J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2012 Aug;16(2):152-158. 10.13104/jksmrm.2012.16.2.152.
Contrast Enhanced Cerebral MR Venography: Comparison between Arterial and Venous Triggering Methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea. bumrad@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2099849
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2012.16.2.152
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the arterial and venous detection sites of triggering methods in contrast-enhanced-MR-venography (CE-MRV) for the evaluation of intracranial venous system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
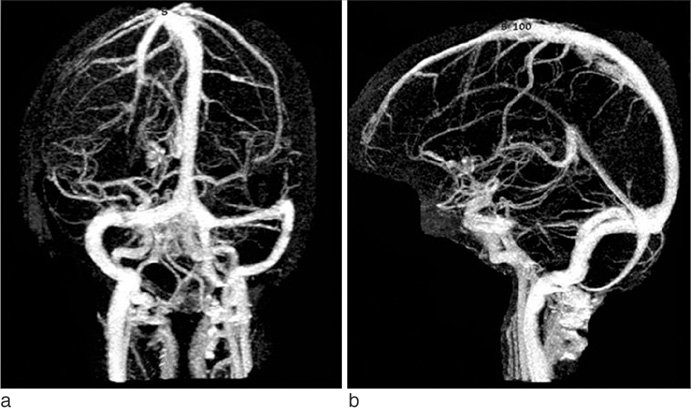
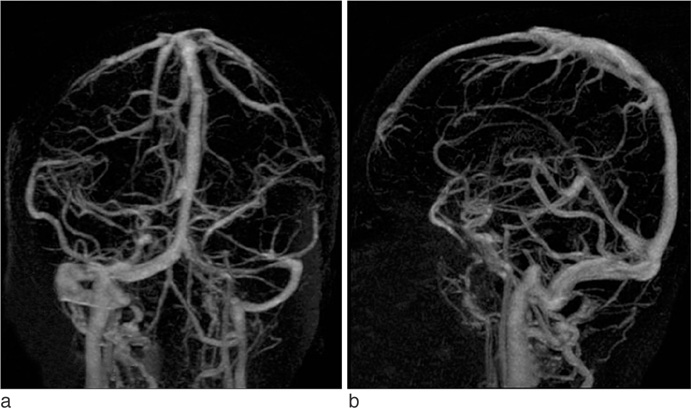
41 healthy patients underwent CE-MRV with autotriggering at either the cavernous segment of internal carotid artery with an inserted time-delay of 6 seconds (n = 20) or the superior sagittal sinus without any time-delay (n = 21). 0.1 mmol/kg gadolinium-based contrast material (Magnevist(R), Schering, Germany) was intravenously injected by hand injection. A sagittal fast-spoiled-gradient-echo-sequence ranging from one ear to the other was performed (TR/TE5.2/1.5, Matrix 310x310, 124 sections in the 15-cm-thick volume). 17 predefined venous structures were evaluated on all venograms by two neuroradiologists and defined as completely visible, partially visible, or none visible.
RESULTS
The rate of completely visible structures were 272 out of 323 (84%) in the arterial triggering CE-MRV and 310 out of 340 (91%) in the venous triggering CE-MRV. The venous triggering CE-MRV demonstrated an overall superior visualization of the cerebral veins than the arterial triggering CE-MRV (Fisher exact test, p < 0.006).
CONCLUSION
CE-MRV using venous autotriggering method provides higher-quality images of the intracranial venous structures compared to that of arterial.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Farb RI. The dural venous sinuses: normal intraluminal architecture defined on contrast-enhanced MR venography. Neuroradiology. 2007. 49:727–732.2. Farb RI, Scott JN, Willinsky RA, Montanera WJ, Wright GA, terBrugge KG. Intracranial venous system: gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography with auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered sequence--initial experience. Radiology. 2003. 226:203–209.3. Kirchhof K, Welzel T, Jansen O, Sartor K. More reliable noninvasive visualization of the cerebral veins and dural sinuses: comparison of three MR angiographic techniques. Radiology. 2002. 224:804–810.4. Liang L, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, et al. Evaluation of the intracranial dural sinuses with a 3D contrast-enhanced MP-RAGE sequence: prospective comparison with 2D-tof MR venography and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:481–492.5. Lovblad KO, Schneider J, Bassetti C, et al. Fast contrast-enhanced MR whole-brain venography. Neuroradiology. 2002. 44:681–688.6. Meckel S, Glucker TM, Kretzschmar M, Scheffler K, Radu EW, Wetzel SG. Display of dural sinuses with time-resolved, contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008. 25:217–224.7. Mermuys KP, Vanhoenacker PK, Chappel P, Van Hoe L. Three-dimensional venography of the brain with a volumetric interpolated sequence. Radiology. 2005. 234:901–908.8. Rollins N, Ison C, Reyes T, Chia J. Cerebral MR venography in children: comparison of 2D time-of-flight and gadolinium-enhanced 3D gradient-echo techniques. Radiology. 2005. 235:1011–1017.9. Wetzel SG, Law M, Lee VS, Cha S, Johnson G, Nelson K. Imaging of the intracranial venous system with a contrast-enhanced volumetric interpolated examination. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:1010–1018.10. Klingebiel R, Bauknecht HC, Bohner G, Kirsch R, Berger J, Masuhr F. Comparative evaluation of 2D time-of-flight and 3D elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR venography in patients with presumptive cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Eur J Neurol. 2007. 14:139–143.11. Leach JL, Wolujewicz M, Strub WM. Partially recanalized chronic dural sinus thrombosis: findings on MR imaging, time-of-flight MR venography, and contrast-enhanced MR venography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:782–789.12. Bozzao A, Finocchi V, Romano A, et al. Role of contrast-enhanced MR venography in the preoperative evaluation of parasagittal meningiomas. Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:1790–1796.13. Mattle HP, Wentz KU, Edelman RR, et al. Cerebral venography with MR. Radiology. 1991. 178:453–458.14. Kanal E, Shellock FG, Talagala L. Safety considerations in MR imaging. Radiology. 1990. 176:593–606.15. Talagala SL, Jungreis CA, Kanal E, et al. Fast three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography of the intra-cranial vasculature. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1995. 5:317–323.16. Liauw L, van Buchem MA, Spilt A, et al. MR angiography of the intracranial venous system. Radiology. 2000. 214:678–682.17. Farb RI, Scott JN, Willinsky RA, Montanera WJ, Wright GA, terBrugge KG. Intracranial venous system: gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography with auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered sequence-initial experience. Radiology. 2003. 226:203–209.18. Fu JH, Lai PH, Hsiao CC, et al. Comparison of real-time three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced elliptic centric-ordered MR venography and two-dimensional time-of-flight MR venography of the intracranialvenous system. J Chin Med Assoc. 2010. 73:131–138.19. Marcello M, Vincenzo BM, Orlando DD, et al. Multiple sclerosis: cerebral circulation time. Radiology. 2012. 262:947–955.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Contrast Enhanced Rapid MR Sequence(True FISP) in Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Subtraction MR Venography Acquired from Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography: Comparison with Phase-Contrast MR Venography and Single-Phase Contrast-Enhanced MR Venography
- The Usefulness of Three-Dimensional Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Venography for the Evaluation of Varices in Lower Extremities
- Gd-DTPA Eenhanced IVIRI of the Cerebral Venous Angiomas: Cornparision with Cerebral Angiography
- Cerebral Venous Angioma Complicated by Non-hemorrhagic Venous Infarction