J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Mar;64(3):203-211. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.3.203.
Comparison of 3D TOF MRA with Contrast Enhanced MRA in Intracranial Atherosclerotic Occlusive Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Medical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. soomee@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097938
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.3.203
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We compared diagnostic performance of 3D Time of flight MRA with contrast-enhanced MRA to detect and quantify intracranial atherosclerotic occlusive disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 2007 to December 2009, we enrolled 95 patients with clinically suspected intracranial atherosclerotic steno-occlusive disease who had undergone 3D TOF-MRA and CE MRA at 1.5T or 3T with DSA. Two radiologists analyzed the post-processed images using a maximum intensity projection. Intracranial vessels were categorized as distal internal carotid artery, middle cerebral artery or vertebrobasillar artery. We graded the degree of stenosis and assigned subjects to one of three groups: low grade occlusion (<50%), high grade occlusion (50-99%) and complete occlusion. Using the McNemar test, we compared the results of CE MRA with those of 3D TOF for detecting >50% stenosis using DSA as a reference standard.
RESULTS
CE MRA had 94.2% sensitivity, 88.1% specificity, 51% positive predictive value, 99.1% negative predictive value and 88.8% diagnostic accuracy for detecting >50% stenosis; In contrast, 3D TOF-MRA showed 94.2% sensitivity, 91.6.1% specificity, 59.8% positive predictive value, 99.1% negative predictive value and 91.9% diagnostic accuracy. Sensitivity and specificity of CE MRA were not significantly different than sensitivity and specificity of 3D TOF MRA (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
3D TOF-MRA provides comparable diagnostic performance with CE-MRA for diagnosis intracranial atherosclerotic disease.
MeSH Terms
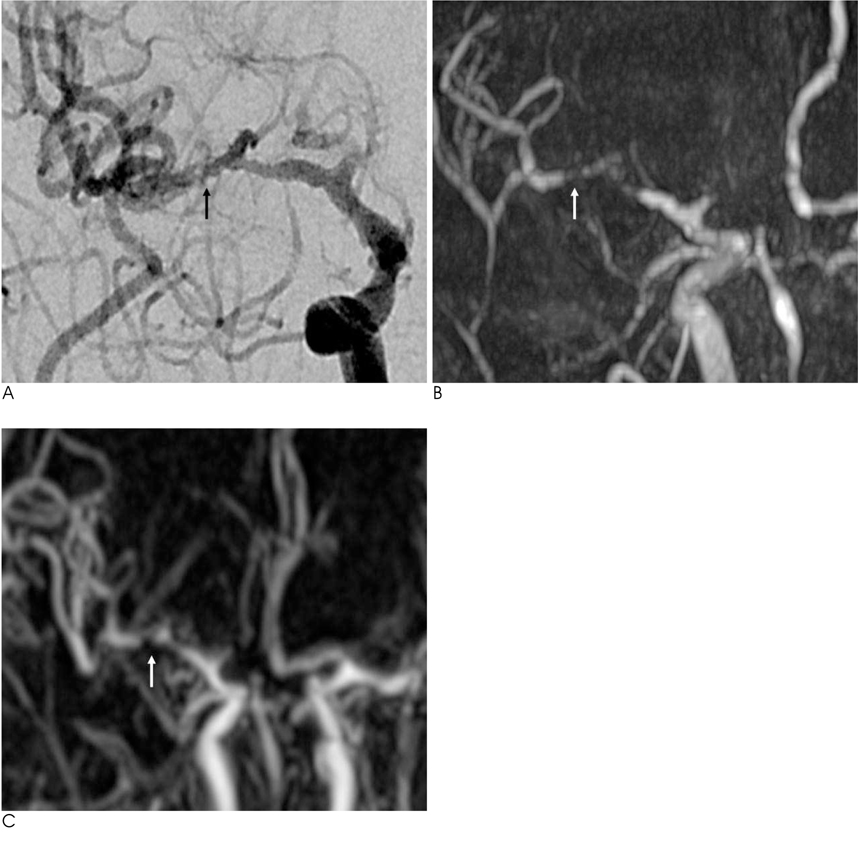
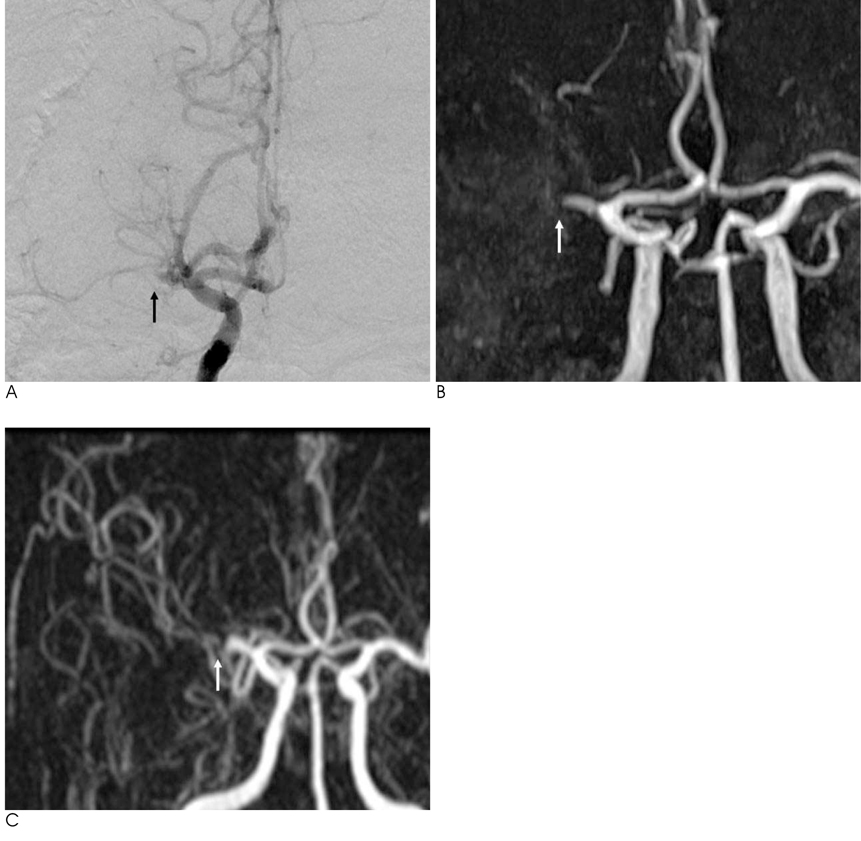
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q, Zamanillo MC. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The northen manhattan stroke study. Stroke. 1995; 26:14–20.2. Chimowitz MI, Kokkinos J, Strong J, Brown MB, Levine SR, Silliman S, et al. The warfarin-aspirin symptomatic intracranial disease study. Neurology. 1995; 45:1488–1493.3. Yoon W, Seo JJ, Cho KH, Kim MK, Kim BC, Park MS. Symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis treated with intracranial angioplasty: experience in 32 patients. Radiology. 2005; 237:620–626.4. Suh DC, Kim SJ, Lee DH, Kim W, Choi CG, Lee JH, et al. Outcome of endovascular treatment in symptomatic intracranial vascular stenosis. Korean J Radiol. 2005; 6:1–7.5. Jang NK, Seo JJ, Chung TW, Jeong GW, Kim JK, Kang HK, Cho KH. The Usefulness of Enhanced 3D-TOF MR Angiography in the Patients with Cerebral Infarction: Comparison with Conventional Angiography. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000; 42:575–583.6. Anzalone N, Scotti R, Iadanza A. MR angiography of the carotid arteries and intracranial circulation: advantage of a high relaxivity contrast agent. Neuroradiology. 