J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 Jun;72(6):411-417. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.6.411.
Radiologic and Pathological Correlation of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. taloo@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Plus Internal Medicine Clinic, Suncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2098021
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.6.411
Abstract
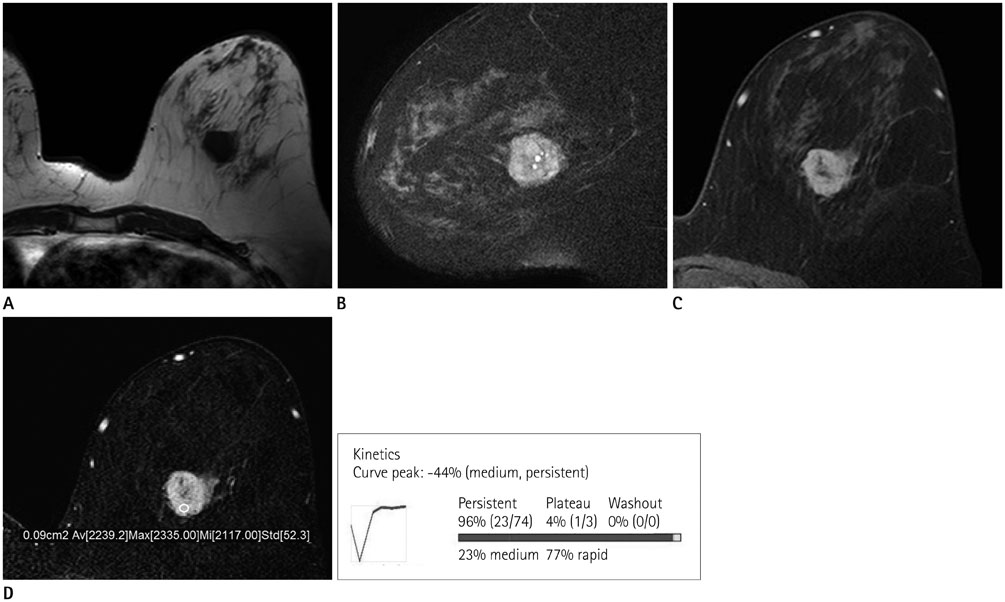
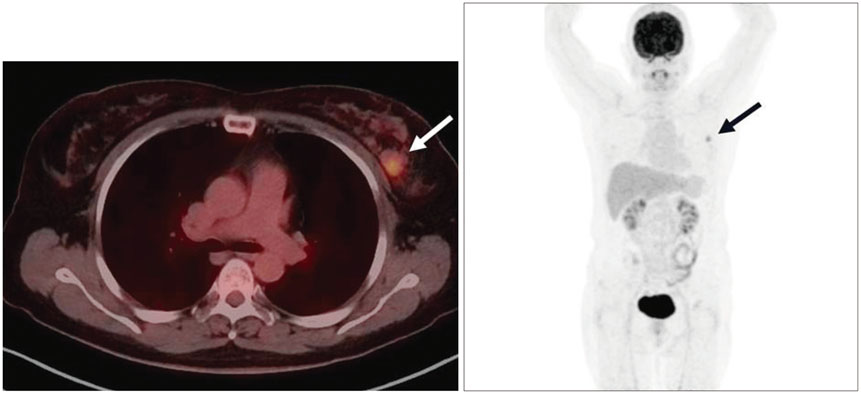
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a subtype of adenocarcinoma that is usually seen in the salivary glands. It has also been reported in other organs including the breast, skin, tracheobronchial tree, cervix, larynx, and Bartholin gland. ACC in the breast is rare, accounting for less than 0.1% of all breast cancers. Furthermore, the imaging characteristics of ACC of the breast have not been well described in the literature, especially regarding the findings with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Here, we report radiologic findings of a rare case of ACC in the breast by mammography, sonography, computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography/CT, and MRI with pathologic correlation and a review of the literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Locoregional Recurrence in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast: A Retrospective, Multicenter Study (KROG 22-14)
Sang Min Lee, Bum-Sup Jang, Won Park, Yong Bae Kim, Jin Ho Song, Jin Hee Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, In Ah Kim, Jong Hoon Lee, Sung-Ja Ahn, Kyubo Kim, Ah Ram Chang, Jeanny Kwon, Hae Jin Park, Kyung Hwan Shin
Cancer Res Treat. 2025;57(1):150-158. doi: 10.4143/crt.2024.201.
Reference
-
1. Santamaría G, Velasco M, Zanón G, Farrús B, Molina R, Solé M, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic appearance and pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 171:1679–1683.2. Rosen PP. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast. A morphologically heterogeneous neoplasm. Pathol Annu. 1989; 24(Pt 2):237–254.3. Lee MS, Kim MK, Kim EK, Park BW, Oh KK. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast: a case report. J Korean Soc Ultrasound Med. 2005; 24:199–202.4. Glazebrook KN, Reynolds C, Smith RL, Gimenez EI, Boughey JC. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1391–1396.5. Youk JH, Kim MJ, Kim EK, Lee JY, Oh KK, Park BW. Recurrence of adenoid cystic carcinoma in the breast after lumpectomy and adjuvant therapy. J Ultrasound Med. 2006; 25:921–924.6. Tsuboi N, Ogawa Y, Inomata T, Nishioka A, Yoshida D, Yoshida S, et al. Dynamic MR appearance of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast in a 67-year-old female. Radiat Med. 1998; 16:225–228.7. Okamoto Y, Sumiyama Y, Arima Y, Sakuta M, Okuda T, Noto Y, et al. A case of adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) of the breast and review of the utility of preoperative imaging diagnose. Breast Cancer. 2001; 8:84–89.8. Santamaría G, Velasco M, Bargalló X, Caparrós X, Farrús B, Luis Fernández P. Radiologic and pathologic findings in breast tumors with high signal intensity on T2-weighted MR images. Radiographics. 2010; 30:533–548.9. Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Sastre-Garau X, Bussolati G, Tavassoli FA, Eusebi V, et al. Invasive breast carcinoma. In : Tavassoli FA, Devilee P, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the breast and female genital organs. 3rd ed. Lyon, France: IARC;2003. p. 13–59.10. Kim M, Lee DW, Im J, Suh KJ, Keam B, Moon HG, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast: a case series of six patients and literature review. Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 46:93–97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast: A Case Report
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast Metastatic to the Scalp
- A case of adenoid basal cell carcinoma in uterine cervix
- Skin Metastasis of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Parotid Gland
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma on the Nipple with Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis