Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):261-267. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.261.
Analysis of Clinical Feature and Management of Fish Bone Ingestion of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. lesaby@hanmail.net
- 2Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Dong-A University Hospital Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Busan, Korea.
- 4Biomedical Research Institute, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2117522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.261
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Fish bone impaction in the upper gastrointestinal tract is a common reason for patients to seek emergent care. The aim of this study was to find a clinical characteristics of patients with fish bone impaction in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
METHODS
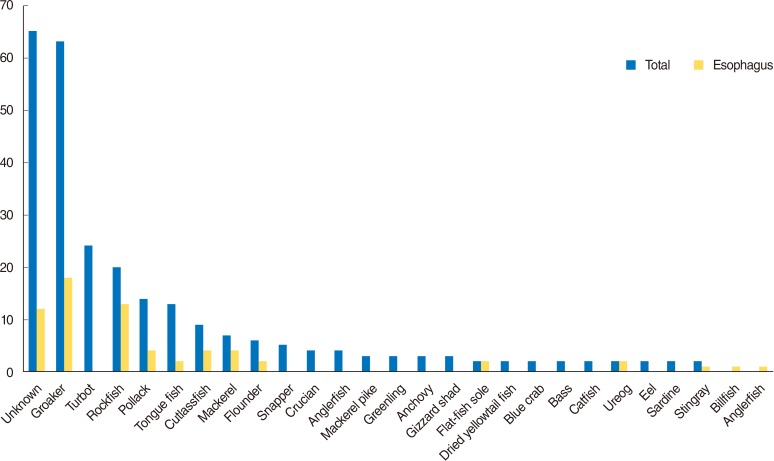
