J Korean Surg Soc.
2009 Mar;76(3):144-148. 10.4174/jkss.2009.76.3.144.
Clinical Features after Rupture of Hydrogel Breast Implants - MDbP206
- Affiliations
-
- 1M.D. Clinic, Seoul, Korea. dahl65@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2096535
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2009.76.3.144
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Since the use of silicone-filled breast implants has been restricted, hydrogel has been used an alternative filler as a silicone elastomer shell filled with polysaccharide gel. However, its use has also been restricted since 2000 because of complications due to metabolic fate. The author observed the postoperative findings after implant rupture.
METHODS
Among 22 cases with previous augmentation mammoplasty using hydrogel implants that received reoperation in M.D. Clinic from February 2006 to June 2008, 12 cases of implant rupture were included in this study.
RESULTS
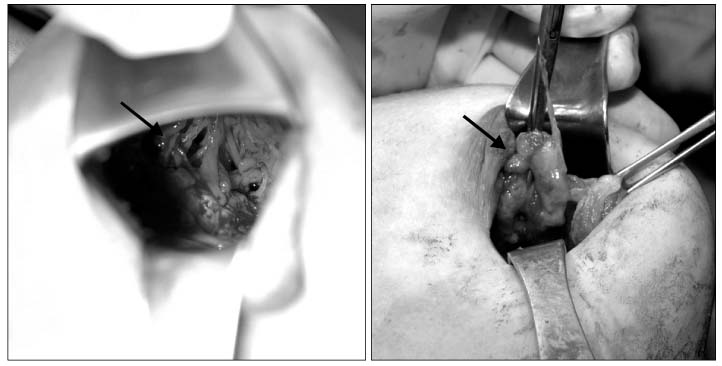
The mean interval from the previous hydrogel surgery was 7 years ranging from 3 to 9 years. Symptoms were unilateral deflation in 4, unilateral breast edema in 4, unilateral changes in texture in 3 and 1 without any symptoms. There was a significant spread of hydrogel into the surrounding tissue in 2 cases of deflation, 2 cases of edema and 1 asymptomatic case. The most severe spreading occurred 6 years after implant in a patient who had been delivered of a baby 2 months before her visit. The author performed total capsulectomy in 11 cases but was unable to remove all gel in 3 cases of multiple spread. Postoperative complications were mild capsular contracture in 2 patients with incomplete removal of surrounding gel and medial herniation in 1 in multiple spreading after childbirth.
CONCLUSION
Rupture of hydrogel breast implants had a high risk of surrounding tissue damage and it is suggested that these implants should not be used for breast augmentation. Patients with hydrogel breast implants should be checked carefully for rupture.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. DA 2000(07) - Breast Implants: PIP Hydrogel® [Internet]. Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. c2009. modified 2006 Sep 25; cited 2009 Feb 5. UK: MHRA;Available from: http://www.mhra.gov.uk. .2. Berthe JV, Van Geertruyden JP. Osmotic instability of hydrogel-filled breast implants. Br J Plast Surg. 2001. 54:465–466.3. Lee CJ, Park JH, Park IS, Lee SI. A case report of prefilled polysaccharide hydrogel breast implant rupture: clinical, MRI, and pathologic findings. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2004. 28:401–404.4. Qiao Q, Wang X, Sun J, Zhao R, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al. Management for postoperative complications of breast augmentation by injected polyacrylamide hydrogel. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005. 29:156–161.5. Zhang Y, Won CY, Chu CC. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable hydrophobic-hydrophilic hydrogel networks with a controlled swelling property. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 2000. 38:2392–2404.6. Ersek RA, Salisbury AV. Textured surface, nonsilicone gel breast implants: four years' clinical outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997. 100:1729–1739.7. Benediktsson K, Perbeck LG. Fluid retention in Bioplasty Misti Gold II breast prostheses with development of capsular contracture. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2000. 34:65–70.8. Piza-Katzer H, Pulzl P, Balogh B, Wechselberger G. Long-term results of MISTI gold breast implants: a retrospective study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. 110:1455–1459.9. Soubirac L, Jougla E, Hezard L, Grolleau JL, Chavoin JP. Deflation of breast implants, pre-filled with saline or hydrogel. Results and analysis of 650 treated patients. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2002. 47:273–279.10. Signorini M, Grisotti A, Ponzielli G, Pajardi G, Gilardino P. Self-expanding prostheses complicating augmentation mammoplasties. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1994. 18:195–199.11. Christensen LH, Breiting VB, Aasted A, Jorgensen A, Kebuladze I. Long-term effects of polyacrylamide hydrogel on human breast tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 111:1883–1890.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rupture of Breast Implants after Augmentation Mammoplasty: A Case Report of Simultaneous Intra-extracapsular Rupture
- Complication of Augmentation Mammoplasty using Polysaccharide Hydrogel Breast implant: Two Cases Report
- Immediate Implant Reconstruction after Eliminating Polyacrylamide Hydrogel (Amazingel) in Complicated Breasts
- A Retrospective Analysis of Ruptured Breast Implants
- Mechanical irritation by protruding bone: A possible cause of breast implant rupture