J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Mar;50(3):429-434. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.3.429.
Bilateral Medial Rectus Recession Posterior to the Functional Equator in Esotropia Over 40 Prism Diopters
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School & Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. Exo70@ jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2111255
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.3.429
Abstract
-
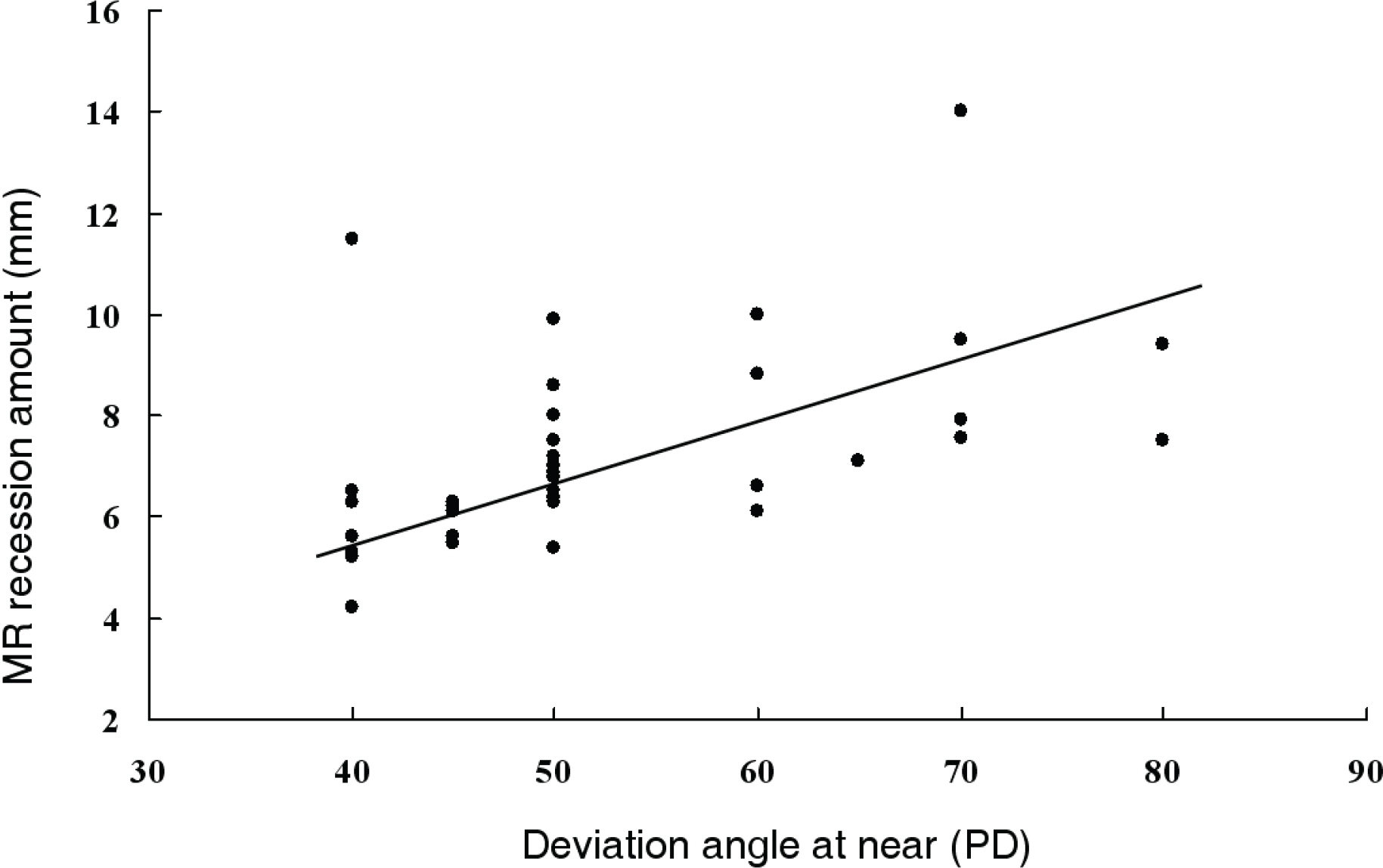
PURPOSE: To investigate bilateral medial rectus recession by considering functional equator as a surgical guideline in esotropia over 40 prism diopters (PD).
METHODS
Forty-one patients who underwent bilateral medial rectus recession, and were followed-up for more than 12 months, were reviewed. The success rate was compared between group 1 and group 2, which were divided to recession site from the functional equator posterior, and also between the hyperopia group and myopia group according to refraction.
