J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Oct;58(4):350-356. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.4.350.
Acute Contralateral Radiculopathy after Unilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. nspsw@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2114372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.4.350
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Cases of contralateral radiculopathy after a transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with a single cage (unilateral TLIF) had been reported, but the phenomenon has not been explained satisfactorily. The purpose of this study was to determine its incidence, causes, and risk factors.
METHODS
We did retrospective study with 546 patients who underwent a unilateral TLIF, and used CT and MRI to study the causes of contralateral radicular symptoms that appeared within a week postoperatively. Clinical and radiological results were compared by dividing the patients into the symptomatic group and asymptomatic group.
RESULTS
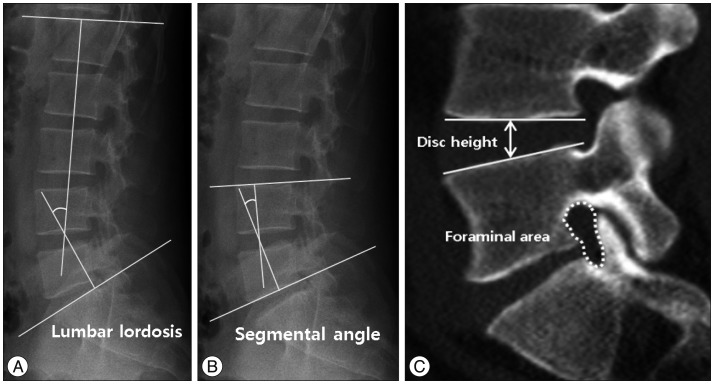
Contralateral symptoms occurred in 32 (5.9%) of the patients underwent unilateral TLIF. The most common cause of contralateral symptoms was a contralateral foraminal stenosis in 22 (68.8%), screw malposition in 4 (12.5%), newly developed herniated nucleus pulposus in 3 (9.3%), hematoma in 1 (3.1%), and unknown origin in 2 patients (6.3%). 16 (50.0%) of the 32 patients received revision surgery. There was no difference in visual analogue scale and Oswestry disability index between the two groups at discharge. Both preoperative and postoperative contralateral foraminal areas were significantly smaller, and postoperative segmental angle was significantly greater in the symptomatic group comparing to those of the asymptomatic group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The incidence rate is not likely to be small (5.9%). If unilateral TLIF is performed for cases when preoperative contralateral foraminal stenosis already exists or when a large restoration of segmental lordosis is required, the probability of developing contralateral radiculopathy is increased and caution from the surgeon is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barnes B, Rodts GE Jr, Haid RW Jr, Subach BR, McLaughlin MR. Allograft implants for posterior lumbar interbody fusion results comparing cylindrical dowels and impacted wedges. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:1191–1198. PMID: 12383364.
Article2. Blume H, Rojas C. Unilateral lumbar interbody fusion (posterior approach) utilizing dowel graft. J Neurol Orthop Surg. 1981; 2:171–175.3. Chiang MF, Zhong ZC, Chen CS, Cheng CK, Shih SL. Biomechanical comparison of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion with one or two cages by finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:E682–E689. PMID: 16946641.
Article4. Cutler AR, Siddiqui S, Mohan AL, Hillard VH, Cerabona F, Das K. Comparison of polyetheretherketone cages with femoral cortical bone allograft as a single-piece interbody spacer in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 5:534–539. PMID: 17176018.
Article5. DiPaola CP, Molinari RW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008; 16:130–139. PMID: 18316711.
Article6. Elias WJ, Simmons NE, Kaptain GJ, Chadduck JB, Whitehill R. Complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion when using a titanium threaded cage device. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93(1 Suppl):45–52. PMID: 10879757.
Article7. Farcy JP, Schwab FJ. Management of flatback and related kyphotic decompensation syndromes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2452–2457. PMID: 9355229.
Article8. Fogel GR, Toohey JS, Neidre A, Brantigan JW. Is one cage enough in posterior lumbar interbody fusion : a comparison of unilateral single cage interbody fusion to bilateral cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20:60–65. PMID: 17285054.
Article9. Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2024–2029. PMID: 16166889.
