Korean J Radiol.
2015 Apr;16(2):314-324. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.2.314.
The Accuracy of Ultrasonography for the Evaluation of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Research Institute for Nursing Science, Keimyung Univercity, Daegu 704-701, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju 220-701, Korea. baiksk@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2070175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.2.314
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Studies have presented conflicting results regarding the accuracy of ultrasonography (US) for diagnosing portal hypertension (PH). We sought to identify evidence in the literature regarding the accuracy of US for assessing PH in patients with liver cirrhosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
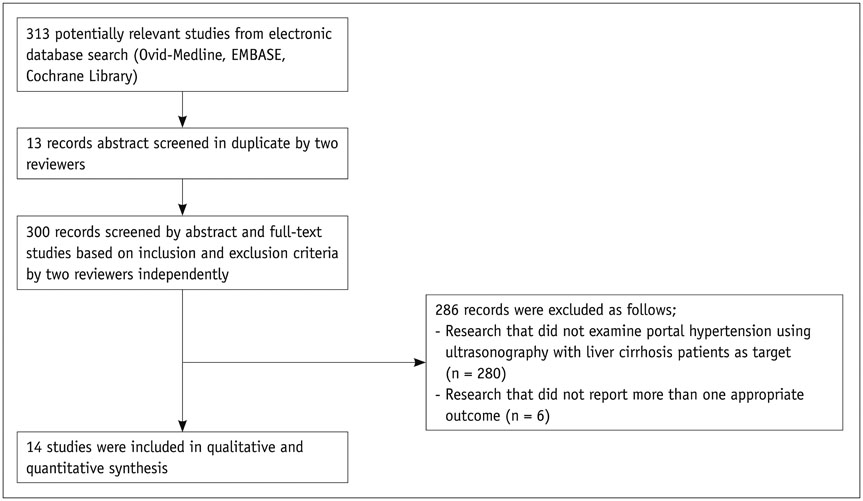
We conducted a systematic review by searching databases, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library, for relevant studies.
RESULTS
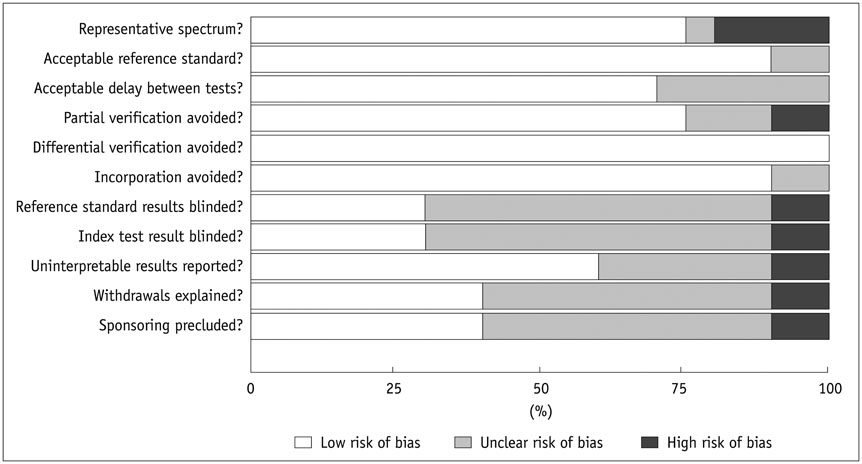
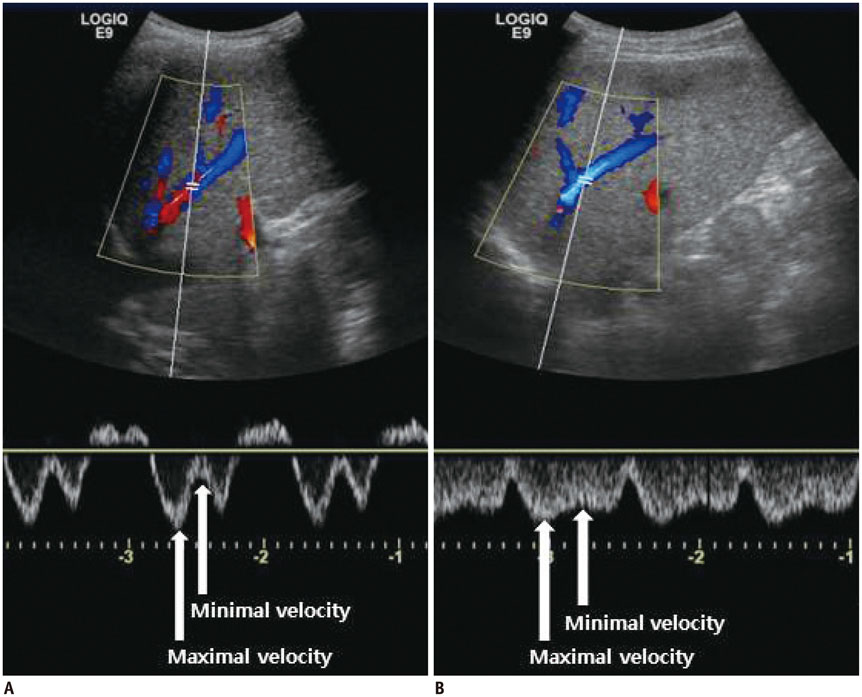
A total of 14 studies met our inclusion criteria. The US indices were obtained in the portal vein (n = 9), hepatic artery (n = 6), hepatic vein (HV) (n = 4) and other vessels. Using hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) as the reference, the sensitivity (Se) and specificity (Sp) of the portal venous indices were 69-88% and 67-75%, respectively. The correlation coefficients between HVPG and the portal venous indices were approximately 0.296-0.8. No studies assess the Se and Sp of the hepatic arterial indices. The correlation between HVPG and the hepatic arterial indices ranged from 0.01 to 0.83. The Se and Sp of the hepatic venous indices were 75.9-77.8% and 81.8-100%, respectively. In particular, the Se and Sp of HV arrival time for clinically significant PH were 92.7% and 86.7%, respectively. A statistically significant correlation between HVPG and the hepatic venous indices was observed (0.545-0.649).
CONCLUSION
Some US indices, such as HV, exhibited an increased accuracy for diagnosing PH. These indices may be useful in clinical practice for the detection of significant PH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim MY, Baik SK. Hyperdynamic circulation in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 54:143–148.2. Kim MY, Baik SK, Suk KT, Yea CJ, Lee IY, Kim JW, et al. Measurement of hepatic venous pressure gradient in liver cirrhosis: relationship with the status of cirrhosis, varices, and ascites in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2008; 14:150–158.3. Baik SK. Haemodynamic evaluation by Doppler ultrasonography in patients with portal hypertension: a review. Liver Int. 2010; 30:1403–1413.4. Baik SK, Park DH, Kim MY, Choi YJ, Kim HS, Lee DK, et al. Captopril reduces portal pressure effectively in portal hypertensive patients with low portal venous velocity. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:1150–1154.5. Lebrec D. Methods to evaluate portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992; 21:41–59.6. Ripoll C, Groszmann R, Garcia-Tsao G, Grace N, Burroughs A, Planas R, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts clinical decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:481–488.7. Vizzutti F, Arena U, Rega L, Pinzani M. Non invasive diagnosis of portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008; 32:6 Suppl 1. 