Yonsei Med J.
2014 May;55(3):753-759. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.753.
Delta Neutrophil Index as an Early Marker for Differential Diagnosis of Adult-Onset Still's Disease and Sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sangwonlee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2068687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.753
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate clinical implications of delta neutrophil index (DNI) to discriminate adult onset Still's disease (AOSD) from sepsis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of 13 patients with AOSD and 33 gender and age-matched patients with sepsis. In all subjects, microbial tests were performed to exclude or confirm sepsis. All laboratory data were measured two or three times during the first 3 days and represented by their mean levels. DNI was measured automatically by ADVIA 2120 for the first 3 days.
RESULTS
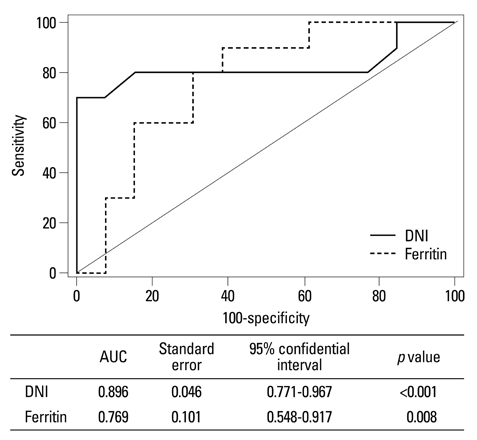
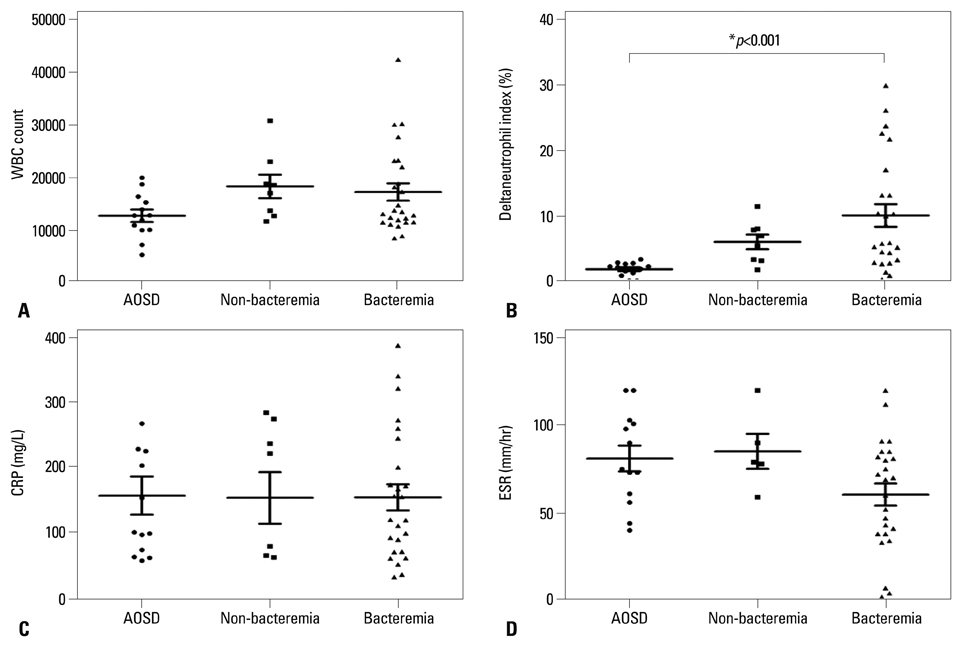
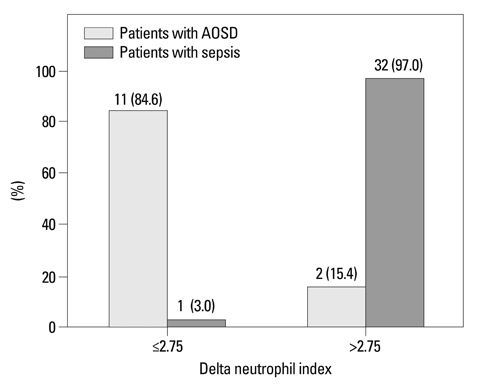
There were no significant differences in white blood cell counts, neutrophil proportion, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein between two groups. AOSD patients had notably lower DNI than sepsis patients regardless of the presence of bacteremia or not. However, both DNI and ferritin were not significant independent factors for predicting sepsis in the multivariate logistic regression analysis. Meanwhile, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of DNI was slightly higher than that of ferritin. When we set DNI of 2.75% as the cut-off value for predicting sepsis, 11 (84.6%) of AOSD patients had a DNI value below 2.75% and 2 (15.4%) of them had a DNI over 2.75% (relative risk for sepsis 176).
