J Bacteriol Virol.
2006 Dec;36(4):229-235. 10.4167/jbv.2006.36.4.229.
Development of a Mass Production Method of Platelet Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, 317-1 Daemyung-5-dong, Nam-gu, Daegu, Korea. doxr7p@yumail.ac.kr
- 2College of Pharmacy, Yeungnam University, Gyongsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2055031
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2006.36.4.229
Abstract
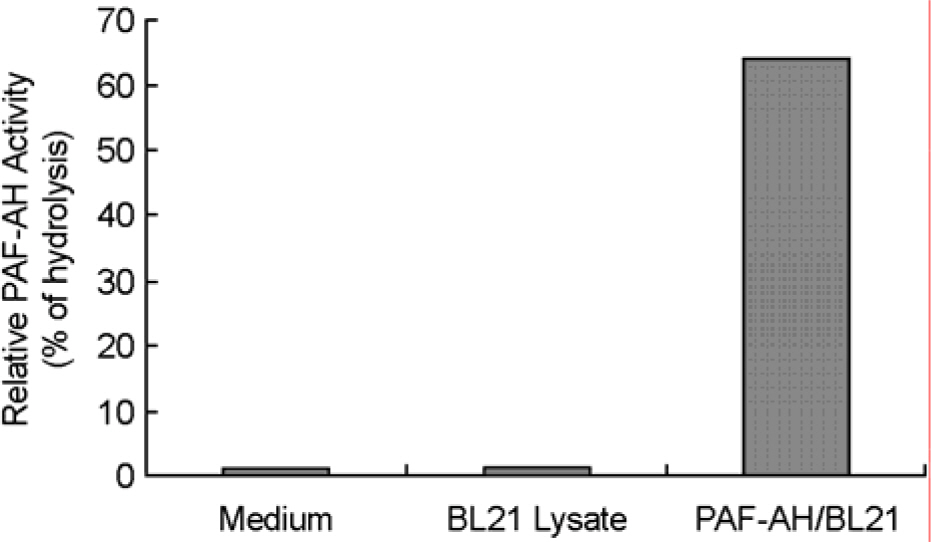
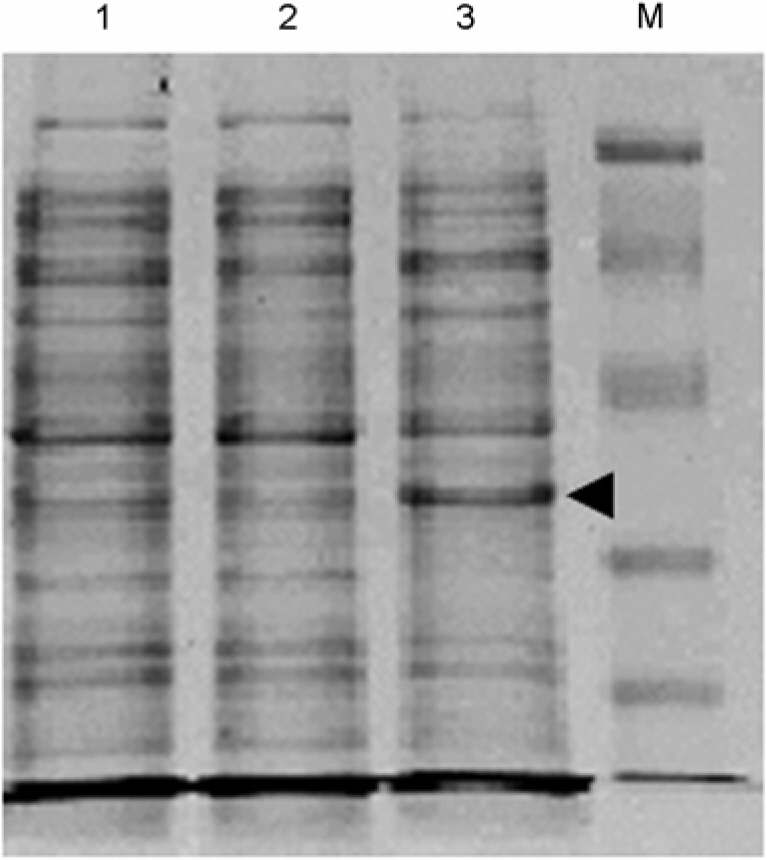
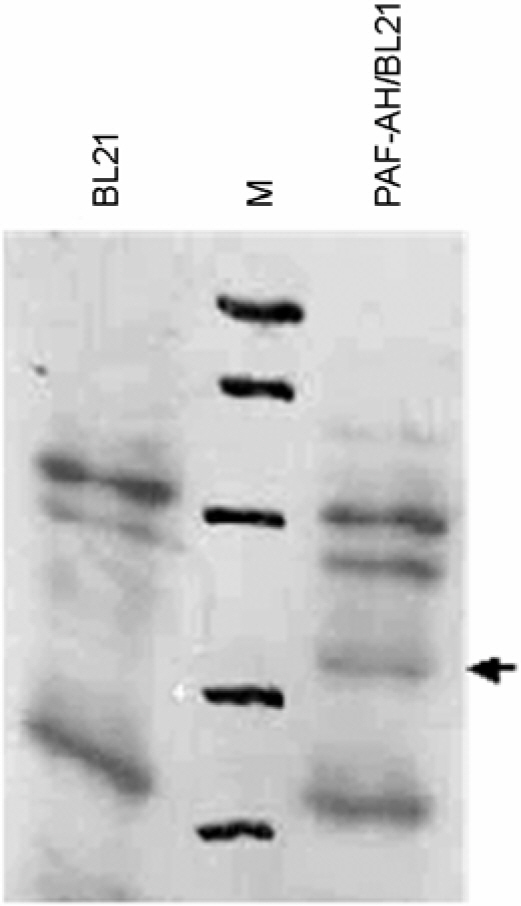
- Platelet activating factor (PAF; 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) is a potent lipid mediator in a variety of physiological events. PAF is also involved in various pathological events including allergy and inflammation. PAF-acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) hydrolyzes PAF to produce inactive lyso-PAF. Thus, overproduction of PAF-AF will be useful for the therapeutic valuation of the enzyme. In this study, we established an overproduction method of bovine PAF-AH in Escherichia coli system. We used bovine mammary gland for cDNA cloning. The cDNA had two mismatches of amino acid sequences (Thr-247 to Met and Ile-431 to Thr) compared with the previously reported PAF-AH cDNA (bovine spleen, NM_174578). The recombinant PAF-AH of 43 kDa in molecular size reacted with human PAF-AH polyclonal antibody and showed a strong PAF-AH enzyme activity in an in vitro assay system. The recombinant PAF-AH produced by this study can be applied for various experiments including in vivo models to test its protective activity against PAF-related diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Akiyama M, Sugatani J, Suzuki T, Suzuki Y, Miwa M. Identification of a major PAF acetylhydrolase in human serum/plasma as a 43 kDa glycoprotein containing about 9 kDa asparagine-conjugated sugar chain(s). J Biochem (Tokyo). 123:786–789. 1998.
Article2). Bazan NG. A signal terminator. Nature (London). 374:501–502. 1995.
