Yonsei Med J.
2014 Nov;55(6):1729-1735. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1729.
Home Mechanical Ventilation in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital and Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromusular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kswoong@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2070224
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1729
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To survey the use of invasive and noninvasive home mechanical ventilation (HMV) methods in South Korea from the perspective of physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For 413 users of HMV, retrospective reviews of PM&R interventions and survey of HMV methods employed from Mar 2000 to Dec 2009.
RESULTS
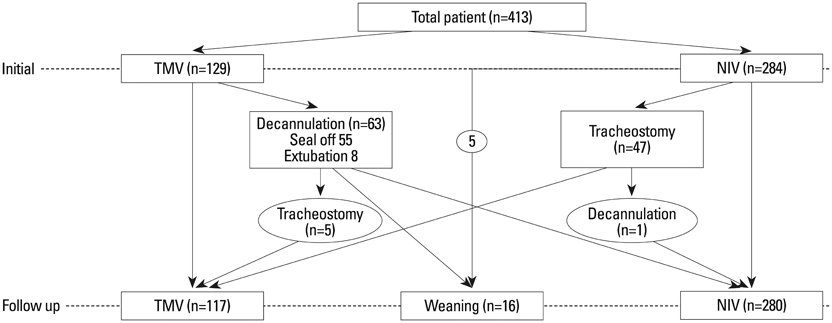
Of the 413 users, the majority of whom with progressive neuromuscular disorders (NMDs) (n=358), 284 patients initially used noninvasive mechanical ventilation (NIV), while 63 others who were using tracheostomy mechanical ventilation switched to NIV as part of their rehabilitation. The NMD patients began HMV at an earlier age (34.9+/-20.3 yrs), and used for longer (14.7+/-7.5) hours than patients with non-neuromuscular causes of respiratory impairment.
CONCLUSION
Noninvasive management was preferred over invasive ones, and transition to the former was a result of PM&R interventions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Early Marker of Myocardial Deformation in Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Assessed Using Echocardiographic Myocardial Strain Analysis
Won Ha Jo, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Jo Won Jung, Jae Young Choi, Seung Woong Gang
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):900-904. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.900.Pulmonary rehabilitation
Seong-Woong Kang
J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59(9):705-712. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.9.705.
Reference
-
1. Racca F, Berta G, Sequi M, Bignamini E, Capello E, Cutrera R, et al. Long-term home ventilation of children in Italy: a national survey. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011; 46:566–572.
Article2. Spruit MA, Clini EM. Towards health benefits in chronic respiratory diseases: pulmonary rehabilitation. Eur Respir Rev. 2013; 22:202–204.
Article3. Hill NS. Pulmonary rehabilitation. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006; 3:66–74.
Article4. Bach JR, Gonçalves MR, Hon A, Ishikawa Y, De Vito EL, Prado F, et al. Changing trends in the management of end-stage neuromuscular respiratory muscle failure: recommendations of an international consensus. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013; 92:267–277.
Article5. Lloyd-Owen SJ, Donaldson GC, Ambrosino N, Escarabill J, Farre R, Fauroux B, et al. Patterns of home mechanical ventilation use in Europe: results from the Eurovent survey. Eur Respir J. 2005; 25:1025–1031.
Article6. Morris JF, Koski A, Johnson LC. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971; 103:57–67.
Article7. Kang SW, Bach JR. Maximum insufflation capacity. Chest. 2000; 118:61–65.
Article8. Lee SC, Park JH, Kang SW, Kim DH, Song SH. External control of exhalation for cough assistance: a method for patients with glottis dysfunction and/or tracheostomy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:1402–1407.
Article9. Bach JR, Saporito LR. Criteria for extubation and tracheostomy tube removal for patients with ventilatory failure. A different approach to weaning. Chest. 1996; 110:1566–1571.
Article10. Kim DH, Kang SW, Choi W, Moon JH, Baek JH, Choi SH, et al. A research on the management of ventilatory insufficiency in patients with neuromuscular diseases. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:347–354.11. Kang SW, Park JH, Ryu HH, Kang YS, Moon JH. Non-invasive mechanical ventilator care for the patients with advanced neuromuscular disease. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004; 28:71–77.12. Dybwik K, Tollåli T, Nielsen EW, Brinchmann BS. Why does the provision of home mechanical ventilation vary so widely? Chron Respir Dis. 2010; 7:67–73.
Article13. Louwerse ES, Visser CE, Bossuyt PM, Weverling GJ. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: mortality risk during the course of the disease and prognostic factors. The Netherlands ALS Consortium. J Neurol Sci. 1997; 152:Suppl 1. S10–S17.14. Bach JR, Martinez D. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: continuous noninvasive ventilatory support prolongs survival. Respir Care. 2011; 56:744–750.
Article15. Ishikawa Y, Miura T, Ishikawa Y, Aoyagi T, Ogata H, Hamada S, et al. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: survival by cardio-respiratory interventions. Neuromuscul Disord. 2011; 21:47–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Home mechanical ventilation in children with chronic respiratory failure: a narrative review
- The Comparative Study of Central Venous Pressure Measurements during Mechanical Ventilation and after Disconnection of Ventilation
- Home Mechanical Ventilation of Pediatric Patients
- Treatment of acute respiratory failure: invasive mechanical ventilation
- Respiratory Failure in Guillain-Barre Syndrome