J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Feb;43(1):118-121. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.118.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Delayed Pseudoaneurysm of Deep Femoral Artery: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongguk University International Hospital, Goyang, Korea. drsky71@duih.org
- KMID: 2106426
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.118
Abstract
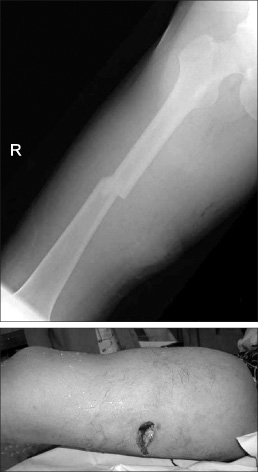
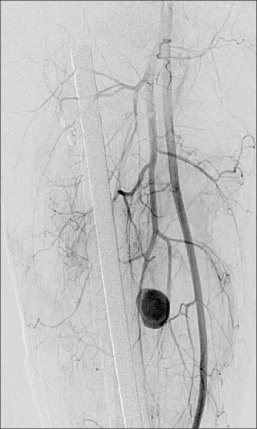
- Post-traumatic arterial injuries are often reported in crushing or penetrating gun-shot injuries that include massive soft tissue damage. In most cases, the injured arteries are treated with early repair or reconstruction surgery. When there is a delayed in diagnosis, a pseudoaneurysm might be detected several weeks or months after the trauma. Pseudoaneurysms after femoral fracture are usually detected in the superficial femoral arteries, but rarely in the very deep femoral arteries, which are protected by the vastus medialis. There are many reports on post-traumatic pseudoaneurysms, most of which are in the superficial femoral arteries, and there are few reports with normal findings in an early angiogram. We report a pseudoaneurysm of the deep femoral artery with a normal angiogram in the early stage that was diagnosed and treated 4weeks after the trauma.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baird RJ, Doran ML. The false aneurysm. Can Med Assoc J. 1964. 91:281–284.2. Matsushita M, NishikimiI N, Sakurai T, Nimura Y. Pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery caused by exostosis of the femur: case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 2000. 32:201–204.
Article3. Nicholson ML, Horrocks M. Delayed presentation of traumatic false aneurysms. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1987. 32:37–38.4. Park SJ, Yang KH. Pseudoaneurysm of the superficial femoral artery following gamma nail fixation for trochanteric fracture -a case report-. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2000. 35:695–697.
Article5. Plagnol P, Diard N, Bruneteau P, Roncheau V. Case report: pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery complicating a total knee replacement: a successful percutaneous endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2001. 21:81–83.6. Queral LA, Flinn WR, Yao JS, Bergan JJ. Management of peripheral arterial aneurysms. Surg Clin North Am. 1979. 59:693–706.
Article7. Sharma S, Bhargava B, Mahapatra M, Malhotra R. Pseudoaneurysm of the superficial femoral artery following accidental trauma: result of treatment by percutaneous stent-graft placement. Eur Radiol. 1999. 9:422–424.
Article8. Spratt EM, Doran ML, Baird RJ. False aneurysms in the lower extremety. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967. 124:562–566.9. Walker TG, Geller SC, Brewster DC. Transcatheter occlusion of a profunda femoral artery pseudoaneurysm using thrombin. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 149:185–186.
Article10. Yoon HK, Kim BK, Shin DE, Kim MD, Chang JH. Pseudoaneurysm of superficial femoral artery following proximal femoral nail fixation. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2004. 17:221–223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed Pseudoaneurysm of Deep Femoral Artery Caused by Migration of Lesser Trochanter, Subsequent to an Intertrochanteric Fracture Surgery - A Case Report -
- Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Femoral Artery Following Gamma nail Fixation for Trochanteric Fracture: A Case Report
- Rupture of the Deep Femoral Artery during Proximal Femoral Nailing Following an Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Case Report
- Pseudoaneurysm of Superficial Femoral Artery Following Proximal Femoral Nail Fixation
- A Case of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Ultrasound-Guided Compression of a Pseudoaneurysm