The study was conducted on 286 fish bone ingestion patients who complained of dysphagia and irritation after eating fish. The patients were treated according to the hospital protocol regarding the removal of fish bone. The parameters for the analysis included the age and sex of the patients, location and characteristics of the foreign body, method of removal, and type of fish.
RESULTS
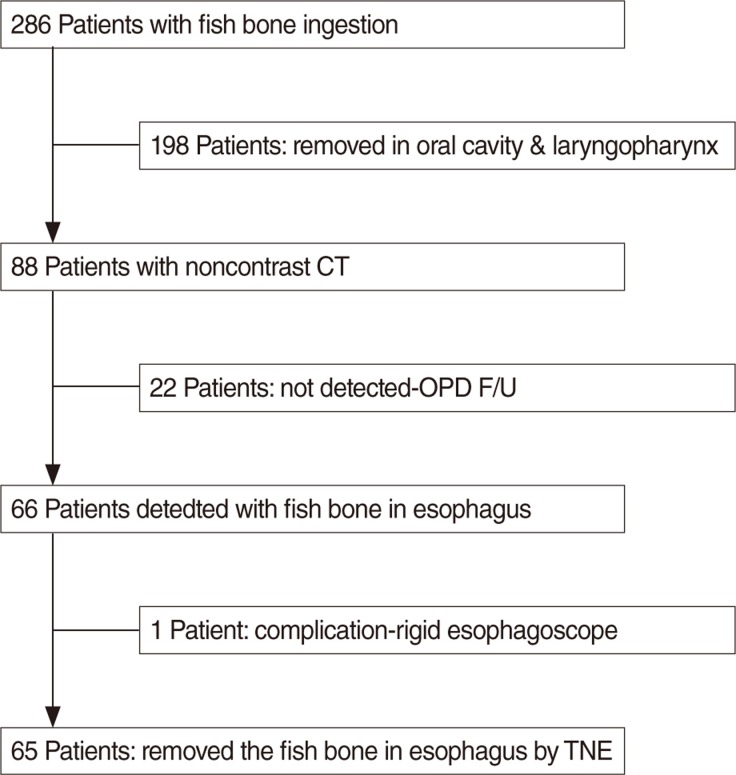
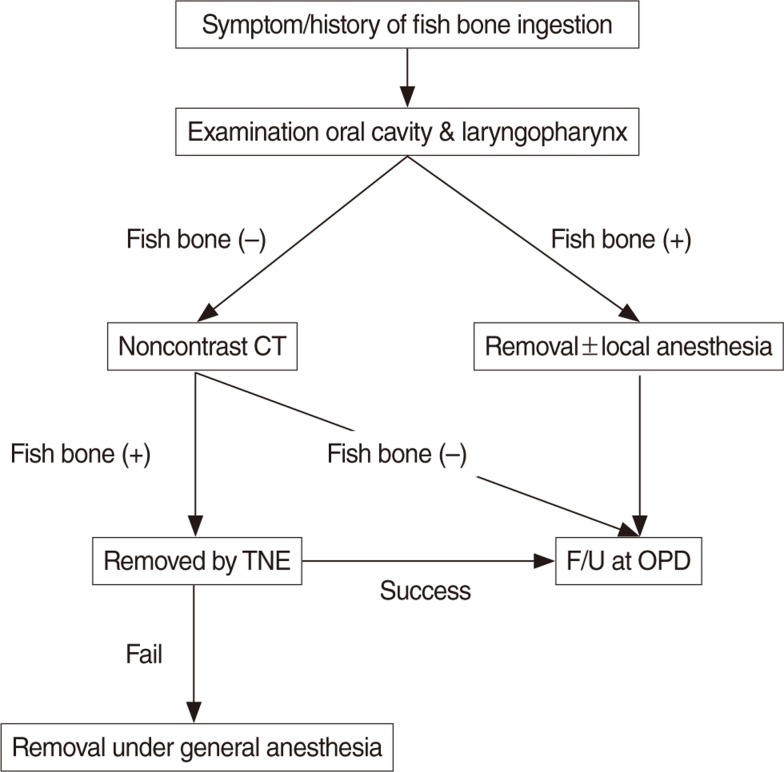
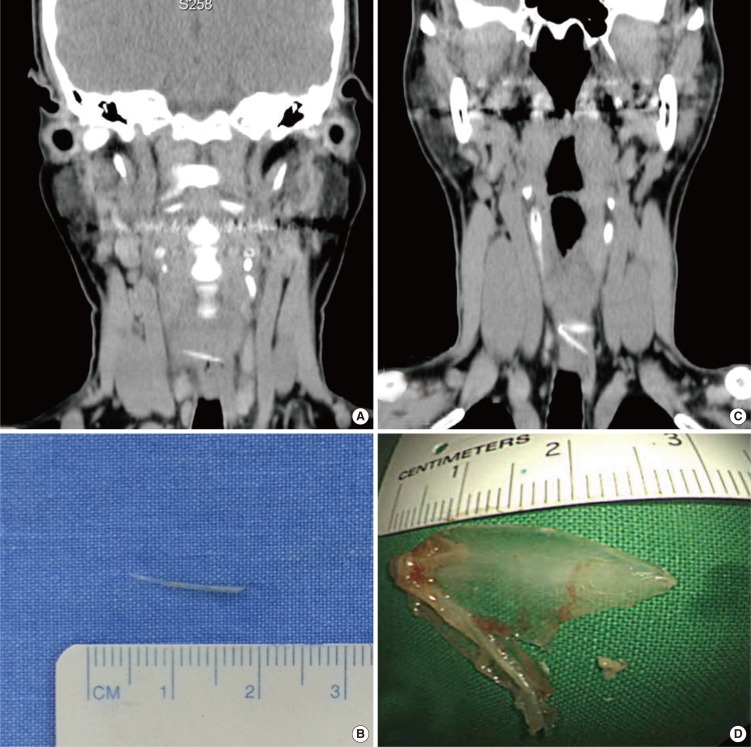
The fish bone could be observed by the physical examination in the oral cavity and laryngopharynx in 198 patients (69.23%). For those patients in whom the foreign body could not be observed in oral cavity and laryngopharynx, noncontrast computed tomography (CT) (from nasopharynx to diaphragm) was performed. The fish bone was discovered in the esophagus of 66 patients (23.08%). The esophageal fish bone was successfully removed by transnasal flexible esophagoscopy (TNE) in 55 patients, the fish bone moved to the stomach in 10 patients and one fish bone was removed by rigid esophagoscopy due to esophageal abscess. The esophageal fish bone was mostly found in patients aged 50 years and older.
