Risk Factors for Falls in Older Korean Adults: The 2011 Community Health Survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mhshinx@paran.com
- 2Gwangju-Jeonnam Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Center for Creative Biomedical Scientists, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2069928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.11.1482
Abstract
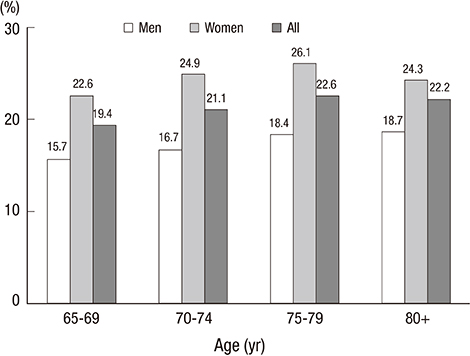
- Falls are a major health problem for elderly populations worldwide. We analyzed data from the 2011 Korean Community Health Survey to identify potential risk factors for falls in a representative population-based sample of community-dwelling older Korean adults. Risk factors for falls were assessed by multivariate survey logistic regression models. The prevalence of falls was 36.5% in males and 63.5% in females. Age and female sex were associated with a higher risk of falls. Similarly, living alone, living in an urban area, poor self-rated health, and high stress were associated with a high risk of falls. Subjects with diabetes mellitus, stroke, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, urinary incontinence, cataracts, or depression had a high risk of falls. However, subjects with hypertension were at low risk for falls. In conclusion, age, female sex, marital status, residence location, self-rated health, stress, and several chronic conditions were significantly associated with the risk for falls in the older Korean adults. Our findings suggest that these risk factors should be addressed in public health policies for preventing falls.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Association of Falls and Fear of Falling with Mortality in Korean Adults: The Dong-gu Study
Jinkyu Oh, Chang Kyun Choi, Sun A Kim, Sun-Seog Kweon, Young-Hoon Lee, Hae-Sung Nam, Kyeong-Soo Park, So-Yeon Ryu, Seong-Woo Choi, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Med J. 2019;55(2):104-108. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.104.Longitudinal Trends in Fall Accidents in Community Dwelling Korean Adults: The 2008–2013 Korean Community Health Survey
Ickpyo Hong, Annie N. Simpson, Sarah Logan, Hee-Soon Woo
Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(4):657-665. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.4.657.Analysis of Fall Accidents of Dizzy Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South Korea (2011-2015)
Sung Kyun Kim, Sung Ho Lee, Seon Heui Lee, Jae Jun Song, Mi Jung Gwak, Hee Seon Lee, Gi Jung Im
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2017;60(6):271-278. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2016.17531.
Reference
-
1. Campbell AJ, Reinken J, Allan BC, Martinez GS. Falls in old age: a study of frequency and related clinical factors. Age Ageing. 1981; 10:264–270.2. Milat AJ, Watson WL, Monger C, Barr M, Giffin M, Reid M. Prevalence, circumstances and consequences of falls among community-dwelling older people: results of the 2009 NSW Falls Prevention Baseline Survey. N S W Public Health Bull. 2011; 22:43–48.3. Siqueira FV, Facchini LA, Silveira DS, Piccini RX, Tomasi E, Thumé E, Silva SM, Dilélio A. Prevalence of falls in elderly in Brazil: a countrywide analysis. Cad Saude Publica. 2011; 27:1819–1826.4. Orces CH. Prevalence and determinants of falls among older adults in ecuador: an analysis of the SABE I survey. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2013; 2013:495468.5. World Health Organization. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2008.6. Cesari M, Landi F, Torre S, Onder G, Lattanzio F, Bernabei R. Prevalence and risk factors for falls in an older community-dwelling population. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002; 57:M722–M726.7. Deandrea S, Lucenteforte E, Bravi F, Foschi R, La Vecchia C, Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology. 2010; 21:658–668.8. Cho JP, Paek KW, Song HJ, Jung YS, Moon HW. Prevalence and associated factors of falls in the elderly community. Korean J Prev Med. 2001; 34:47–54.9. Sohng KY, Moon JS, Song HH, Lee KS, Kim YS. Risk factors for falls among the community-dwelling elderly in Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2004; 34:1483–1490.10. Yoo IY. Recurrent falls among community-dwelling older Koreans: prevalence and multivariate risk factors. J Gerontol Nurs. 2011; 37:28–40.11. Craven R, Bruno P. Teach the elderly to prevent falls. J Gerontol Nurs. 1986; 12:27–33.12. Sheahan SL, Coons SJ, Robbins CA, Martin SS, Hendricks J, Latimer M. Psychoactive medication, alcohol use, and falls among older adults. J Behav Med. 1995; 18:127–140.13. Fletcher PC, Hirdes JP. Risk factors for serious falls among community-based seniors: results from the national population health survey. Can J Aging. 2002; 21:103–116.14. de Rekeneire N, Visser M, Peila R, Nevitt MC, Cauley JA, Tylavsky FA, Simonsick EM, Harris TB. Is a fall just a fall: correlates of falling in healthy older persons. The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003; 51:841–846.15. Gill T, Taylor AW, Pengelly A. A population-based survey of factors relating to the prevalence of falls in older people. Gerontology. 2005; 51:340–345.16. Fletcher PC, Hirdes JP. Risk factors for falling among community-based seniors using home care services. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002; 57:M504–M510.17. Campbell AJ, Spears GF, Borrie MJ. Examination by logistic regression modelling of the variables which increase the relative risk of elderly women falling compared to elderly men. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990; 43:1415–1420.18. Lin MR, Hwang HF, Lin PS, Chen CY. Relations of osteoporosis and follow-up duration to recurrent falls in older men and women. Osteoporos Int. 2014; 25:863–871.19. Tromp AM, Smit JH, Deeg DJ, Bouter LM, Lips P. Predictors for falls and fractures in the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. J Bone Miner Res. 1998; 13:1932–1939.20. Wu TY, Chie WC, Yang RS, Kuo KL, Wong WK, Liaw CK. Risk factors for single and recurrent falls: a prospective study of falls in community dwelling seniors without cognitive impairment. Prev Med. 2013; 57:511–517.21. Leung A, Chi I, Lou VW, Chan KS. Psychosocial risk factors associated with falls among Chinese community-dwelling older adults in Hong Kong. Health Soc Care Community. 2010; 18:272–281.22. Xie LQ, Zhang JP, Peng F, Jiao NN. Prevalence and related influencing factors of depressive symptoms for empty-nest elderly living in the rural area of YongZhou, China. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2010; 50:24–29.23. Cwikel J. Falls among elderly people living at home: medical and social factors in a national sample. Isr J Med Sci. 1992; 28:446–453.24. Cwikel J, Fried AV, Galinsky D. Falls and psychosocial factors among community-dwelling elderly persons: a review and integration of findings from Israel. Public Health Rev. 1989; 17:39–50.25. Hedman AM, Fonad E, Sandmark H. Older people living at home: associations between falls and health complaints in men and women. J Clin Nurs. 2013; 22:2945–2952.26. Vellas BJ, Wayne SJ, Garry PJ, Baumgartner RN. A two-year longitudinal study of falls in 482 community-dwelling elderly adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1998; 53:M264–M274.27. Kwok T, Liddle J, Hastie IR. Postural hypotension and falls. Postgrad Med J. 1995; 71:278–280.28. Craig GM. Clinical presentation of orthostatic hypotension in the elderly. Postgrad Med J. 1994; 70:638–642.29. Yu PL, Qin ZH, Shi J, Zhang J, Xin MZ, Wu ZL, Sun ZQ. Prevalence and related factors of falls among the elderly in an urban community of Beijing. Biomed Environ Sci. 2009; 22:179–187.30. Campbell AJ. Drug treatment as a cause of falls in old age. A review of the offending agents. Drugs Aging. 1991; 1:289–302.31. Butt DA, Mamdani M, Austin PC, Tu K, Gomes T, Glazier RH. The risk of falls on initiation of antihypertensive drugs in the elderly. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:2649–2657.32. Tinetti ME, Kumar C. The patient who falls: "Its alway's a trade-off". JAMA. 2010; 303:258–266.33. Sibley KM, Voth J, Munce SE, Straus SE, Jaglal SB. Chronic disease and falls in community-dwelling Canadians over 65 years old: a population-based study exploring associations with number and pattern of chronic conditions. BMC Geriatr. 2014; 14:22.34. Möller J, Hallqvist J, Laflamme L, Mattsson F, Ponzer S, Sadigh S, Engström K. Emotional stress as a trigger of falls leading to hip or pelvic fracture. Results from the ToFa study - a case-crossover study among elderly people in Stockholm, Sweden. BMC Geriatr. 2009; 9:7.35. Chapman GJ, Hollands MA. Evidence that older adult fallers prioritise the planning of future stepping actions over the accurate execution of ongoing steps during complex locomotor tasks. Gait Posture. 2007; 26:59–67.36. Wojszel ZB, Bień B. Falls amongst older people living in the community. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst. 2004; 49:280–284.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Correction of Prevalence of Falls by Sex in Article 'Risk Factors for Falls in Older Korean Adults: The 2011 Community Health Survey'
- Factors Associated with Physical Activity in Older Adults by Region: Based on the 2017 Community Health Survey
- Factors Influencing Fall Experiences among the Older Adults in Community: Using the 2021 Community Health Survey
- Development of a Knowledge Scale of Fall Risk Factors for Community-dwelling Older Adults
- Peripheral Neuropathy in Older Adults