J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2014 Jun;19(2):65-69. 10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.2.65.
Acute Traumatic Irreducible Anterior Dislocation and Fracture of the Radial Head in an Adult
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sby2409@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097611
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.2.65
Abstract
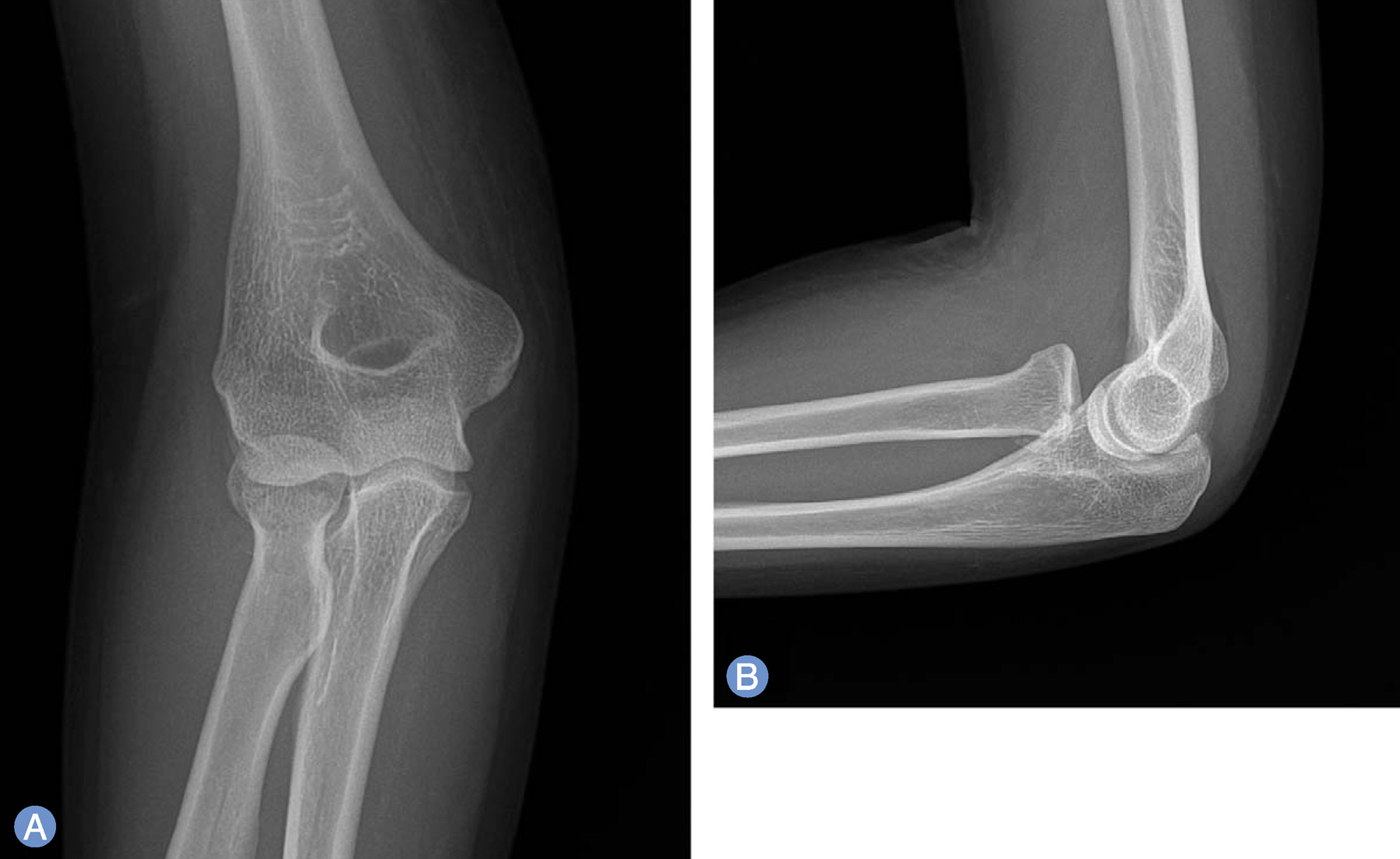
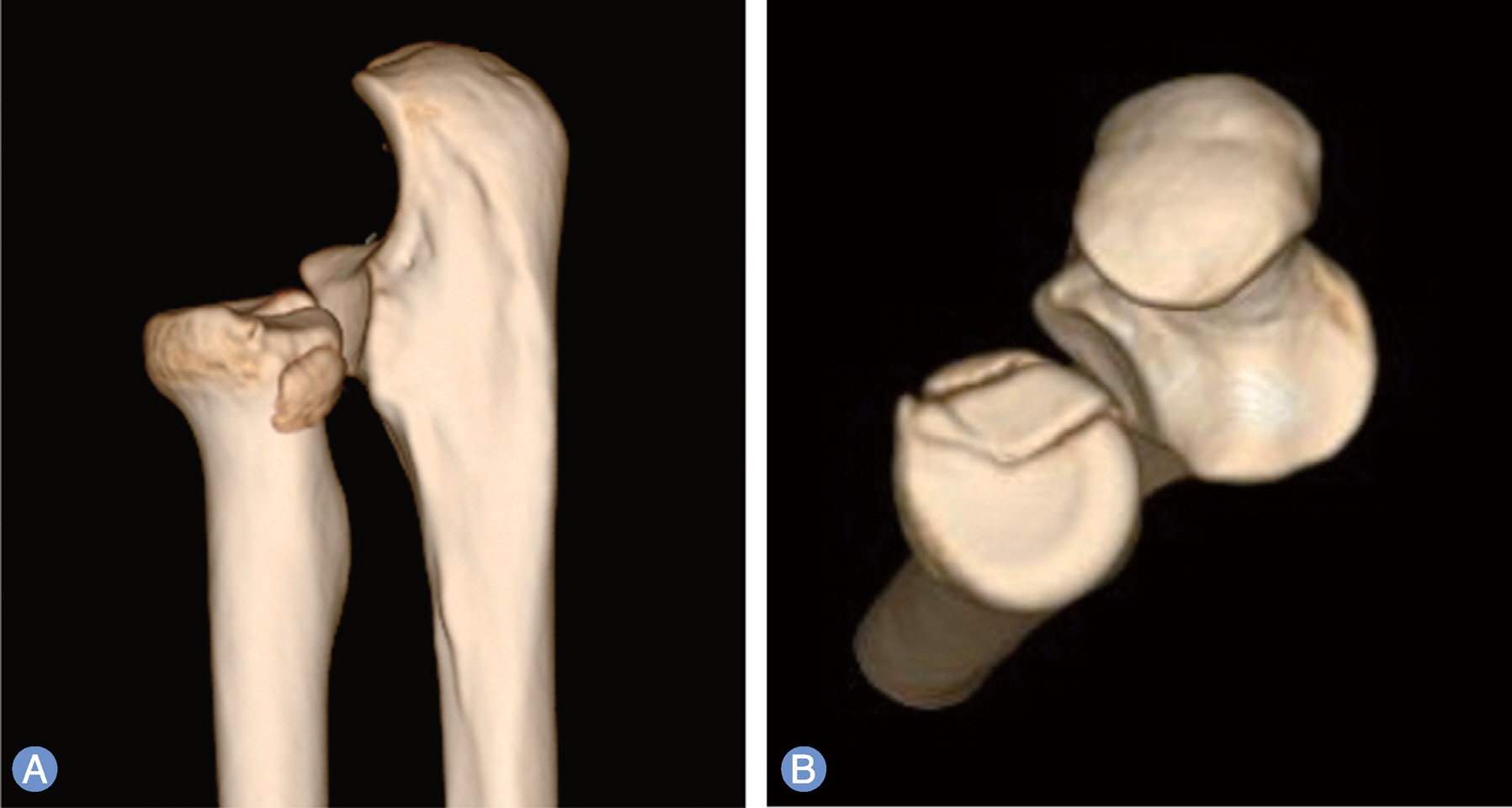
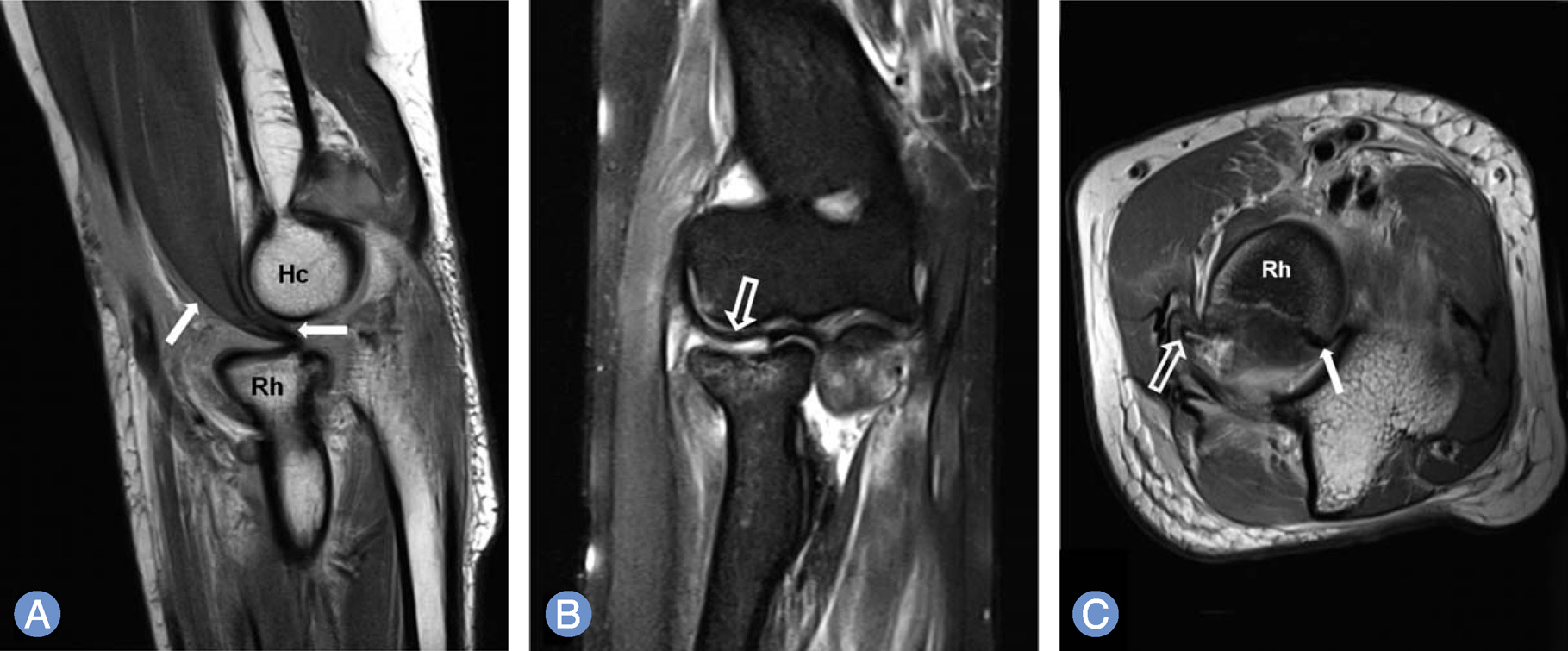
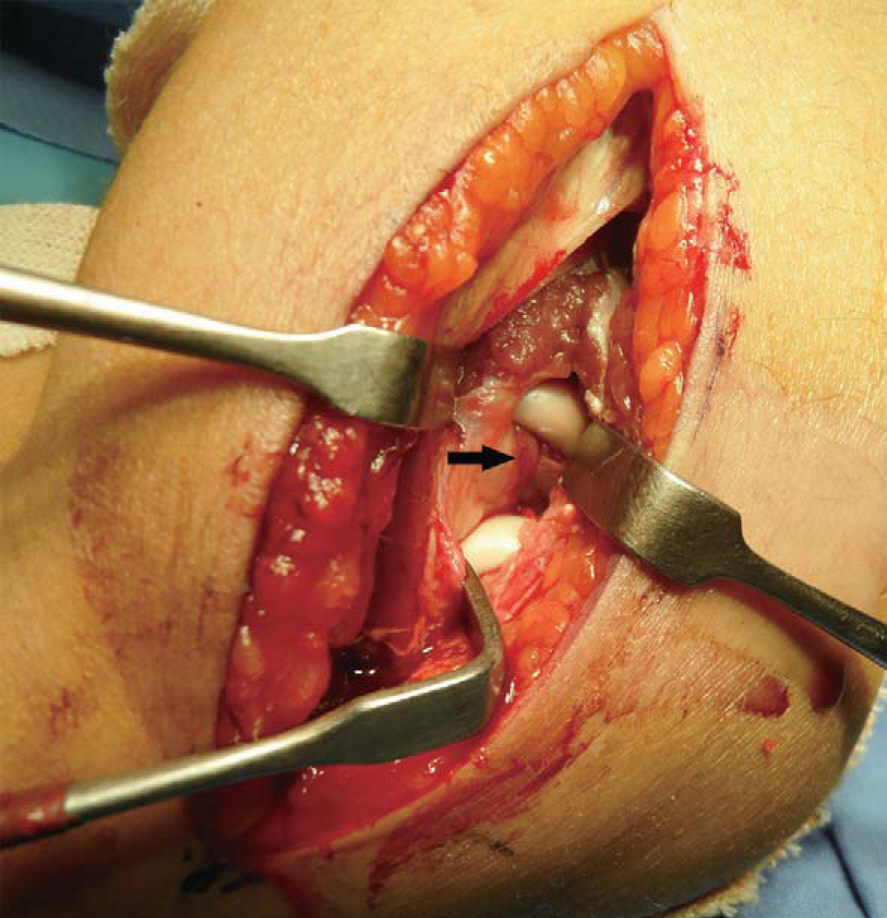
- Traumatic dislocation of the radial head without fracture of the olecranon is very rare, especially in adults. We experienced a case of irreducible radial head dislocation with fracture without