80–87.8. Kim MY, Suk KT, Baik SK, Kim HA, Kim YJ, Cha SH, et al. Hepatic vein arrival time as assessed by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the assessment of portal hypertension in compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2012; 56:1053–1062.9. Schepke M, Raab P, Hoppe A, Schiedermaier P, Brensing KA, Sauerbruch T. Comparison of portal vein velocity and the hepatic venous pressure gradient in assessing the acute portal hemodynamic response to propranolol in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:2905–2909.10. Ohnishi K, Saito M, Nakayama T, Iida S, Nomura F, Koen H, et al. Portal venous hemodynamics in chronic liver disease: effects of posture change and exercise. Radiology. 1985; 155:757–761.11. Vizzutti F, Arena U, Rega L, Romanelli RG, Colagrande S, Cuofano S, et al. Performance of Doppler ultrasound in the prediction of severe portal hypertension in hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2007; 27:1379–1388.12. Kim SY, Jeong WK, Kim Y, Heo JN, Kim MY, Kim TY, et al. Changing waveform during respiration on hepatic vein Doppler sonography of severe portal hypertension: comparison with the damping index. J Ultrasound Med. 2011; 30:455–462.13. Kim MY, Baik SK, Park DH, Lim DW, Kim JW, Kim HS, et al. Damping index of Doppler hepatic vein waveform to assess the severity of portal hypertension and response to propranolol in liver cirrhosis: a prospective nonrandomized study. Liver Int. 2007; 27:1103–1110.14. Tasu JP, Rocher L, PEletier G, Kuoch V, Kulh E, Miquel A, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradients measured by duplex ultrasound. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57:746–752.15. Schneider AW, Kalk JF, Klein CP. Hepatic arterial pulsatility index in cirrhosis: correlation with portal pressure. J Hepatol. 1999; 30:876–881.16. Taourel P, Blanc P, Dauzat M, Chabre M, Pradel J, Gallix B, et al. Doppler study of mesenteric, hepatic, and portal circulation in alcoholic cirrhosis: relationship between quantitative Doppler measurements and the severity of portal hypertension and hepatic failure. Hepatology. 1998; 28:932–936.17. Baik SK, Kim JW, Kim HS, Kwon SO, Kim YJ, Park JW, et al. Recent variceal bleeding: Doppler US hepatic vein waveform in assessment of severity of portal hypertension and vasoactive drug response. Radiology. 2006; 240:574–580.18. Bolognesi M, Sacerdoti D, Merkel C, Bombonato G, Gatta A. Noninvasive grading of the severity of portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients by echo-color-Doppler. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2001; 27:901–907.19. Merkel C, Sacerdoti D, Bolognesi M, Bombonato G, Gatta A. Doppler sonography and hepatic vein catheterization in portal hypertension: assessment of agreement in evaluating severity and response to treatment. J Hepatol. 1998; 28:622–630.20. Berzigotti A, Rossi V, Tiani C, Pierpaoli L, Zappoli P, Riili A, et al. Prognostic value of a single HVPG measurement and Doppler-ultrasound evaluation in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:687–695.21. Berzigotti A, Casadei A, Magalotti D, Castaldini N, Losinno F, Rossi C, et al. Renovascular impedance correlates with portal pressure in patients with liver cirrhosis. Radiology. 