Yonsei Med J.
2014 Nov;55(6):1606-1610. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1606.
Feasibility of the Short Hospital Stays after Laparoscopic Appendectomy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jakii@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2070209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1606
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of short hospital stays after laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
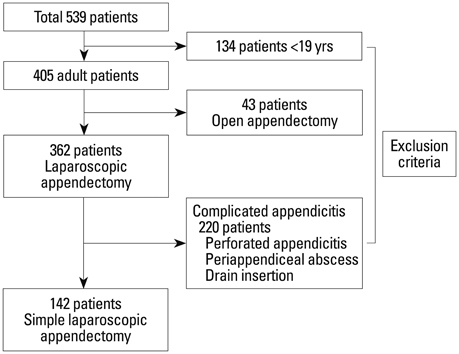
The records of 142 patients who underwent laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis from January 2010 to December 2012 were analyzed retrospectively. Patients were allocated to an early (<48 hours) or a late (>48 hours) group by postoperative hospital stay. Postoperative complications and readmission rates in the two groups were evaluated and compared.
RESULTS
Overall mean patient age was 50.1 (+/-16.0) years, and mean hospital stay was 3.8 (+/-2.8) days. Fifty-four patients (group E, 38.0%) were discharged within 48 hours of surgery, and 88 patients (group L, 62.0%) stayed more than 48 hours. Overall complication rates were similar in the two groups (14.8% vs. 21.6%, p=0.318), and wound complications (13.0% vs. 12.5%), postoperative bowel obstruction (1.9% vs. 2.3%), and abdominal pain (1.9% vs. 3.4%) were not significantly different.
CONCLUSION
Patients that undergo laparoscopic appendectomy due to uncomplicated appendicitis may be safely discharged within 48 hours. Further study should be conducted to determine the optimal length of hospital stay after laparoscopic appendectomy to reduce hospital costs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cash CL, Frazee RC, Smith RW, Davis ML, Hendricks JC, Childs EW, et al. Outpatient laparoscopic appendectomy for acute appendicitis. Am Surg. 2012; 78:213–215.
Article2. Dubois L, Vogt KN, Davies W, Schlachta CM. Impact of an outpatient appendectomy protocol on clinical outcomes and cost: a case-control study. J Am Coll Surg. 2010; 211:731–737.
Article3. Jain A, Mercado PD, Grafton KP, Dorazio RA. Outpatient laparoscopic appendectomy. Surg Endosc. 1995; 9:424–425.
Article4. Frutos MD, Abrisqueta J, Lujan J, Abellan I, Parrilla P. Randomized prospective study to compare laparoscopic appendectomy versus umbilical single-incision appendectomy. Ann Surg. 2013; 257:413–418.
Article5. Wang CC, Tu CC, Wang PC, Lin HC, Wei PL. Outcome comparison between laparoscopic and open appendectomy: evidence from a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68662.
Article6. Lee HJ, Park YH, Kim JI, Choi PW, Park JH, Heo TG, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and hospital cost between open appendectomy and laparoscopic appendectomy. J Korean Surg Soc. 2011; 81:321–325.
Article7. Lee JS, Hong TH, Kim JG. A comparison of the periumbilical incision and the intraumbilical incision in laparoscopic appendectomy. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 83:360–366.
Article8. Shin CS, Kim JI, Roh YN, Choi PW, Heo TG, Park JH. Clinical outcomes and costs of laparoscopic versus open appendectomy for appendicitis. J Surg. 2013; 1:37–42.
Article9. Kim CB, Kim MS, Hong JH, Lee HY, Yu SH. Is laparoscopic appendectomy useful for the treatment of acute appendicitis in Korea? A meta-analysis. Yonsei Med J. 2004; 45:7–16.
Article10. Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2012; 344:e2156.
Article11. Reddick EJ, Olsen DO. Outpatient laparoscopic laser cholecystectomy. Am J Surg. 1990; 160:485–487.
Article12. Swank HA, Eshuis EJ, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Bemelman WA. Short- and long-term results of open versus laparoscopic appendectomy. World J Surg. 2011; 35:1221–1226.
Article13. Tenconi SM, Boni L, Colombo EM, Dionigi G, Rovera F, Cassinotti E. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy as day-surgery procedure: current indications and patients' selection. Int J Surg. 2008; 6:Suppl 1. S86–S88.
Article14. Marinis A, Stamatakis E, Tsaroucha A, Dafnios N, Anastasopoulos G, Polymeneas G, et al. Safety and effectiveness of outpatient laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a teaching hospital: a prospective study of 110 consecutive patients. BMC Res Notes. 2010; 3:207.
Article15. Ramírez-Plaza CP, Perales JL, Camero NM, Rodríguez-Cañete A, Bondía-Navarro JA, Santoyo-Santoyo J. Outpatient laparoscopic adrenalectomy: a new step ahead. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2570–2573.
Article16. Skattum J, Edwin B, Trondsen E, Mjåland O, Raede J, Buanes T. Outpatient laparoscopic surgery: feasibility and consequences for education and health care costs. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:796–801.
Article17. Kehagias I, Karamanakos SN, Panagiotopoulos S, Panagopoulos K, Kalfarentzos F. Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: which way to go? World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:4909–4914.
Article18. Abunnaja S, Cuviello A, Sanchez JA. Enteral and parenteral nutrition in the perioperative period: state of the art. Nutrients. 2013; 5:608–623.
Article19. Bendavid Y, Martel K, Sideris L, Drolet P, Dubé P. Impact of early postoperative enteral feeding on hospital length of stay in patients undergoing colonic surgery: results of a prospective randomized trial. Surg Sci. 2012; 3:537–541.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy is Feasible for All Forms of Appendicitis
- Irrigation Versus Suction Alone During Laparoscopic Appendectomy for Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis
- Safety of laparoscopic appendectomy for the management of acute appendicitis during pregnancy
- Gasless Laparoscopic Assisted Transumbilical Appendectomy
- Comparison of Laparoscopic and Open Appendectomies