RESULTS
According to preoperative deviation angle, 21 patients underwent recession to less than 10 mm posterior to the functional equator (group 1) and 20 patients had recession to 1.5 mm to 2.0 mm posterior to the functional equator (group 2). No significant difference in success rate between group 1 (71.4%) and group 2 (75.0%) was detected at the last follow-up. When divided into a hyperopia group (26 patients) and myopia group (15 patients), the success rate in the myopia group was higher than in the hyperopia group, as observed at the last follow-up, but the difference was not significant. There was 1 case of overcorrection in each group.
CONCLUSIONS
A successful outcome was achieved in 30 patients (73.2%), and overcorrection in 2 patients (4.9%) when recessed to 2.0 mm posterior to functional posterior in esotropia over 40PD.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hutcheson KA. Childhood esotropia. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004; 15:444–8.
Article2. Kowal L, Wong E, Yahalom C. Botulinum Toxin in the treatment of strabismus. A review of its use and effects. Disabil Rehabil. 2007; 29:1823–31.
Article3. Scott WE, Reese PD, Hirsh CR, Flabetich CA. Surgery for large angle congenital esotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:374–7.4. Ramasamy B, Rowe F, Whitfield K, et al. Bilateral combined resection and recession of the medial rectus muscle for convergence excess esotropia. J AAPOS. 2007; 11:307–9.
Article5. Stager DR, Weakley DR Jr, Everett M, Birch EE. Delayed consecutive exotropia following 7-millimeter bilateral medial rectus recession for congenital esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1994; 31:147–50.
Article6. Ing M, Costenbader FD, Parks MM, Albert DG. Early surgery for congenital esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 61:1419–27.
Article7. Szmyd SM, Nelson LB, Calhoun JH, Spratt C. Large bimedial rectus recessions in congenital esotropia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1985; 69:271–4.
Article8. Keskinbora KH, Pulur NK. Long-term results of bilateral medial rectus recession for congenital esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2004; 41:351–5.
Article9. Park HY, Park SW, Park YG. The study of axial length and functional equator in strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:827–36.10. Kim DJ, Park SW, Park YG. Surgical Outcome of Esotropia Considering the Functional Equator. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:778–86.11. Kushner BJ, Fisher MR, Lucchese NJ, Morton GV. How far can a medial rectus safely be recessed? J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1994; 31:138–46.
Article12. Mittelman D, Folk ER. The surgical treatment of undercorrected esotropia: an evaluation of the effect of recession of the medial rectus muscle 13.5 mm from the limbus. Trans Sect Ophthalmol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1975; 79:783–44.13. Hess JB, Calhoun JH. A new rationale for the management of large angle esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1979; 16:345–8.
Article14. West CE, Pepka MX. A comparison of surgical techniques for the treatment of acquired esotropia with increased AC/A ratio. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1994; 31:232–7.15. Kushner BJ, Preslan MW, Vrabec M. Artifacts of measuring during strabismus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1987; 24:159–64.
Article16. Felius J, Stager DR Jr, Beauchamp GR, Stager DR. Re- recession of the medial rectus muscles in patients with recurrent esotropia. J AAPOS. 2001; 5:381–7.17. Tran HM, Mims JL 3rd, Wood RC. A new dose-response curve for bilateral medial rectus recessions for infantile esotropia. J AAPOS. 2002; 6:112–9.
Article18. Von Norden GK. A reassessment of infantile esotropia. Am J ophthalmol. 1988; 105:1–10.19. Willshaw HE, Mashhoudi N, Powell S. Augmented medial rectus recession in the management of esotropia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1986; 70:840–3.
Article20. Lee HD, Lew H, Lee JB, Han SH. Clinical analysis of large recession of bimedial rectus muscles in esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:555–61.21. Nelson LB, Calhoun JH, Simon JW, et al. Surgical management of large angle congenital esotropia. Br J ophthalmol. 1987; 71:380–3.
Article22. Weakley DR Jr, Stager DR, Everett ME. Seven-millimeter bilateral medial rectus recessions in infantile esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991; 28:113–5.
Article23. Prieto-Diaz J. Large bilateral medial rectus recession in early esotropia with bilateral limitation of abduction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1980; 17:101–5.
Article24. Kushner BJ, Lucchese NJ, Morton GV. The influence of axial length on the response to strabismus surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:1616–8.
Article25. Kushner BJ, Lucchese NJ, Morton GV. Variation in axial length and anatomical landmarks in strabismic patients. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:400–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Result of Unilateral Medial Rectus Recession in Moderate Angle Esotropia
- The Study of Axial Length and Functional Equator in Strabismus Surgery
- Comparison of Functional Equator-Considering and Parks Methods in Bilateral Medial Rectus Recession for Esotropia
- Effect of Both Medial Rectus Recession in Large Angle Infantile Esotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Rectus Muscle Recession and Lateral Rectus Muscle Recession and Medial Rectus Muscle Resection in Exotropia Over 40 Prism Diopters