Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2015 Sep;58(5):346-352. 10.5468/ogs.2015.58.5.346.
Risk of cesarean section after induced versus spontaneous labor at term gestation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drmaxmix.choi@samsung.com
- KMID: 2058457
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2015.58.5.346
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate whether the cesarean section (CS) rate is increased in women whose labor was induced compared to those who had spontaneous labor at term pregnancy.
METHODS
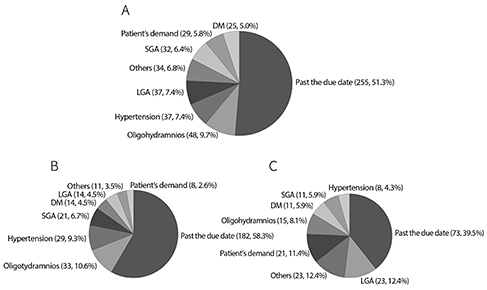
A retrospective study was performed in women whose labor was either induced (induction group, n=497) or spontaneous (spontaneous group, n=878) at 37+0 to 41+6 weeks of gestation from January 2008 to June 2009. Maternal age, parity, body mass index (BMI), Bishop scores, gestational age, hypertension, diabetes, delivery mode, indications for CS, neonatal outcome were compared between the two groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to examine the association between the CS rate and labor induction after adjusting for potential confounding variables.
RESULTS
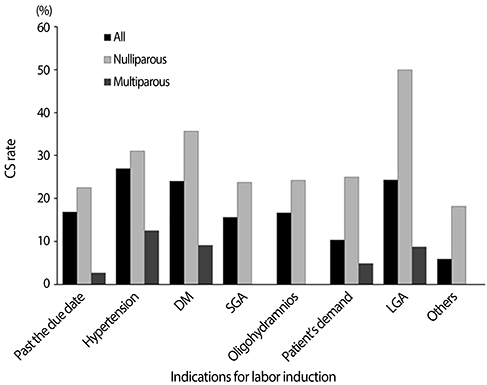
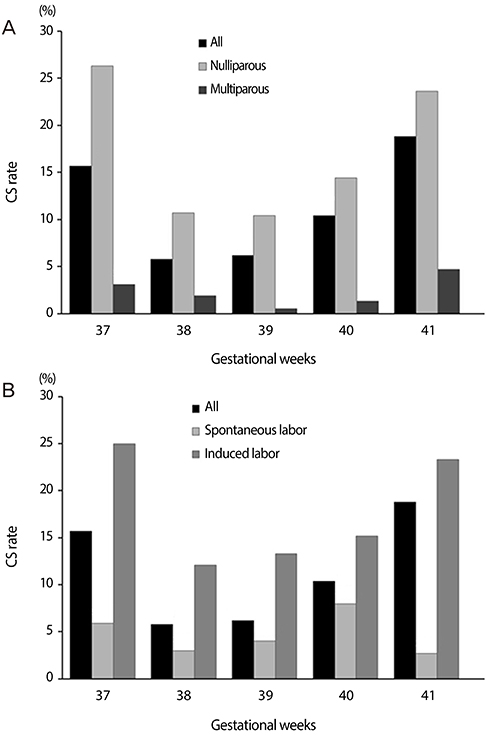
CS (17.3% vs. 5.3%, P<0.001) and vacuum-assisted delivery (10.7% vs. 6.4%, P<0.001) rates were significantly higher in the induction group compared to the spontaneous group. The CS rate in the induction group was higher than the spontaneous group not only in nulliparous women (25.3% vs. 8.6%, P<0.001), but also in multiparous women (3.8% vs. 0.3%, P=0.002). However, after adjusting confounding factors, the higher CS rate was significantly associated with advanced maternal age, higher BMI, lower Bishop scores and nulliparity, with no demonstrable tie to labor induction. Neonatal outcome in the two groups were comparable.