Article3). Chen CH. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase: is it good or bad for you? Curr Opin Lipidol. 15:337–341. 2004.
Article4). Fukuda Y, Kawashima H, Saito K, Inomata N, Matsui M, Nakanishi T. Effect of human plasma-type platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in two anaphylactic shock models. Eur J Pharmacol. 390:203–207. 2000.
Article5). Graham RM, Stephens CJ, Silvester W, Leong LL, Sturm MJ, Taylor RR. Plasma degradation of platelet-activating factor in severely ill patients with clinical sepsis. Crit Care Med. 22:204–212. 1994.
Article6). Hattori M, Arai H, Inoue K. Purification and characterization of bovine brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. J Biol Chem. 268:18748–18753. 1993.
Article7). Hattori K, Hattori M, Adachi H, Tsujimoto M, Arai H, Inoue K. Purification and Characterization of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase II from bovine liver Cytosol. J Biol Chem. 270:22308–22313. 1995.
Article8). Henderson WR Jr, Lu J, Poole KM, Dietsch GN, Chi EY. Recombinant human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase inhibits airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mouse asthma model. J Immunol. 164:3360–3367. 2000.9). Imaizumi TA, Stafforini DM, Yamada Y, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM, Zimmerman GA. Platelet-activating factor: a mediator for clinicians. J Intern Med. 238:520. 1995.
Article10). Ishii S, Nagase T, Tashiro F, Ikuta K, Sato S, Waga I, Kume K, Miyazaki J, Shimizu T. Bronchial hyperreactivity, increased endotoxin lethality and melanocytic tumorigenesis in transgenic mice overexpressing platelet-activating factor receptor. EMBO J. 16:133–142. 1997.
Article11). Ishii S, Kuwaki T, Nagase T, Maki K, Tashiro F, Sunaga S, Cao WH, Kume K, Fukuchi Y, Ikuta K, Miyazaki J, Kumada M, Shimizu T. Impaired anaphylactic responses with intact sensitivity to endotoxin in mice lacking a platelet-activating factor receptor. J Exp Med. 187:1779–1788. 1998.
