent. 2008; 99:369–76.14. Manicone PF, Rossi Iommetti P, Raffaelli L. An overview of zirconia ceramics: basic properties and clinical applications. J Dent. 2007; 35:819–26.
Article15. Adatia ND, Bayne SC, Cooper LF, Thompson JY. Fracture resistance of yttria-stabilized zirconia dental implant abutments. J Prosthodont. 2009; 18:17–22.
Article16. Yildirim M, Fischer H, Marx R, Edelhoff D. In vivo fracture resistance of implant-supported all-ceramic restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2003; 90:325–31.
Article17. Butz F, Heydecke G, Okutan M, Strub JR. Survival rate, fracture strength and failure mode of ceramic implant abutments after chewing simulation. J Oral Rehabil. 2005; 32:838–43.
Article18. Gehrke P, Dhom G, Brunner J, Wolf D, Degidi M, Piattelli A. Zirconium implant abutments: fracture strength and influence of cyclic loading on retaining-screw loosening. Quintessence Int. 2006; 37:19–26.19. Yang B1, Lange-Jansen HC, Scharnberg M, Wolfart S, Ludwig K, Adelung R, Kern M. Influence of saliva contamination on zirconia ceramic bonding. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:508–13.
Article20. Sakaguchi RL, Douglas WH, DeLong R, Pintado MR. The wear of a posterior composite in an artificial mouth: a clinical correlation. Dent Mater. 1986; 2:235–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Zirconia Abutment Fracture in the Anterior Region: Case Series
- Fracture resistance of zirconia and resin nano ceramic implant abutments according to thickness after thermocycling
- The effect of reduced thickness in different regions on the fracture resistance of monolithic zirconia crowns
- Effect of abutment shade, ceramic thickness, and coping type on the final shade of zirconia all-ceramic restorations: in vitro study of color masking ability
- Comparison of marginal and internal fit of zirconia abutments with titanium abutments in internal hexagonal implants