Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2015 Oct;3(2):141-146. 10.14791/btrt.2015.3.2.141.
Remote Cerebellar Infarction after Supratentorial Craniotomy and Its Management: Two Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yedamin@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2114663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2015.3.2.141
Abstract
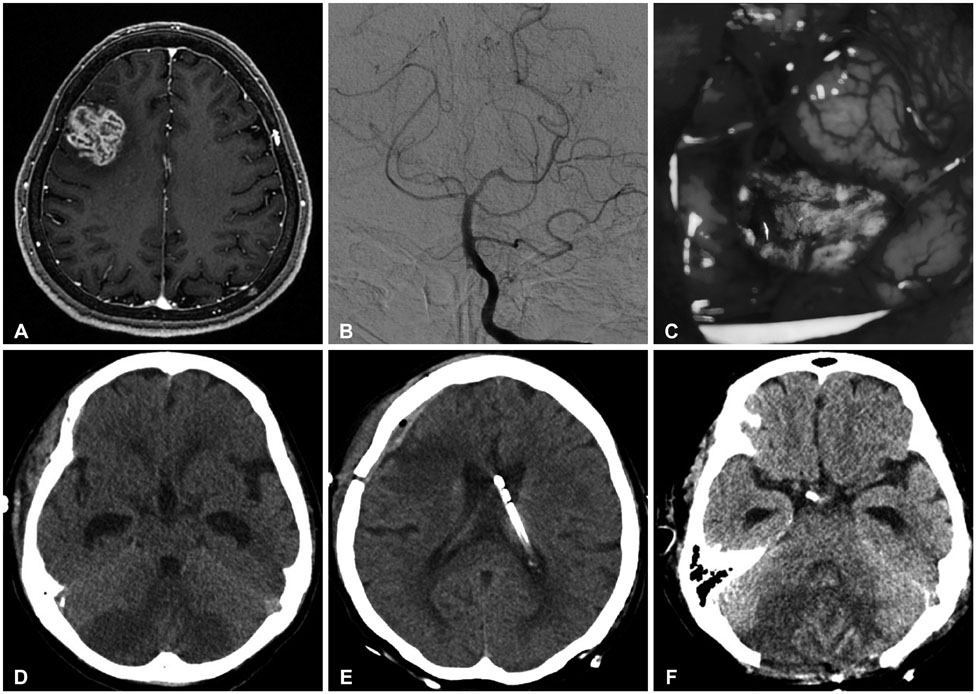
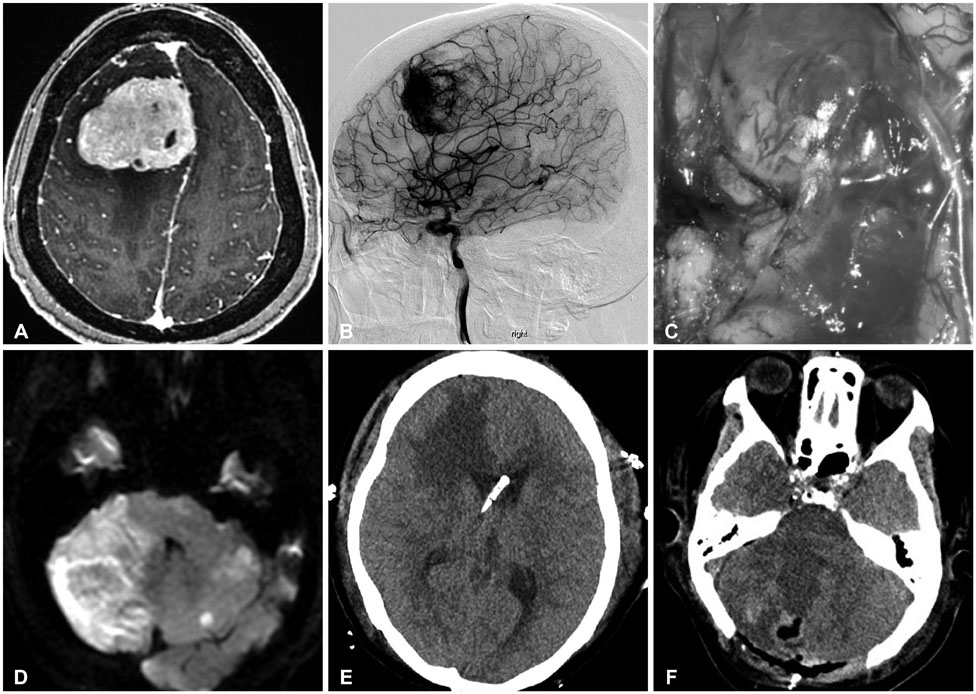
- The cerebellar infarction resulting from supratentorial craniotomy is uncommon event and its management has been controversial. After removal of space occupying lesion on right frontal area, two cases of remote cerebellar infarctions occurred. We reviewed each cases and the techniques to manage such complications are discussed. Early extraventricular catheter insertion and midline suboccipital craniectomy were effectively performed in obtunded patients from cerebellar infarction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brisman MH, Bederson JB, Sen CN, Germano IM, Moore F, Post KD. Intracerebral hemorrhage occurring remote from the craniotomy site. Neurosurgery. 1996; 39:1114–1121. discussion 1121-2
Article2. Cavanilles-Walker JM, Tomasi SO, Sgier F, Kröber M. Remote cerebellar haemorrhage after lumbar spine surgery: case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:1645–1648.
