J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2014 Dec;21(4):189-193. 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.4.189.
Epidural Gas-containing Pseudocyst in Lumbar Spine: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. yslee2080@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2097871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2014.21.4.189
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report.
OBJECTIVES
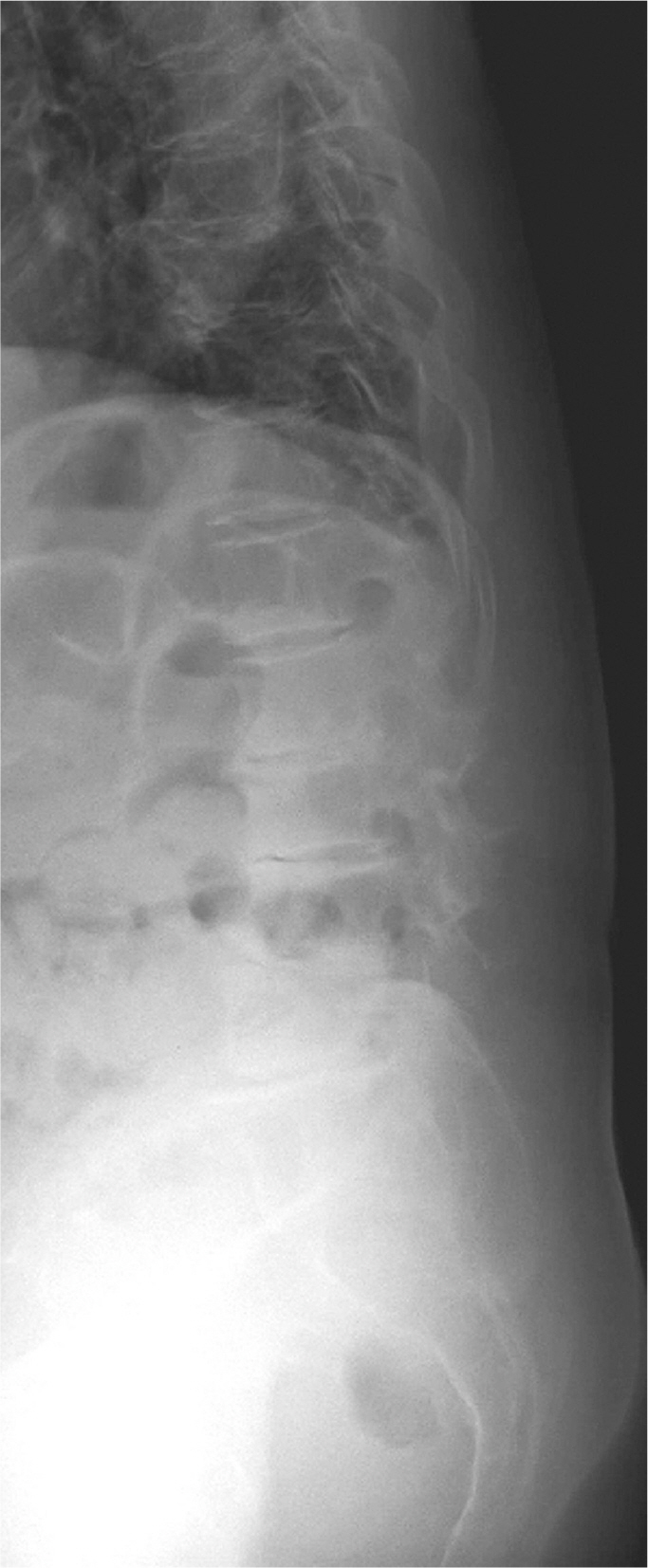
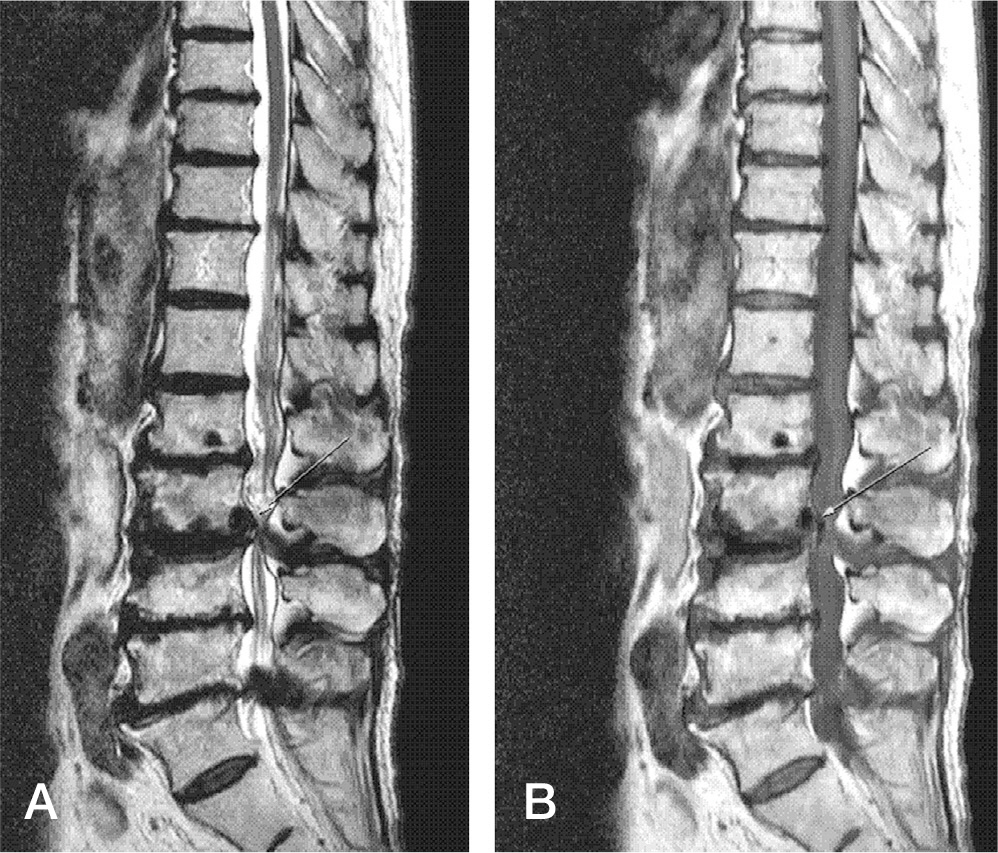
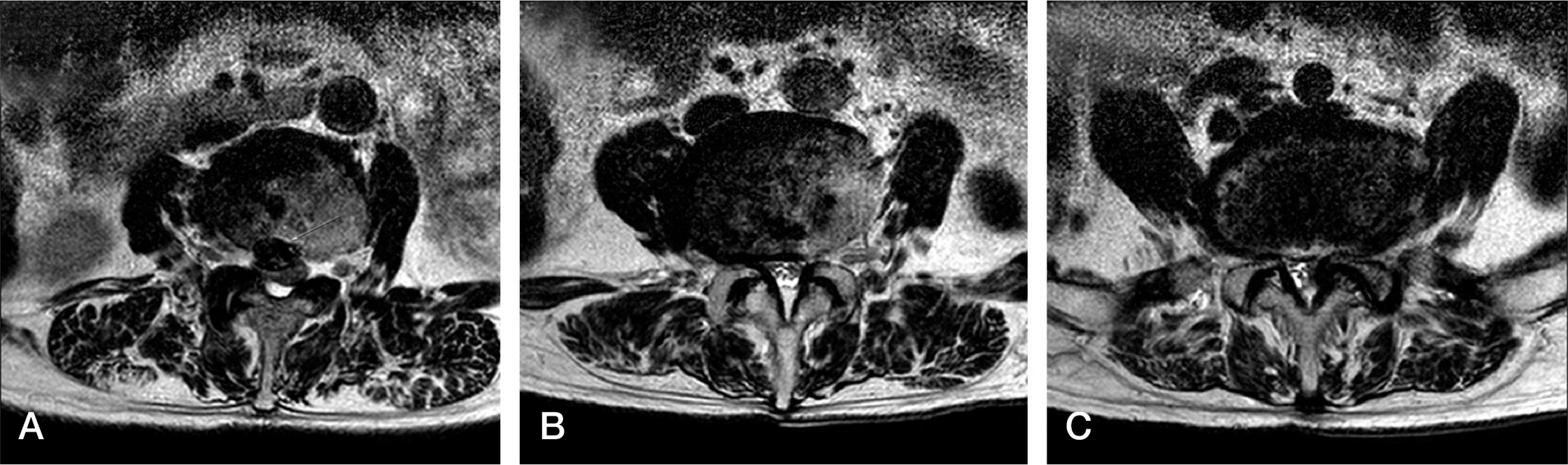
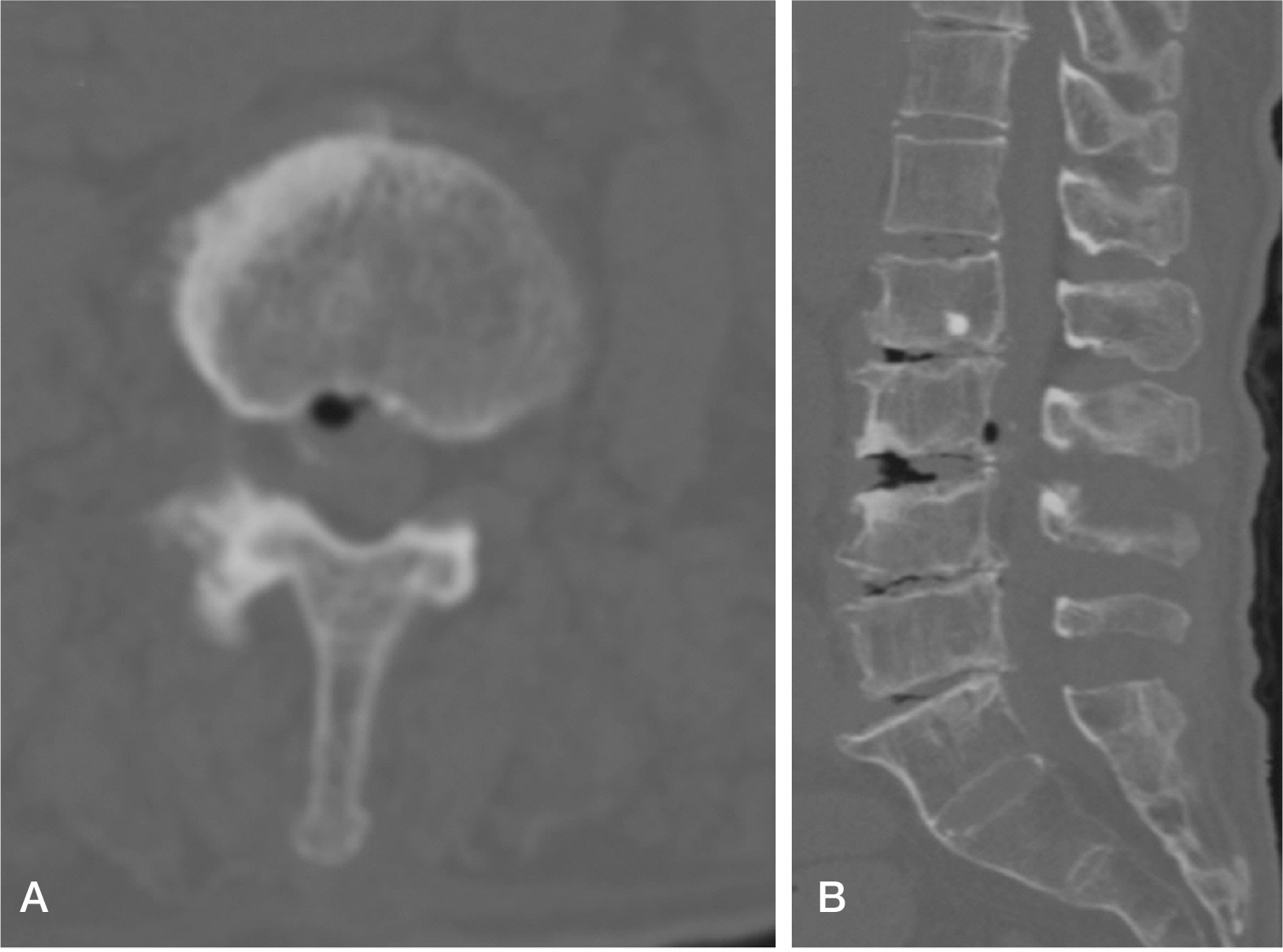
We report two cases regarding epidural air pseudocyst at the lumbar spine. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Epidural air pseudocyst at the lumbar spine that provokes radiating pain and neurologic symptoms can be misdiagnosed as an epidural tumor or HIVD. Consequently, proper diagnosis and treatment of the epidural air pseudocyst at the lumbar spine is necessary.