CONCLUSION
We suggest that DNI may be a useful marker for differential diagnosis of AOSD from sepsis in the early phase as supplementary to ferritin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Delta Neutrophil Index Is Associated with Vasculitis Activity and Risk of Relapse in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
Juyoung Yoo, Sung Soo Ahn, Seung Min Jung, Jason Jungsik Song, Yong-Beom Park, Sang-Won Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(3):397-405. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.3.397.Delta Neutrophil Index as a Prognostic Marker in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
In Suk Sol, Hyun Bin Park, Min Jung Kim, Seo Hee Yoon, Yoon Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Kyu-Earn Kim
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2016;31(4):351-358. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00171.
Reference
-
1. Bagnari V, Colina M, Ciancio G, Govoni M, Trotta F. Adult-onset Still's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:855–862.
Article2. Fautrel B, Zing E, Golmard JL, Le Moel G, Bissery A, Rioux C, et al. Proposal for a new set of classification criteria for adult-onset still disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2002; 81:194–200.
Article3. Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992; 19:424–430.4. Rau M, Schiller M, Krienke S, Heyder P, Lorenz H, Blank N. Clinical manifestations but not cytokine profiles differentiate adult-onset Still's disease and sepsis. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37:2369–2376.
Article5. Jung SY, Park YB, Ha YJ, Lee KH, Lee SK. Serum calprotectin as a marker for disease activity and severity in adult-onset Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37:1029–1034.
Article6. Van Reeth C, Le Moel G, Lasne Y, Revenant MC, Agneray J, Kahn MF, et al. Serum ferritin and isoferritins are tools for diagnosis of active adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:890–895.7. Cantarini L, Giani T, Fioravanti A, Iacoponi F, Simonini G, Pagnini I, et al. Serum amyloid A circulating levels and disease activity in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:1045–1048.
Article8. Nahm CH, Choi JW, Lee J. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2008; 38:241–246.9. Ansari-Lari MA, Kickler TS, Borowitz MJ. Immature granulocyte measurement using the Sysmex XE-2100. Relationship to infection and sepsis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003; 120:795–799.
Article10. Selig C, Nothdurft W. Cytokines and progenitor cells of granulocytopoiesis in peripheral blood of patients with bacterial infections. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:104–109.
Article11. Cavallazzi R, Bennin CL, Hirani A, Gilbert C, Marik PE. Is the band count useful in the diagnosis of infection? An accuracy study in critically ill patients. J Intensive Care Med. 2010; 25:353–357.
Article12. Park BH, Kang YA, Park MS, Jung WJ, Lee SH, Lee SK, et al. Delta neutrophil index as an early marker of disease severity in critically ill patients with sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. 2011; 11:299.
Article13. Seok Y, Choi JR, Kim J, Kim YK, Lee J, Song J, et al. Delta neutrophil index: a promising diagnostic and prognostic marker for sepsis. Shock. 2012; 37:242–246.14. Kim HA, Sung JM, Suh CH. Therapeutic responses and prognosis in adult-onset Still's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:1291–1298.
Article15. Ohta A, Yamaguchi M, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima H, Kashiwagi H, et al. Adult Still's disease: a multicenter survey of Japanese patients. J Rheumatol. 1990; 17:1058–1063.16. Zeng T, Zou YQ, Wu MF, Yang CD. Clinical features and prognosis of adult-onset still's disease: 61 cases from China. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:1026–1031.
Article17. Fautrel B. Adult-onset Still disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 22:773–792.
Article18. Gauer RL. Early recognition and management of sepsis in adults: the first six hours. Am Fam Physician. 2013; 88:44–53.19. Fautrel B. Ferritin levels in adult Still's disease: any sugar? Joint Bone Spine. 2002; 69:355–357.
Article20. Fautrel B, Le Moël G, Saint-Marcoux B, Taupin P, Vignes S, Rozenberg S, et al. Diagnostic value of ferritin and glycosylated ferritin in adult onset Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:322–329.21. Min JK, Cho CS, Kim HY, Oh EJ. Bone marrow findings in patients with adult Still's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003; 32:119–121.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delta Neutrophil Index as an Early Marker of Sepsis in Burn Patients
- Assessment of Perforation of Acute Appendicitis using the Delta Neutrophil Index Reflecting Peripheral Immature Granulocyte Count
- Which patients with intestinal obstruction need surgery? The delta neutrophil index as an early predictive marker
- Delta Neutrophil Index as a Prognostic Marker of Early Mortality in Gram Negative Bacteremia
- The usefulness of serum biomarker C-reactive protein, delta neutrophil index, lactic acid and ammonia for differential diagnosis in patients with drowsy mentality in emergency department