Article10. Goz V, Weinreb JH, Schwab F, Lafage V, Errico TJ. Comparison of complications, costs, and length of stay of three different lumbar interbody fusion techniques : an analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database. Spine J. 2014; 14:2019–2027. PMID: 24333459.
Article11. Hackenberg L, Halm H, Bullmann V, Vieth V, Schneider M, Liljenqvist U. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion : a safe technique with satisfactory three to five year results. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:551–558. PMID: 15672243.
Article12. Harms JG, Jeszenszky D. The unilateral, transforaminal approach for posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Traumatol. 1998; 6:88–99.13. Hasegawa T, An HS, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH. Lumbar foraminal stenosis : critical heights of the intervertebral discs and foramina. A cryomicrotome study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:32–38. PMID: 7822353.14. Hey HW, Hee HT. Lumbar degenerative spinal deformity : surgical options of PLIF, TLIF and MI-TLIF. Indian J Orthop. 2010; 44:159–162. PMID: 20419002.
Article15. Houten JK, Post NH, Dryer JW, Errico TJ. Clinical and radiographically/neuroimaging documented outcome in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 2006; 20:E8. PMID: 16599424.
Article16. Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O'Shaughnessy BA, Sugrue P, Salehi S, Ondra S, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion : implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 7:379–386. PMID: 17933310.
Article17. Hu SS, Tribus CB, Diab M, Ghanayem AJ. Spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:656–671. PMID: 18326106.18. Humphreys SC, Hodges SD, Patwardhan AG, Eck JC, Murphy RB, Covington LA. Comparison of posterior and transforaminal approaches to lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:567–571. PMID: 11242386.
Article19. Hunt T, Shen FH, Shaffrey CI, Arlet V. Contralateral radiculopathy after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 16(Suppl 3):2007; 311–314. PMID: 17487514.
Article20. Iwata T, Miyamoto K, Hioki A, Fushimi K, Ohno T, Shimizu K. Morphologic changes in contralateral lumbar foramen in unilateral cantilever transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using kidney-type intervertebral spacers. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28:E270–E276. PMID: 23381185.
Article21. Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, Kim SK, Han KM, Maeng DH. Surgical treatment of failed back surgery syndrome due to sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:3081–3087. PMID: 18091505.
Article22. Kim CW, Siemionow K, Anderson DG, Phillips FM. The current state of minimally invasive spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:582–596. PMID: 21411709.23. Kim JT, Shin MH, Lee HJ, Choi DY. Restoration of lumbopelvic sagittal alignment and its maintenance following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): comparison between straight type versus curvilinear type cage. Eur Spine J. 2015; [Epub ahead of print].
Article24. Kim SB, Jeon TS, Heo YM, Lee WS, Yi JW, Kim TK, et al. Radiographic results of single level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative lumbar spine disease : focusing on changes of segmental lordosis in fusion segment. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009; 1:207–213. PMID: 19956478.
Article25. Lee CK, Park JY, Zhang HY. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using a single interbody cage and a tubular retraction system : technical tips, and perioperative, radiologic and clinical outcomes. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:219–224. PMID: 21082048.
Article26. Lee YS, Kim YB, Park SW, Chung C. Comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with direct lumbar interbody fusion : clinical and radiological results. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014; 56:469–474. PMID: 25628805.
Article27. Molinari RW, Gerlinger T. Functional outcomes of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in active-duty US servicemen : a comparison with nonoperative management. Spine J. 2001; 1:215–224. PMID: 14588350.
Article28. Mummaneni PV, Dhall SS, Eck JC, Groff MW, Ghogawala Z, Watters WC 3rd, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 11: interbody techniques for lumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 21:67–74. PMID: 24980588.
Article29. Potter BK, Freedman BA, Verwiebe EG, Hall JM, Polly DW Jr, Kuklo TR. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion : clinical and radiographic results and complications in 100 consecutive patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18:337–346. PMID: 16021015.30. Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V. Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance : how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:2224–2231. PMID: 21102297.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Uniportal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Mini-invasive unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation
- Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Percutaneous Instrumentation: A Technical Note
- Contralateral Lower Limb Radiculopathy Following Minimally Invasive Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease
- Minimal Invasive Unilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion by Sublaminar Decompression: Comparison to Bilateral Approach