Article12). Izumi T, Shimizu T. Platelet-activating factor receptor: gene expression and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1259:317–333. 1995.
Article13). Karasawa K, Harada A, Satoh N, Inoue K, Setaka M. Plasma platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH). Prog Lipid Res. 42:93–114. 2003.
Article14). Karasawa K, Kuge O, Kawasaki K, Nishijima M, Nakano Y, Tomita M, Yokoyama K, Setaka M, Nojima S. Cloning, expression and characterization of plasma platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase from guinea pig. J Biochem (Tokyo). 120:838–844. 1996.
Article15). Murakami K, Okajima K, Uchiba M, Johno M, Okabe H, Takatsuki K. A novel platelet activating factor antagonist, SM-12502, attenuates endotoxin-induced disseminated intra-vascular coagulation and acute pulmonary vascular injury by inhibiting TNF production in rats. Thromb Haemost. 75:965–970. 1996.
Article16). Nagase T, Ishii S, Katayama H, Fukuchi Y, Ouchi Y, Shimizu T, Tashiro F, Ikuta K, Sato S, Waga I, Kume K, Miyazaki J, Kuwaki T, Maki K, Sunaga S, Cao WH, Kumada M. Airway responsiveness in transgenic mice over-expressing platelet-activating factor receptor. Roles of thromboxanes and leukotrienes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 156:1621–1627. 1997.17). Nagase T, Ishii S, Kume K, Uozumi N, Izumi T, Ouchi Y, Shimizu T. Platelet-activating factor mediates acid-induced lung injury in genetically engineered mice. J Clin Invest. 104:1071–1076. 1999.
Article18). Peplow PV. Regulation of platelet-activating factor (PAF) activity in human diseases by phospholipase A2 inhibitors, PAF acetylhydrolases, PAF receptor antagonists and free radical scavengers. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 61:6582. 1999.19). Pinckard RN, Farr RS, Hanahan DJ. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IgE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IgE sensitized basophils. J Immunol. 123:1847–1857. 1979.20). Satoh K, Yoshida H, Imaizumi T, Takamatsu S, Mizuno S. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in plasma lipoproteins from patients with ischemic stroke. Stroke. 23:1090–1092. 1992.
Article21). Snyder F. Platelet-activating factor and its analogs: metabolic pathways and related intracellular processes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1254:231–249. 1995.
Article22). Stafforini DM, McIntyre TM, Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolases. J Biol Chem. 272:17895–17898. 1997.
Article23). Tew DG, Southan C, Rice SQ, Lawrence MP, Li H, Boyd HF, Moores K, Gloger IS, Macphee CH. Purification, properties, sequencing, and cloning of a lipoprotein-associated, serine-dependent phospholipase involved in the oxidative modification of low-density lipoproteins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 16:591–599. 1996.
Article24). Tjoelker LW, Eberhardt C, Unger J, Trong HL, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM, Stafforini DM, Prescott SM, Gray PW. Plasma Platelet-activating Factor Acetylhydrolase is a secreted phospholipase A2 with a catalytic triad. J Biol Chem. 270:25481–25487. 1995.
Article25). Tjoelker LW, Wilder C, Eberhardt C, Stafforini DM, Dietsch G, Schimpf B, Hooper S, Le Trong H, Cousens LS, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM, Stafforini DM, Prescott SM, Gray PW. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature (London). 374:549–553. 1995.
Article26). Tsukioka K, Matsuzaki M, Nakamata M, Kayahara H, Nakagawa T. Increased plasma level of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and decreased serum PAF acetylhydrolase (PAFAH) activity in adults with bronchial asthma. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 6:22–29. 1996.27). Venable ME, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM. Platelet-activating factor: a phospholipid autacoid with diverse actions. J Lipid Res. 34:691–702. 1993.
Article28). Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM, Stafforini DM. Platelet-activating factor: antagonists, terminators, molecular mimics, and microbial opportunism. J Intern Med. 239:463–466. 1996.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Platelet activating factor is an eosinophil activator in asthma
- The effects on the production of platelet activating factor in the cultured human endothelial cells by interleukin-6 and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor
- Effect of platelet activating factor on the secretion of progesterone in the rabbit
- The effects of carnitine and platelet activating factor on the motility parameters of human spermatozoa
- The Effects of Hantaan Virus on the Expression of Platelet Activating Factor Receptor and on the Activity of Platelet Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase