J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2013 Feb;48(1):1-8. 10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.1.1.
The Effect of a Lumbar Spinal Lesion on the Clinical Results of Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea. wscho@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Bundang Chuk Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2106656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.1.1
Abstract
- PURPOSE
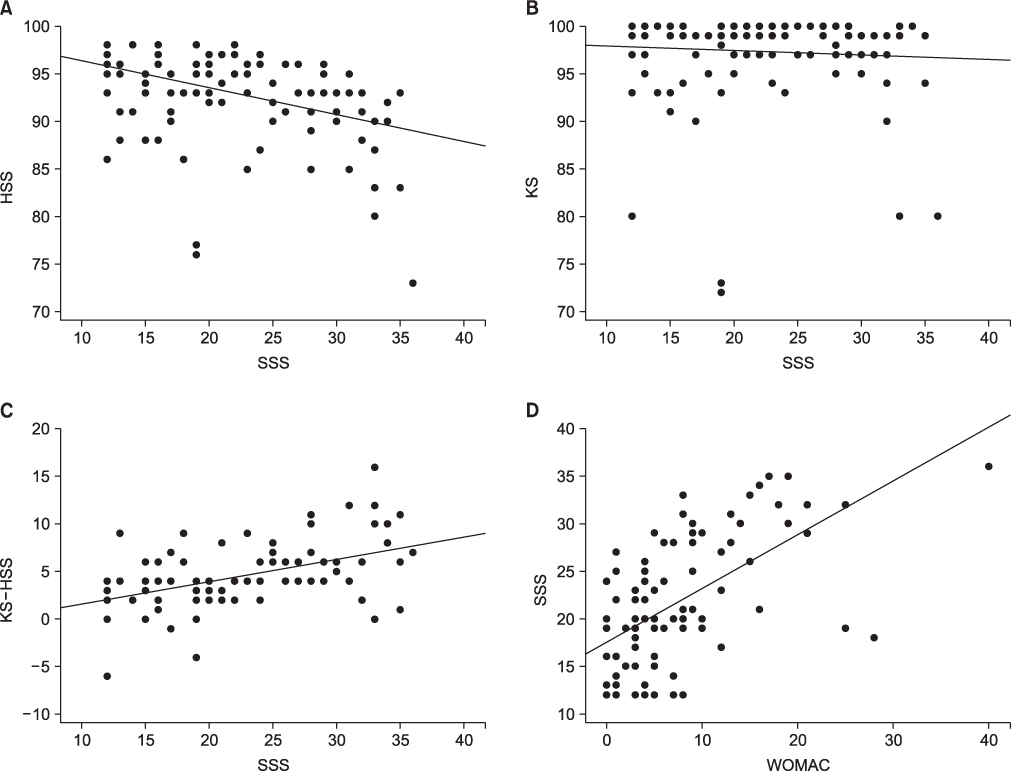
Patients with osteoarthritis of knee joint often concomitantly suffer from degenerative disease of the spine. Furthermore, resulting spinal problems could influence function and pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA), and hence, cause the results of TKA to be misinterpreted. The purpose of this prospective study was to evaluate the effect of spinal disorders, as assessed by Swiss Spinal Stenosis score (SSS scores), on knee function as assessed by knee scores, the Hospital for Special Surgery scale (HSS scale) and Western Ontario & McMaster Osteoarthritis Index scores (WOMAC scores) in patients that after TKA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
One hundred and forty nine osteoarthritic knees of 87 patients were enrolled in this study. All patients received TKA by single surgeon (W-S Cho) from August 2009 to May 2010. Preoperative and postoperative 1- and 2-years HSS scale, Knee, WOMAC, and SSS scores were recorded and analyzed.
RESULTS
Postoperative HSS scale, Knee, and WOMAC scores showed marked improvements versus preoperative scores, and scores at 2 years postoperatively were better than at 1 year postoperatively. No significant correlation was found between postoperative Knee scores and SSS scores. On the other hand, statistically significant correlations were found between HSS and SSS scores and between WOMAC and SSS scores. Interestingly, differences between Knee scores and HSS scores were found to be significantly correlated with SSS scores.
CONCLUSION
When evaluating outcome after TKA, spinal problems should be investigated concomitantly. SSS scores appear to provide a suitable means of assessing spinal problems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anderson JG, Wixson RL, Tsai D, Stulberg SD, Chang RW. Functional outcome and patient satisfaction in total knee patients over the age of 75. J Arthroplasty. 1996. 11:831–840.
Article2. Bonnin M, Laurent JR, Parratte S, Zadegan F, Badet R, Bissery A. Can patients really do sport after TKA? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010. 18:853–862.
Article3. Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, Mahomed NN, Charron KD. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010. 468:57–63.
