Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):295-297. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.295.
Treatment of Verruca Vulgaris in Both External Auditory Canals Using Bleomycin Injections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsburm@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2117527
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.295
Abstract
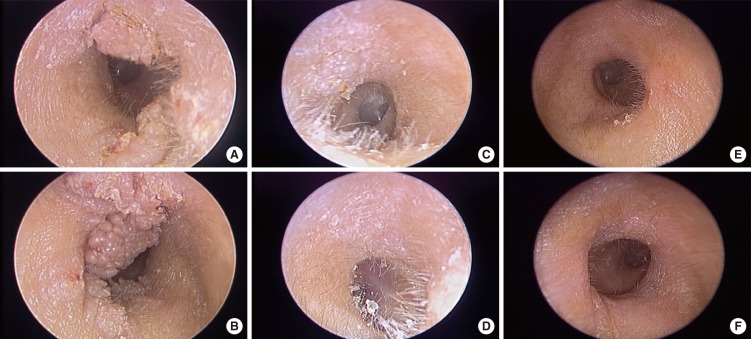
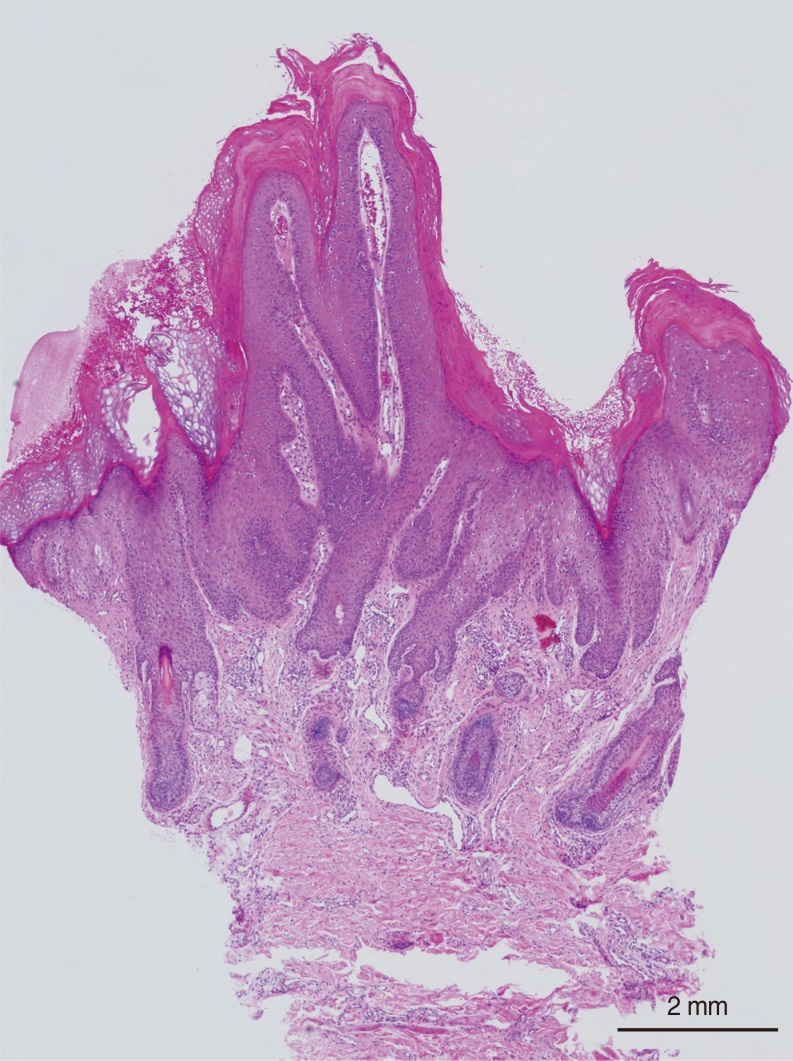
- Verruca vulgaris is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. Verruca in the external auditory canal (EAC) has rarely been reported. A previous case report introduced surgical excision as a treatment for verruca in the EAC. We present a case of verruca vulgaris in both EACs that was successfully treated with an intralesional bleomycin injection. A 32-year-old male patient presented with ear fullness and palpable lumps in both EACs. Both of his canals were filled with multiple pinkish, papillomatous masses. Verruca vulgaris was confirmed by skin biopsy. An otolaryngologist referred this patient and recommended surgical excision. However, we performed intralesional bleomycin injections for treatment. Twice intralesional bleomycin injections at one-month intervals had excellent results without recurrence, ulceration or scar formation. This result indicates that bleomycin injections may prove to be an effective first-line treatment of verruca in the EAC.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Androphy EJ, Kirnbauer R. Human papilloma virus infections. In : Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, Wolff K, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 2421–2433.2. Kim J, Lee DH, Cho KJ, Lee SY. Huge verruca vulgaris (wart) of the external auditory canal. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 12. 139(6):865–866. PMID: 19041521.
Article3. Wang S, Yee H, Wen HY, Wang BY. Papillomas of the external ear canal: report of ten cases in Chinese patients with HPV in situ hybridization. Head Neck Pathol. 2009; 9. 3(3):207–211. PMID: 20596973.
Article4. Chang NC, Chien CY, Wu CC, Chai CY. Squamous papilloma in the external auditory canal: a common lesion in an uncommon site. World J Clin Cases. 2013; 5. 1(2):92–95. PMID: 24303475.
Article5. Xia MY, Zhu WY, Lu JY, Lu Q, Chen L. Ultrastructure and human papillomavirus DNA in papillomatosis of external auditory canal. Int J Dermatol. 1996; 5. 35(5):337–339. PMID: 8734655.
Article6. Sterling JC, Handfield-Jones S, Hudson PM. British Association of Dermatologists. Guidelines for the management of cutaneous warts. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 1. 144(1):4–11. PMID: 11167676.
Article7. Saitta P, Krishnamurthy K, Brown LH. Bleomycin in dermatology: a review of intralesional applications. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 10. 34(10):1299–1313. PMID: 18616538.
Article8. Yamamoto T. Bleomycin and the skin. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 11. 155(5):869–875. PMID: 17034512.
Article9. Burm JS, Oh SJ. Intralesional Bleomycin injection for the treatment of Warts. J Korean Soc Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1997; 10. 3(1):81–87.10. Templeton SF, Solomon AR, Swerlick RA. Intradermal bleomycin injections into normal human skin: a histopathologic and immunopathologic study. Arch Dermatol. 1994; 5. 130(5):577–583. PMID: 7513985.
Article