CONCLUSION
Fish bone foreign body ingestion in the esophagus appeared to be more common in older patients. Incorporating noncontrast CT and TNE can facilitate decision-making and adequate treatment for patients with fish bone impactions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Oroesophageal Fish Bone Foreign Body
Heung Up Kim
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(4):318-326. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.087.A Missed and Delayed Detected Fish Bone Impaction in Subglottis
Chung Man Sung, Hyung Chae Yang, Sung Min Jin, Chul Ho Jang
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2019;62(1):57-59. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2017.00304.
Reference
-
1. Vizcarrondo FJ, Brady PG, Nord HJ. Foreign bodies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 1983; 8. 29(3):208–210. PMID: 6618118.
Article2. Henderson CT, Engel J, Schlesinger P. Foreign body ingestion: review and suggested guidelines for management. Endoscopy. 1987; 3. 19(2):68–71. PMID: 3552641.
Article3. Nandi P, Ong GB. Foreign body in the oesophagus: review of 2394 cases. Br J Surg. 1978; 1. 65(1):5–9. PMID: 623968.
Article4. Webb WA. Management of foreign bodies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1988; 1. 94(1):204–216. PMID: 3275566.
Article5. Devanesan J, Pisani A, Sharma P, Kazarian KK, Mersheimer WL. Metallic foreign bodies in the stomach. Arch Surg. 1977; 5. 112(5):664–665. PMID: 857769.
Article6. Schwartz GF, Polsky HS. Ingested foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract. Am Surg. 1976; 4. 42(4):236–238. PMID: 1267274.7. Lue AJ, Fang WD, Manolidis S. Use of plain radiography and computed tomography to identify fish bone foreign bodies. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 10. 123(4):435–438. PMID: 11020181.
Article8. Watanabe K, Kikuchi T, Katori Y, Fujiwara H, Sugita R, Takasaka T, et al. The usefulness of computed tomography in the diagnosis of impacted fish bones in the oesophagus. J Laryngol Otol. 1998; 4. 112(4):360–364. PMID: 9659498.
Article9. Bennett AM, Sharma A, Price T, Montgomery PQ. The management of foreign bodies in the pharynx and oesophagus using transnasal flexible laryngo-oesophagoscopy (TNFLO). Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008; 1. 90(1):13–16. PMID: 18201491.
Article10. Sheth N, Diner WC. Swallowing problems in the elderly. Dysphagia. 1988; 2(4):209–215. PMID: 3251696.
Article11. Evans RM, Ahuja A, Rhys Williams S, Van Hasselt CA. The lateral neck radiograph in suspected impacted fish bones: does it have a role? Clin Radiol. 1992; 8. 46(2):121–123. PMID: 1395399.12. Marco De Lucas E, Sadaba P, Lastra Garcia-Baron P, Ruiz-Delgado ML, Gonzalez Sanchez F, Ortiz A, et al. Value of helical computed tomography in the management of upper esophageal foreign bodies. Acta Radiol. 2004; 7. 45(4):369–374. PMID: 15323387.
Article13. Sundgren PC, Burnett A, Maly PV. Value of radiography in the management of possible fishbone ingestion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1994; 8. 103(8 Pt 1):628–631. PMID: 8060057.
Article14. Eliashar R, Dano I, Dangoor E, Braverman I, Sichel JY. Computed tomography diagnosis of esophageal bone impaction: a prospective study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 7. 108(7 Pt 1):708–710. PMID: 10435934.
Article15. Woo SH, Kim KH. Proposal for methods of diagnosis of fish bone foreign body in the esophagus. Laryngoscope. 2015; 5. 11. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1002/lary.25340.
Article16. Liu YC, Zhou SH, Ling L. Value of helical computed tomography in the early diagnosis of esophageal foreign bodies in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2013; 9. 31(9):1328–1332. PMID: 23896013.
Article17. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Guideline for the management of ingested foreign bodies. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995; 12. 42(6):622–625. PMID: 8674946.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of intra-abdominal abscess caused by unconsciously ingestion of fish bone in elderly patient
- A Case of a Pharyngeal Impacted Fish Bone Foreign Body Detected by Finger Palpation
- A Case of Fish Bone Induced Colon Perforation Presented as an Intraabdominal Mass
- Review of 78 Cases Foreign Body in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
- A Case of Epoxy Resin Induced Thermal Injury in Upper Gastrointestinal Tract