Article4. Hawker G, Wright J, Coyte P, et al. Health-related quality of life after knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:163–173.
Article5. Heck DA, Robinson RL, Partridge CM, Lubitz RM, Freund DA. Patient outcomes after knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 356:93–110.
Article6. Noble PC, Gordon MJ, Weiss JM, Reddix RN, Conditt MA, Mathis KB. Does total knee replacement restore normal knee function? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 431:157–165.
Article7. Robertsson O, Dunbar M, Pehrsson T, Knutson K, Lidgren L. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27,372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000. 71:262–267.
Article8. Wylde V, Learmonth I, Potter A, Bettinson K, Lingard E. Patient-reported outcomes after fixed- versus mobile-bearing total knee replacement: a multi-centre randomised controlled trial using the Kinemax total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. 90:1172–1179.9. Fokter SK, Yerby SA. Patient-based outcomes for the operative treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2006. 15:1661–1669.
Article10. Hansraj KK, Cammisa FP Jr, O'Leary PF, et al. Decompressive surgery for typical lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 384:10–17.
Article11. Iversen MD, Katz JN. Examination findings and self-reported walking capacity in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Phys Ther. 2001. 81:1296–1306.
Article12. Zucherman JF, Hsu KY, Hartjen CA, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized trial evaluating the X STOP interspinous process decompression system for the treatment of neurogenic intermittent claudication: two-year follow-up results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30:1351–1358.13. Cho WS, Park SS, Kim DH, Jeong YG, Baek SK, Park CJ. The reliability of HSS knee rating system. J Korean Knee Soc. 2000. 12:43–48.14. Cho WS, Kim MY, Youm YS. Cho's knee joint arthroplasty. 2007. 2nd ed. Seoul: Young-chang publisher;130–143.15. Bonnin MP, Basiglini L, Archbold HA. What are the factors of residual pain after uncomplicated TKA? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. 19:1411–1417.
Article16. Al-Hadithy N, Rozati H, Sewell MD, Dodds AL, Brooks P, Chatoo M. Causes of a painful total knee arthroplasty. Are patients still receiving total knee arthroplasty for extrinsic pathologies? Int Orthop. 2012. 36:1185–1189.
Article17. North American Spine Society. Evidence-based clinical guidelines for multidisciplinary spine care: diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. 2007. Burr Ridge: North American Spine Society.18. Kalichman L, Cole R, Kim DH, et al. Spinal stenosis prevalence and association with symptoms: the Framingham Study. Spine J. 2009. 9:545–550.
Article19. Issack PS, Cunningham ME, Pumberger M, Hughes AP, Cammisa FP Jr. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012. 20:527–535.20. Stucki G, Liang MH, Fossel AH, Katz JN. Relative responsiveness of condition-specific and generic health status measures in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995. 48:1369–1378.
Article21. Stucki G, Daltroy L, Liang MH, Lipson SJ, Fossel AH, Katz JN. Measurement properties of a self-administered outcome measure in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996. 21:796–803.
Article22. Pratt RK, Fairbank JC, Virr A. The reliability of the Shuttle Walking Test, the Swiss Spinal Stenosis Questionnaire, the Oxford Spinal Stenosis Score, and the Oswestry Disability Index in the assessment of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. 27:84–91.
Article23. Tuli SK, Yerby SA, Katz JN. Methodological approaches to developing criteria for improvement in lumbar spinal stenosis surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. 31:1276–1280.
Article24. Tomkins CC, Battié MC, Hu R. Construct validity of the physical function scale of the Swiss Spinal Stenosis Questionnaire for the measurement of walking capacity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. 32:1896–1901.
Article25. Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 248:13–14.
Article26. Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:1833–1840.27. Wohlrab D, Hube R, Zeh A, Hein W. Clinical and radiological results of high flex total knee arthroplasty: a 5 year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009. 129:21–24.28. Lee DH, Choi J, Nha KW, Kim HJ, Han SB. No difference in early functional outcomes for mini-midvastus and limited medial parapatellar approaches in navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. 19:66–73.
Article29. Song EK, Seon JK, Yoon TR, Park SJ, Bae BH, Cho SG. Functional results of navigated minimally invasive and conventional total knee arthroplasty: a comparison in bilateral cases. Orthopedics. 2006. 29:S145–S147.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Accompanied by Severe Osteoarthritis of Knee: Comparison between Staged Operations and Same-day Operations
- Vital sign changes associated with tourniquet use under spinal anesthesia for total knee arthroplasty
- Factors Affecting the Effect of Lateral Retinacular Release in Total Knee Joint Arthroplasty
- A Case of Candida Glabrata Infection after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Clinical and Radiological Results of Total Knee Arthroplasty with Patellar Retention