Article3. Ha SH, Kim EM, Ju HM, Lee WK, Min KT. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after unruptured cerebral aneurysm surgery: two cases report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 67:213–216.
Article4. Karaeminogullari O, Atalay B, Sahin O, et al. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after a spinal surgery complicated by dural tear: case report and literature review. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57:1 Suppl. E215. discussion E215.
Article5. Morofuji Y, Tsunoda K, Takeshita T, et al. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage following thoracic spinal surgery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2009; 49:117–119.6. Konya D, Ozgen S, Pamir MN. Cerebellar hemorrhage after spinal surgery: case report and review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:95–99.
Article7. Ivamoto HS, Numoto M, Donaghy RM. Surgical decompression for cerebral and cerebellar infarcts. Stroke. 1974; 5:365–370.
Article8. Chen HJ, Lee TC, Wei CP. Treatment of cerebellar infarction by decompressive suboccipital craniectomy. Stroke. 1992; 23:957–961.
Article9. Rieke K, Krieger D, Adams HP, Aschoff A, Meyding-Lamade U, Hacke W. Therapeutic Strategies in Space-Occupying Cerebellar Infarction Based on Clinical, Neuroradiological and Neurophysiological Data. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1993; 3:45–55.
Article10. Baldauf J, Oertel J, Gaab MR, Schroeder HW. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for occlusive hydrocephalus caused by cerebellar infarction. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59:539–544. discussion 539-44
Article11. Heros RC. Surgical treatment of cerebellar infarction. Stroke. 1992; 23:937–938.
Article12. Vahedi K, Hofmeijer J, Juettler E, et al. Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: a pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:215–222.
Article13. Frank JI, Schumm LP, Wroblewski K, et al. Hemicraniectomy and durotomy upon deterioration from infarction-related swelling trial: randomized pilot clinical trial. Stroke. 2014; 45:781–787.
Article14. Ropper AH. Hemicraniectomy--to halve or halve not. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1159–1160.15. Jüttler E, Unterberg A, Woitzik J, et al. Hemicraniectomy in older patients with extensive middle-cerebral-artery stroke. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1091–1100.
Article16. Vahedi K, Vicaut E, Mateo J, et al. Sequential-design, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of early decompressive craniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (DECIMAL Trial). Stroke. 2007; 38:2506–2517.
Article17. Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1493–1502.
Article18. Cho DY, Chen TC, Lee HC. Ultra-early decompressive craniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction. Surg Neurol. 2003; 60:227–232. discussion 232-3
Article19. Mathew P, Teasdale G, Bannan A, Oluoch-Olunya D. Neurosurgical management of cerebellar haematoma and infarct. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 59:287–292.
Article20. Seelig JM, Selhorst JB, Young HF, Lipper M. Ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus in cerebellar hemorrhage. Neurology. 1981; 31:1537–1540.
Article21. You SH, Son KR, Lee NJ, Suh JK. Remote cerebral and cerebellar hemorrhage after massive cerebrospinal fluid leakage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 51:240–243.
Article22. Papanastassiou V, Kerr R, Adams C. Contralateral cerebellar hemorrhagic infarction after pterional craniotomy: report of five cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1996; 39:841–851. discussion 851-2
Article23. Rapanà A, Lamaida E, Pizza V. Multiple postoperative intracerebral haematomas remote from the site of craniotomy. Br J Neurosurg. 1998; 12:364–368.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Remote Cerebellar Hemorrhage After Supratentorial Aneurysm Surgery: Report of 2 Cases
- Remote cerebellar hemorrhage following surgical clipping of an unruptured cerebral aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery
- Remote Intracerebral Hematoma after Supratentorial Graniotomy
- Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Supratentorial Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Remote Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Supratentorial Aneurysmal Surgery: Report of Six Cases