J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Feb;64(2):103-108. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.2.103.
Angiographic Pattern in the Early Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. nschangsub@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2097923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.2.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The incidence of early branches arising from the prebifurcation trunk of the middle cerebral artery is very high. However, no reports have addressed these early branches of middle cerebral arteries in the Korean population. The purpose of this study was to characterize these early branches in Koreans.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective review was performed on transfemoral cerebral angiograms performed at Jeju National University Hospital between May 2005 and March 2010. A total of 78 hemispheric angiogram sites met the study inclusion criteria. The digital subtraction anterior-posterior view was the basic image for the inspection, which was supplemented by a three-dimensional reconstructed image.
RESULTS
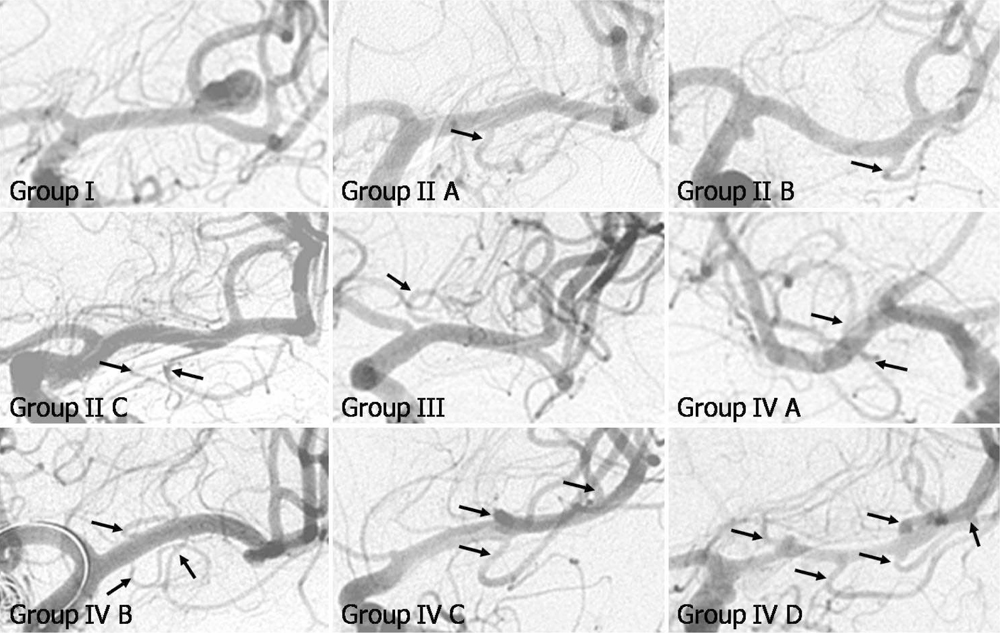
We identified 86 early branches of the middle cerebral artery in 58 (74.4%) out of 78 hemisphere angiogram sites. The type of early branches in the 78 hemispheric angiograms included 20 angiograms that were classified as Group I (25.6%), 23 as Group II A (29.5%), 10 as Group II B (12.8%), 7 as Group II C (9.0%), 7 as Group III (9.0%), and 11 as Group IV (14.1%).
CONCLUSION
The incidence of early branches arising from the prebifurcation trunk of the middle cerebral artery was found to be high in the Korean population and showed many morphological variations.