involvement of ulna. Open reduction and internal fixation was performed. During surgery, brachialis was interposed between capitellum and radial head, and also interposed between the fragments at the fracture site of the radial head. At 12 months after operation, the radial head was well reduced with normal rotation.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Watanabe K, Iwabu S, Hosoya T. Traumatic isolated anterior dislocation of the radial head in an adult: a case report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005; 14:554–6.
Article2. Sasaki K, Miura H, Iwamoto Y. Unusual anterior radial head dislocation associated with transposed biceps tendon: a case report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006; 15:e15–9.
Article3. Upasani VV, Hentzen ER, Meunier MJ, Abrams RA. Anteromedial radial head fracture-dislocation associated with a transposed biceps tendon: a case report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20:e14–8.
Article4. Heo YM, Kim WS, Kim SH, Jeon TS, Kim SB, Oh BH. Isolated anterior dislocation of the radial head in adult: a case report. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 2007; 10:131–5.5. Kong KC. Irreducible isolated dislocation of the radial head in a skeletally mature teenager. A case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993; 112:304–5.6. Takami H, Takahashi S, Ando M. Irreducible isolated dislocation of the radial head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (345):168–70.
Article7. Bonatus T, Chapman MW, Felix N. Traumatic anterior dislocation of the radial head in an adult. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:441–4.
Article8. Baraza N, Saithna A, Krkovic MK. Acute persistent traumatic anterior dislocation of the fractured radial head: a case report and surgical technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012; 21:e5–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Traumatic Radial Head Anterior Dislocation Treated with Open Reduction in Children
- Traumatic Bowing of the Ulna with the Dislocation of the Radial Head: Report of a Case
- Old Unreduced Isolated Anterior Dislocation of Radial Head: Report of 2 Cases
- An Irreducible Hip Dislocation with Femoral Head Fracture
- Treatment of Traumatic Sternoclavicular Joint Anterior Dislocation with a Sternal Fracture