2006; 240:581–586.22. Berzigotti A, Reverter E, García-Criado A, Abraldes JG, Cerini F, García-Pagán JC, et al. Reliability of the estimation of total hepatic blood flow by Doppler ultrasound in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:717–722.23. Ozdogan O, Atalay H, Cimsit C, Tahan V, Tokay S, Giral A, et al. Role of echo Doppler ultrasonography in the evaluation of postprandial hyperemia in cirrhotic patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:260–264.24. Choi YJ, Baik SK, Park DH, Kim MY, Kim HS, Lee DK, et al. Comparison of Doppler ultrasonography and the hepatic venous pressure gradient in assessing portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:424–429.25. Kim MY, Jeong WK, Baik SK. Invasive and non-invasive diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4300–4315.26. Kim MY, Choi H, Baik SK, Yea CJ, Won CS, Byun JW, et al. Portal hypertensive gastropathy: correlation with portal hypertension and prognosis in cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:3561–3567.27. Baik SK, Jeong PH, Ji SW, Yoo BS, Kim HS, Lee DK, et al. Acute hemodynamic effects of octreotide and terlipressin in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized comparison. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:631–635.28. Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, García-Pagan JC. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 6:573–582.29. D'Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006; 44:217–231.30. Kayacetin E, Efe D, Doğan C. Portal and splenic hemodynamics in cirrhotic patients: relationship between esophageal variceal bleeding and the severity of hepatic failure. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:661–667.31. Bolondi L, Gaiani S, Barbara L. Accuracy and reproducibility of portal flow measurement by Doppler US. J Hepatol. 1991; 13:269–273.32. Zoli M, Marchesini G, Brunori A, Cordiani MR, Pisi E. Portal venous flow in response to acute beta-blocker and vasodilatatory treatment in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1986; 6:1248–1251.33. Sato S, Ohnishi K, Sugita S, Okuda K. Splenic artery and superior mesenteric artery blood flow: nonsurgical Doppler US measurement in healthy subjects and patients with chronic liver disease. Radiology. 1987; 164:347–352.34. Sacerdoti D, Gaiani S, Buonamico P, Merkel C, Zoli M, Bolondi L, et al. Interobserver and interequipment variability of hepatic, splenic, and renal arterial Doppler resistance indices in normal subjects and patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1997; 27:986–992.35. Lim AK, Taylor-Robinson SD, Patel N, Eckersley RJ, Goldin RD, Hamilton G, et al. Hepatic vein transit times using a microbubble agent can predict disease severity non-invasively in patients with hepatitis C. Gut. 2005; 54:128–133.36. Grier S, Lim AK, Patel N, Cobbold JF, Thomas HC, Cox IJ, et al. Role of microbubble ultrasound contrast agents in the non-invasive assessment of chronic hepatitis C-related liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:3461–3465.37. Moon KM, Kim G, Baik SK, Choi E, Kim MY, Kim HA, et al. Ultrasonographic scoring system score versus liver stiffness measurement in prediction of cirrhosis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19:389–398.