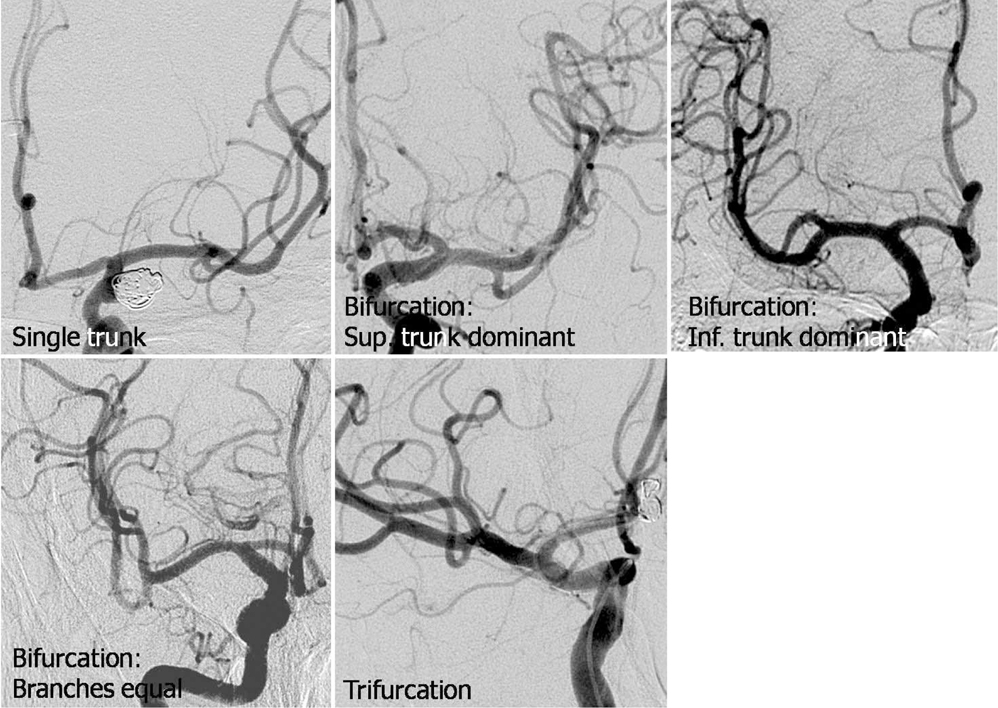
Figure
Reference
-
1. Osborn AG. Diagnostic cerebral angiography. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999. p. 137.2. Gibo H, Carver CC, Rhoton AL Jr, Lenkey C, Mitchell RJ. Microsurgical anatomy of the middle cerebral artery. J Neurosurg. 1981; 54:151–169.3. Rhoton AL Jr. The supratentorial arteries. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:S53–S120.4. Tanriover N, Kawashima M, Rhoton AL Jr, Ulm AJ, Mericle RA. Microsurgical anatomy of the early branches of the middle cerebral artery: morphometric analysis and classification with angiographic correlation. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:1277–1290.5. Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T. Middle cerebral artery variations: duplicated and accessory arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:45–49.6. Teal JS, Rumbaugh CL, Bergeron RT, Segall HD. Anomalies of the middle cerebral artery: accessory artery, duplication, and early bifurcation. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1973; 118:567–575.7. Takahashi S, Hoshino F, Uemura K, Takahashi A, Sakamoto K. Accessory middle cerebral artery: is it a variant form of the recurrent artery of Heubner? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989; 10:563–568.8. Umansky F, Dujovny M, Ausman JI, Diaz FG, Mirchandani HG. Anomalies and variations of the middle cerebral artery: a microanatomical study. Neurosurgery. 1988; 22:1023–1027.9. Marinkovic SV, Kovacevic MS, Marinkovic JM. Perforating branches of the middle cerebral artery. Microsurgical anatomy of their extracerebral segments. J Neurosurg. 1985; 63:266–271.10. Rosner SS, Rhoton AL Jr, Ono M, Barry M. Microsurgical anatomy of the anterior perforating arteries. J Neurosurg. 1984; 61:468–485.11. Türe U, Yasargil MG, Al-Mefty O, Yasargil DC. Arteries of the insula. J Neurosurg. 2000; 92:676–687.12. Umansky F, Gomes FB, Dujovny M, Diaz FG, Ausman JI, Mirchandani HG, et al. The perforating branches of the middle cerebral artery. A microanatomical study. J Neurosurg. 1985; 62:261–268.13. Osborn AG. Diagnostic cerebral angiography. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999. p. 120.14. Grand W. Microsurgical anatomy of the proximal middle cerebral artery and the internal carotid artery bifurcation. Neurosurgery. 1980; 7:215–218.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microsurgical Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery
- Angiographic Analysis of Middle Cerebral Artery Bifurcation Aneurysm
- Microsurgical Anatomy of the Basilar Artery and Posterior Cerebral Artery
- Clinical Analysis of the Pattern of Anterior-Posterior Circulation in Patients with Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm
- A Case of Extra Intracranial Arterial By-pass Graft