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We report on two patients with radiculopathy and neurologic symptoms resulting from epidural air pseudocysts. In one patient, the epidural air pseudocyst was found within the epidural ligament flavum area on an MRI, and fluoroscopic-guided FNA (fine needle aspiration) was performed. In the other, the epidural air pseudocyst was found behind the posterior longitudinal ligament and was accompanied by spinal stenosis. In this patient, we conducted open cystectomy and posterior decompression surgery. Results: After treatment, all patients have showed symptom improvement and they are currently living without discomfort.
RESULTS
After treatment, all patients have showed symptom improvement and they are currently living without discomfort.
CONCLUSIONS
Due to frequent misdiagnosis, the careful diagnosis of lumbar epidural air pseudocyst is necessary. Physicians should select a proper treatment plan concerning the patient's condition and the location of the lesion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee DY, Lee S. L2 radicular compression caused by a foraminal extradural gas pseudocyst. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:232–4.
Article2. Kakitsubata Y, Theodorou SJ, Theodorou DJ, et al. Symptomatic epidural gas cyst associated with discal vacuum phenomenon. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:E784–9.
Article3. Qasho R, Santoro A, Vangelista T, et al. Nerve root compression by a gascontaining cyst associated with stenotic lateral recess. Case report and reviewof the literature. J Neurosurg Sci. 2001; 45:181–4.4. Sei A, Mizutamari M, Fujimoto T, et al. Gas-filled intradural cysts of the lumbar spine and the possible pathogenesis. Spine J. 2009; 9:E6–8.
Article5. Giraud F, Fontana A, Mallet J, et al. Sciatica caused by epidural gas. Four case reports. Joint Bone Spine. 2001; 68:434–7.
Article6. Bosser V, Dietemann JL, Warter JM, et al. L5 radicular pain related to lumbar extradural gascontaining pseudocyst. Role of CT-guided aspiration. Neuroradiology. 1990; 31:552–3.7. Kaymaz M, Oztanir N, Emmez H, et al. Epidural air en-trapment after spinal surgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2005; 107:421–4.8. Kuh SU, Heo DH, Kim KS, Cho YJ. Lumar epidural gas-contining pseudocysts as a cause of severe radicular pain. Joint Bone Spine. 2011; 78:398–401.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidural Pneumatic Pseudocyst with Lumbar Radiculopathy: Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
- L2 Radicular Compression Caused by a Foraminal Extradural Gas Pseudocyst
- Rapidly Progressive Gas-containing Lumbar Spinal Epidural Abscess
- Symptomatic Spinal Epidural Gas-Containing Cystic Lesions: Reports of 2 Cases
- Symptomatic Epidural Gas-containing Cyst from Intervertebral Vacuum Phenomenon