J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Jul;56(1):71-74. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.1.71.
Stereotactic Mesencephalotomy for Cancer - Related Facial Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Eulji General Hospital, College of Medicine, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. sbc@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Catholic Neuroscience Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2067082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.1.71
Abstract
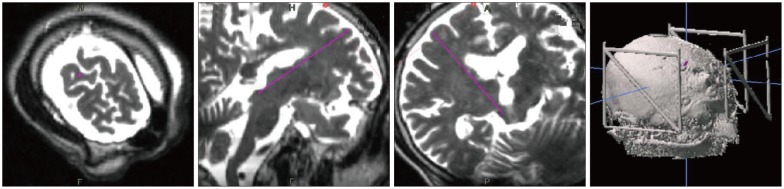
- Cancer-related facial pain refractory to pharmacologic management or nondestructive means is a major indication for destructive pain surgery. Stereotactic mesencephalotomy can be a valuable procedure in the management of cancer pain involving the upper extremities or the face, with the assistance of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and electrophysiologic mapping. A 72-year-old man presented with a 3-year history of intractable left-sided facial pain. When pharmacologic and nondestructive measures failed to provide pain alleviation, he was reexamined and diagnosed with inoperable hard palate cancer with intracranial extension. During the concurrent chemoradiation treatment, his cancer-related facial pain was aggravated and became medically intractable. After careful consideration, MRI-based stereotactic mesencephalotomy was performed at a point 5 mm behind the posterior commissure, 6 mm lateral to and 5 mm below the intercommissural plane using a 2-mm electrode, with the temperature of the electrode raised to 80degrees C for 60 seconds. Up until now, the pain has been relatively well-controlled by intermittent intraventricular morphine injection and oral opioids, with the pain level remaining at visual analogue scale 4 or 5. Stereotactic mesencephalotomy with the use of high-resolution MRI and electrophysiologic localization is a valuable procedure in patients with cancer-related facial pain.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amano K, Iseki H, Notani M, Kawabatake H, Tanikawa T, Kawamura H, et al. : Rostral mesencephalic reticulotomy for pain relief. Report of 15 cases. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1980; 30:391–393. PMID: 6937114.2. Amano K. Destructive central lesions for persistent pain. Outcome. In : Gildenberg PL, Tasker RR, Franklin , Patricia O, editors. Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. New York: McGraw-Hill;1998. p. 1425–1429.3. Black PM, Moriarty T, Alexander E 3rd, Stieg P, Woodard EJ, Gleason PL, et al. Development and implementation of intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging and its neurosurgical applications. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:831–842. discussion 842-845. PMID: 9316044.
Article4. Bullitt E, Tew JM, Boyd J. Intracranial tumors in patients with facial pain. J Neurosurg. 1986; 64:865–871. PMID: 3009737.
Article5. Colombo F. Somatosensory-evoked potentials after mesencephalic tractotomy for pain syndromes. Neuroradiologic and clinical correlations. Surg Neurol. 1984; 21:453–458. PMID: 6369589.
Article6. Fountas KN, Lane FJ, Jenkins PD, Smith JR. MR-based stereotactic mesencephalic tractotomy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2004; 82:230–234. PMID: 15637444.
Article7. Frank F, Fabrizi AP, Gaist G. Stereotactic mesencephalic tractotomy in the treatment of chronic cancer pain. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1989; 99:38–40. PMID: 2667283.
Article8. Frank F, Tognetti F, Gaist G, Frank G, Galassi E, Sturiale C. Stereotaxic rostral mesencephalotomy in treatment of malignant faciothoracobrachial pain syndromes. A survey of 14 treated patients. J Neurosurg. 1982; 56:807–811. PMID: 7042931.
