J Korean Soc Transplant.
2009 Sep;23(2):169-171. 10.4285/jkstn.2009.23.2.169.
Necrotizing Fasciitis following Liver Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Daegu Catholic Univerty College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. hyskhk@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2009.23.2.169
Abstract
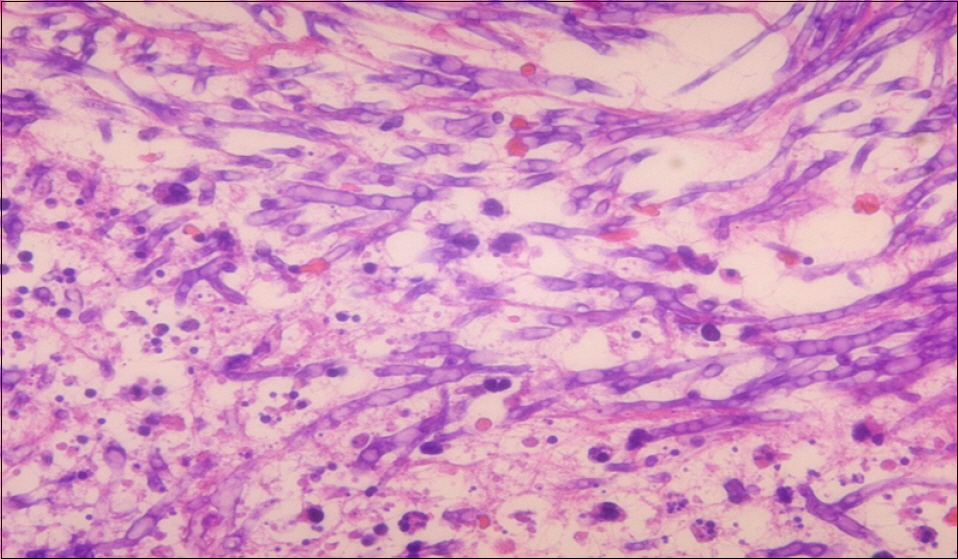
- Necrotizing fasciitis is a rapidly spreading subcutaneous infection. It can occur in patients after solid organ transplantation. But, the reports for necrotizing fasciitis after liver transplantation are very unusual. We report 2 patients with necrotizing fasciitis caused by bacterial and Aspergillus species infection. Their pre-transplantation condition was very poor due to hepatic encephalopathy, pressure sore, and admission for several months. Patients had a fulminant course for early potent immunosuppression period, despite of aggressive surgical debridement, withdrawal of immunosuppression, and adequate antibacterial and antifungal therapy. Therefore, necrotizing fasciitis has to be recognized as a potential complication after liver transplantation and Aspergillus species has to be added to the list of potential pathogens of surgical wound infections, especially in the setting of liver transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Wall DB, de Virgilio C, Black S, Klein SR. Objective criteria may assist in distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from nonnecrotizing soft tissue infection. Am J Surg. 2000; 179:17–21.
Article2). Elliott D, Kufera JA, Myers RA. The microbiology of necrotizing soft tissue infections. Am J Surg. 2000; 179:361–6.
Article3). Kobayashi S, Kato T, Nishida S, Buttrago E, Maldini G, Mittal N, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis following liver and small intestine transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2002; 6:344–7.
Article4). Lendoire J, Trigo P, Aziz H, Cueto G, Ando Y, Ohlsson PI, et al. Liver transplantation in transthyretin familial amy-loid polyneuropathy: first report from argentina. Amyloid. 1999; 6:297–300.
Article5). Ohkohchi N, Katoh H, Orii T, Fujimori K, Shimaoka S, Satomi S. Complications and treatments of donors and recipients in living-related liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1998; 30:3218–20.
Article6). Plá MP, Berenguer J, Arzuaga JA, Bañares R, Polo JR, Bouza E. Surgical wound infection by Aspergillus fumi-gatus in liver transplant recipients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992; 15:703–6.
Article7). Kumar A, Will EJ. Necrotizing fasciitis and Legionnaires' disease after combined renal and pancreatic transplantation: a penalty of overseas travel. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999; 14:1781–3.
Article8). Majeski JA, Rajagopalan PR, Fitts CT, Eddy GL, Holtz GL, Turner W, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis in a renal transplant patient. South Med J. 1988; 81:1315–6.
Article9). Wai PH, Ewing CA, Johnson LB, Lu AD, Attinger C, Kuo PC. Candida fasciitis following renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2001; 72:477–9.
Article10). Sia IG, Paya CV. Infectious complications following renal transplantation. Surg Clin North Am. 1998; 78:95–112.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fatal Necrotizing Fasciitis Due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa After Vaccination : A Case Report
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Chest Wall Complicating Acupuncture
- Fatal Necrotizing Fasciitis Due to Streptococcus pneumoniae: A Case Report
- A Case of Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Face
- A Case of Necrotizing Fasciitis