CONCLUSION
Although CS rate was higher in women whose labor was induced than those who had spontaneous labor, this higher rate was associated with maternal age, BMI, Bishop scores and parity, but was not impacted by labor induction per se.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Predicting factors for success of vaginal delivery in preterm induction with prostaglandin E2
Yoo Min Kim, Ju Young Park, Ji-Hee Sung, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-young Oh, Cheong-Rae Roh, Jong-Hwa Kim
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017;60(2):163-169. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2017.60.2.163.
Reference
-
1. Vrouenraets FP, Roumen FJ, Dehing CJ, van den Akker ES, Aarts MJ, Scheve EJ. Bishop score and risk of cesarean delivery after induction of labor in nulliparous women. Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 105:690–697.2. Caughey AB, Sundaram V, Kaimal AJ, Gienger A, Cheng YW, McDonald KM, et al. Systematic review: elective induction of labor versus expectant management of pregnancy. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:252–263. W53–W63.3. Ehrenthal DB, Jiang X, Strobino DM. Labor induction and the risk of a cesarean delivery among nulliparous women at term. Obstet Gynecol. 2010; 116:35–42.4. Heffner LJ, Elkin E, Fretts RC. Impact of labor induction, gestational age, and maternal age on cesarean delivery rates. Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 102:287–293.5. Cammu H, Martens G, Ruyssinck G, Amy JJ. Outcome after elective labor induction in nulliparous women: a matched cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 186:240–244.6. Maslow AS, Sweeny AL. Elective induction of labor as a risk factor for cesarean delivery among low-risk women at term. Obstet Gynecol. 2000; 95(6 Pt 1):917–922.7. Osmundson S, Ou-Yang RJ, Grobman WA. Elective induction compared with expectant management in nulliparous women with an unfavorable cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117:583–587.8. Park KH, Hong JS, Ko JK, Cho YK, Lee CM, Choi H, et al. Comparative study of induction of labor in nulliparous women with premature rupture of membranes at term compared to those with intact membranes: duration of labor and mode of delivery. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2006; 32:482–488.9. Son GH, Kim JH, Kwon JY, Kim YH, Park YW. Risk factors for cesarean delivery after induction of labor in nulliparous women with an unfavorable cervix at or beyond 41 weeks of gestation. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2013; 76:254–259.10. Johnson DP, Davis NR, Brown AJ. Risk of cesarean delivery after induction at term in nulliparous women with an unfavorable cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 188:1565–1569.11. Roos N, Sahlin L, Ekman-Ordeberg G, Kieler H, Stephansson O. Maternal risk factors for postterm pregnancy and cesarean delivery following labor induction. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2010; 89:1003–1010.12. Seyb ST, Berka RJ, Socol ML, Dooley SL. Risk of cesarean delivery with elective induction of labor at term in nulliparous women. Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 94:600–607.13. Vahratian A, Zhang J, Troendle JF, Sciscione AC, Hoffman MK. Labor progression and risk of cesarean delivery in electively induced nulliparas. Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 105:698–704.14. Yeast JD, Jones A, Poskin M. Induction of labor and the relationship to cesarean delivery: a review of 7001 consecutive inductions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 180(3 Pt 1):628–633.15. Michelson KA, Carr DB, Easterling TR. The impact of duration of labor induction on cesarean rate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 09. 199(3):299.e1–299.e4.16. Kunze M, Hart JE, Lynch AM, Gibbs RS. Intrapartum management of premature rupture of membranes: effect on cesarean delivery rate. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 118:1247–1254.17. Caughey AB, Nicholson JM, Cheng YW, Lyell DJ, Washington AE. Induction of labor and cesarean delivery by gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006; 195:700–705.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Benefits and risks of induction of labor at 39 or more weeks in uncomplicated nulliparous women: a retrospective, observational study
- Induction of labor in patients with a previous cesarean birth
- Obstetric outcome of induction of labor using prostaglandin gel in patients with previous one cesarean section
- Vaginal birth after cesarean
- Prostaglandin E2 for Induction of Labor in Patients with Premature Rupture of Membranes at Term