Article9. Gildenberg PL. Mesencephalotomy for cancer pain. In : Lozano AM, Gildenberg PL, Tasker RR, editors. Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. ed 2. Berlin: Springer;2009. p. 2533–2540.10. Gybels JM, Sweet WH. Neurosurgical treatment of persistent pain. Physiological and pathological mechanisms of human pain. Pain Headache. 1989; 11:1–402. PMID: 2666976.11. International Headache Society Headache Classification Subcommittee. The International Classification of Headache Disorders. ed 2. Oxford: Blackwell Pub.;2004. p. 1–160.12. Mazars G, Merienne L, Cioloca C. [Present state of pain surgery]. Neurochirurgie. 1976; 22(Suppl 1):5–164. PMID: 787819.13. Miller JP, Acar F, Burchiel KJ. Trigeminal neuralgia and vascular compression in patients with trigeminal schwannomas : case report. Neurosurgery. 2008; 62:E974–E975. discussion E975. PMID: 18496167.14. Nashold BS Jr. Extensive cephalic and oral pain relieved by midbrain tractotomy. Confin Neurol. 1972; 34:382–388.
Article15. Nashold BS Jr, Wilson WP, Slaughter DG. Stereotaxic midbrain lesions for central dysesthesia and phantom pain. Preliminary report. J Neurosurg. 1969; 30:116–126. PMID: 4889016.16. Nomura T, Ikezaki K, Matsushima T, Fukui M. Trigeminal neuralgia. differentiation between intracranial mass lesions and ordinary vascular compression as causative lesions. Neurosurg Rev. 1994; 17:51–57. PMID: 8078609.
Article17. Ohye C. Stereotactic treatment of central pain. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998; 70:71–76. PMID: 9780401.
Article18. Pillay PK, Hassenbusch SJ. Bilateral MRI-guided stereotactic cingulotomy for intractable pain. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1992; 59:33–38. PMID: 1295044.
Article19. Pollock BE, Iuliano BA, Foote RL, Gorman DA. Stereotactic radiosurgery for tumor-related trigeminal pain. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:576–582. discussion 582-583. PMID: 10719853.
Article20. Raslan AM, Cetas JS, McCartney S, Burchiel KJ. Destructive procedures for control of cancer pain : the case for cordotomy. J Neurosurg. 2011; 114:155–170. PMID: 20690810.
Article21. Roeder F, Orthner H. [Experiences with stereotactic surgery. III. On cerebral surgery of pain with special reference to medical mesencephalotomy in thalamic hyperpathia and anesthesia dolorosa]. Confin Neurol. 1961; 21:51–97. PMID: 13742670.22. Shieff C, Nashold BS Jr. Stereotactic mesencephalic tractotomy for the relief of thalamic pain. Br J Neurosurg. 1987; 1:305–310. PMID: 3077269.
Article23. Shieff C, Nashold BS Jr. Stereotactic mesencephalotomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1990; 1:825–839. PMID: 2136172.
Article24. Spiegel EA, Kletzkin M, Szekely EG. Pain reactions upon stimulation of the tectum mesencephali. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1954; 13:212–220. PMID: 13118386.
Article25. Spiegel EA, Kletzkin M, Szekely EG, Wycis HT. Role of hypothalamic mechanisms in thalamic pain. Neurology. 1954; 4:739–751. PMID: 13214275.
Article26. Spiegel EA, Wycis HT. Mesencephalotomy in treatment of intractable facial pain. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953; 69:1–13.
Article27. Spiegel EA, Wycis HT. Present status of stereoencephalotomies for pain relief. Confin Neurol. 1966; 27:7–17. PMID: 5334024.
Article28. Spiller WG. The location within the spinal cord of the fibers for temperature and pain sensations. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1905; 32:318–320.
Article29. Toda K. Etiology of trigeminal neuralgia. Oral Sci Int. 2007; 4:10–18.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Treatment of Intractable Cancer Pain by Stereotactic Bilateral Anterior Cingulotomy
- Frameless stereotactic brain biopsy: technical considerations and clinical results regarding safety and efficacy
- Stereotactic Sphenopalatine Ganglionotomy Using Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation: Case reports
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Intracranial Schwannoma