2006; 48:9–17.7. Sadikin C, Teng MM, Chen TY, Luo CB, Chang FC, Lirng JF, et al. The current role of 1.5T non-contrast 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography to detect intracranial steno-occlusive disease. J Formos Med Assoc. 2007; 106:691–669.8. Choi HS, Kim DI, Kim DJ, Kim J, Kim ES, Lee SK. Accuracy of 3T MR angiography in vertebral artery stenosis and coincidence with other cerebrovascular stenoses. Neuororadiology. 2010; 52:893–898.9. Babiarz LS, Romero JM, Murphy EK, Brobeck B, Schaefer PW, González RG, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR angiography is not more accurate than unenhanced 2D time-of-flight MR angiography for determining > or = 70% internal carotid artery stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:761–768.10. Oelerich M, Lentschig MG, Zunker P, Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Schuierer G. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: comparison of 3D time-of-flight and 3D phase-contrast MR angiography. Neuroradiology. 1998; 40:567–573.11. Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH, Pyun HW, Kang DW, Kwon SU, et al. Detection of intracranial atherosclerotic steno-occlusive disease with 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography with sensitivity encoding at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:439–446.12. Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, Tillis M, Kidwell C, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1012–1021.13. Stock KW, Radue EW, Jacob AL, Bao XS, Steinbrich W. Intracranial arteries: prospective blinded comparative study of MR angiography and DSA in 50 patients. Radiology. 1995; 195:451–456.14. Atkinson D, Brant-Zawadzki M, Gillan G, Purdy D, Laub G. Improved MR angiography: magnetization transfer suppression with variable flip angle excitation and increased resolution. Radiology. 1994; 190:890–894.16. Villablanca JP, Nael K, Habibi R, Nael A, Laub G, Finn JP. 3T contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for evaluation of the intracranial arteries: comparison with time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography and multislice computed tomography angiography. Invest Radiol. 2006; 41:799–805.17. Fűrst G, Hofer M, Steinmetz H, Kambergs J, Paselk C, Liebsch D, et al. Intracranial stenoocclusive disease: MR angiography with magnetization transfer and variable flip angle. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1749–1757.18. Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Nakagawa T, Mabuchi N, Watabe T, Shiokawa Y, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: MR angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:135–143.19. Heiserman JE, Drayer BP, Keller PJ, Fram EK. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: evaluation with three-dimensional timeof-flight MR angiography. Radiology. 1992; 185:667–673.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Time-Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MRA on 3.0T: a Non-Invasive Follow-Up Technique after Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization of the Intracranial Aneurysm
- Comparison of MR Angiography with Conventional Angiography in Cervical and Intracranial Vascular Diseases
- Comparison of Clinical Application Modes of 3D TOF MR Angiography in the Brain: Normal Volunteers Study
- Turnover in Intracranial Aneurysm Phantoms: Its Relation to Neck Size
- Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms by MRA and Conventional Angiography