Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2010 Sep;53(9):838-841. 10.5468/kjog.2010.53.9.838.
Thoraco-omphalopagus conjoined twins diagnosed at 14 weeks of gestation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. leegsr@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2078002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/kjog.2010.53.9.838
Abstract
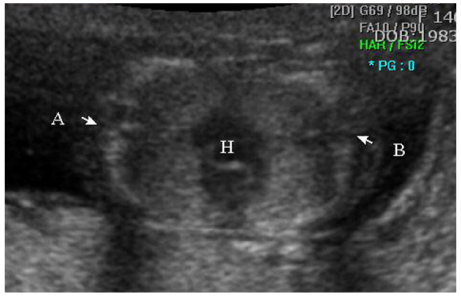
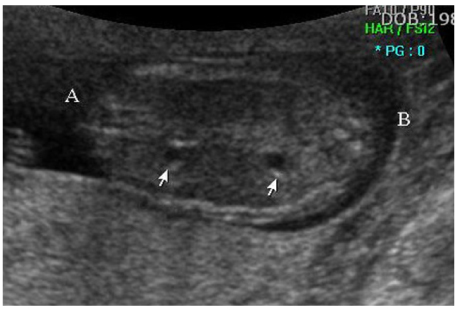
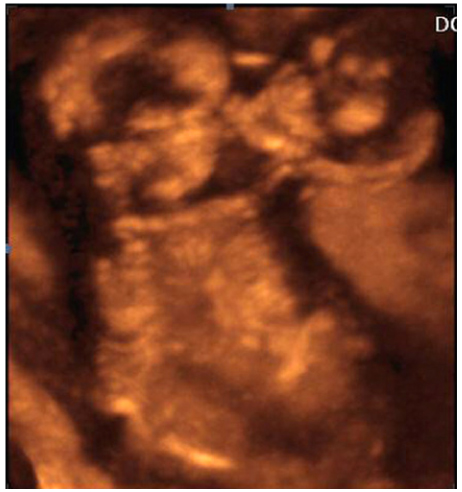
- Conjoined twins are very rare and the mortality rate of the fetus is extremely high. Early prenatal diagnosis is crucial, as it provides the opportunity for the mother and father to help in recognizing the conjunction of the twins and to help medical team in defining the prognosis of conjoined twins. We present a case of thoraco-omphalopagus conjoined twins diagnosed by two-dimensional and three-dimensional transabdominal sonography at 14(+2) weeks of gestation.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sebire NJ, Sepulveda W, Jeanty P, Nyberg DA, Nicolaides KH. Nyberg DA, McGahan JP, Pretorius DH, Pilu G, editors. Multiple gestations. Diagnostic imaging of fetal anomalies. 2003. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;777–813.2. Edmonds LD, Layde PM. Conjoined twins in the united states, 1970-1977. Teratology. 1982. 25:301–308.3. McHugh K, Kiely EM, Spitz L. Imaging of conjoined twins. Pediatr Radiol. 2006. 36:899–910.4. Kohli N. Ethical issues surrounding separation of conjoined twins. J La State Med Soc. 2001. 153:559–564.5. Barth RA, Filly RA, Goldberg JD, Moore P, Silverman NH. Conjoined twins: prenatal diagnosis and assessment of associated malformations. Radiology. 1990. 177:201–207.6. Kaufman MH. The embryology of conjoined twins. Childs Nerv Syst. 2004. 20:508–525.7. Pajkrt E, Jauniaux E. First-trimester diagnosis of conjoined twins. Prenat Diagn. 2005. 25:820–826.8. Hill LM. The sonographic detection of early first-trimester conjoined twins. Prenat Diagn. 1997. 17:961–963.9. Taner MZ, Kurdoglu M, Taskiran C, Kurdoglu Z, Himmetoglu O, Balci S. Early prenatal diagnosis of conjoined twins at 7 weeks and 6 days' gestation with two-dimensional Doppler ultrasound: a case report. Cases J. 2009. 2:8330.10. Abu-Rustum RS, Adra AM. Three-dimensional sonographic diagnosis of conjoined twins with fetal death in the first trimester. J Ultrasound Med. 2008. 27:1662–1663.11. Harper RG, Kenigsberg K, Sia CG, Horn D, Stern D, Bongiovi V. Xiphopagus conjoined twins: a 300-year review of the obstetric, morphopathologic, neonatal, and surgical parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980. 137:617–629.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful separation of thoraco-omphalopagus conjoined twins, preoperative evaluation and surgical management
- A case of Conjoined Twins: Omphalopagus
- Anesthesia for Surgical Separation of Thoraco - xiphopagus Conjoined Twins
- A case of thoraco-omphalopagus with omphalocele with 3D ultrasonography and MRI
- A Case of Conjoined Twin