Hip Pelvis.
2014 Sep;26(3):143-149. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.3.143.
The Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating on Long-term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty with Hydroxyapatite-coated Anatomic Femoral Stem
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. paedic@chol.com
- KMID: 2054177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.3.143
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiological results, as well as the survival rate, associated with total hip arthroplasty using a hydroxyapatite (HA)-coated anatomical femoral stem at a follow-up of > or =12 years.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 1992 to May 1997, 86 patients (102 hips) underwent total hip arthroplasty with a HA-coated ABG I (Anatomical Benoist Giraud; Howmedica) hip prosthesis. The average age at the time of surgery was 53.4 years and the mean duration of follow-up was 17.1 years (range, 12.1-21.0 years). The Harris hip score (HHS) and radiographic assessments of thigh pain were used to evaluate the clinical results. We observed osteointegration, cortical hypertrophy, reactive line, calcar resorption and osteolysis around the femoral stems. The survival rate of the femoral stems was evaluated by using the span of time to a revision operation for any reasons was defined as the end point.
RESULTS
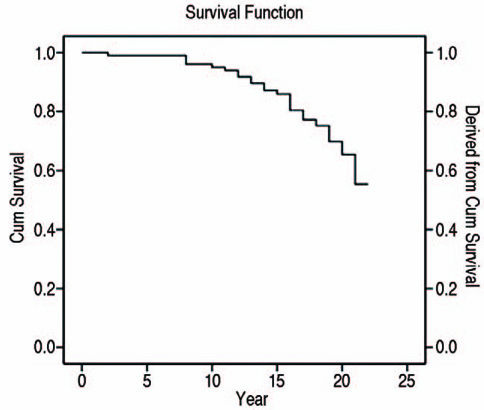
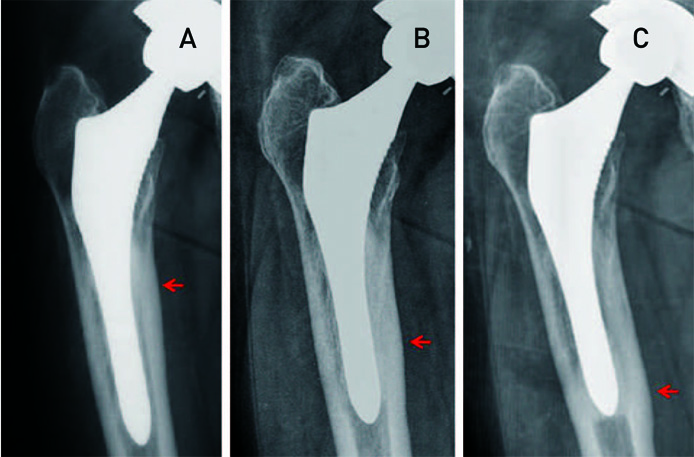
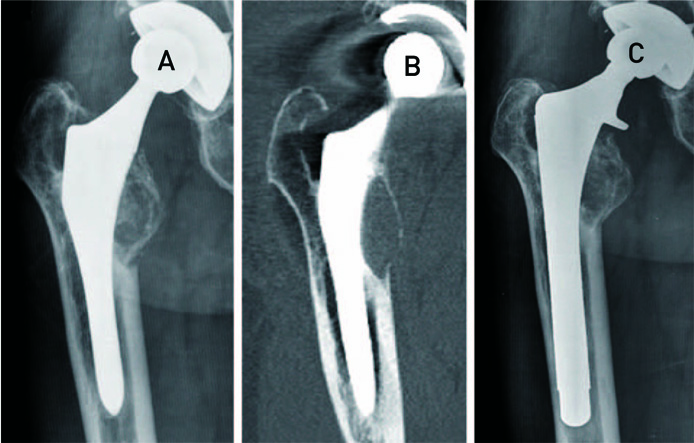
The mean HHS was 50.5 preoperatively and 84.2 at the time of last follow-up. Osteolysis only around the HA-coated proximal portion of the femoral stem was observed in 72 hips, cortical hypertrophy all around the distal portion of the femoral stem was observed in 38 hips, and calcar resorption was observed in 44 hips. A reactive line was observed in 13 hips, but was unrelated to component loosening. Stem revision operations were performed in 24 (23%) hips due to osteolysis (14 hips), fracture (5 hips) and infection (5 hips). The femoral stem survival rate was 75% over the mean duration of follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Total hip arthroplasty using a HA-coated anatomical femoral stem showed necessitated a high rate of revision operations due to osteolysis around the femoral stem in this long term follow-up study.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Emerson RH Jr, Head WC, Emerson CB, Rosenfeldt W, Higgins LL. A comparison of cemented and cementless titanium femoral components used for primary total hip arthroplasty: a radiographic and survivorship study. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17:584–591.
Article2. Capello WN. Uncemented total hip replacement. J Japanese Orthop Assoc. 1990; 64:S86.
Article3. American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard specifications for tricalcium phosphate for surgical implants. Philadelphia: American Society for Testing and Materials;1987. p. F-1088-7.4. American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard specifications for ceramic hydroxyapatite for surgical implants. Philadelphia: American Society for Testing and Materials;1989. p. F-1185-9.5. Tonino AJ, Romanini L, Rossi P, et al. Hydroxyapatite-coated hip prostheses. Early results from an international study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (312):211–225.6. Garcia Araujo C, Fernandez Gonzalez J, Tonino A. International ABG Study Group. Rheumatoid arthritis and hydroxyapatite-coated hip prostheses: five-year results. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:660–667.7. Søballe K, Hansen ES, Brockstedt-Rasmussen H, Bünger C. Hydroxyapatite coating converts fibrous tissue to bone around loaded implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:270–278.8. Castoldi F, Rossi R, La Russa M, Sibelli P, Rossi P, Ranawat AS. Ten-year survivorship of the Anatomique Benoist Girard I total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:363–368.
Article9. Reikerås O, Gunderson RB. Failure of HA coating on a gritblasted acetabular cup: 155 patients followed for 7-10 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002; 73:104–108.
Article10. Duffy P, Sher JL, Partington PF. Premature wear and osteolysis in an HA-coated, uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:34–38.
Article11. Rajaratnam SS, Jack C, Tavakkolizadeh A, et al. Long-term results of a hydroxyapatite-coated femoral component in total hip replacement: a 15- to 21-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:27–30.12. Giannikas KA, Din R, Sadiq S, Dunningham TH. Medium-term results of the ABG total hip arthroplasty in young patients. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17:184–188.
Article13. Bidar R, Kouyoumdjian P, Munini E, Asencio G. Long-term results of the ABG-1 hydroxyapatite coated total hip arthroplasty: analysis of 111 cases with a minimum follow-up of 10 years. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009; 95:579–587.
Article14. McNally SA, Shepperd JA, Mann CV, Walczak JP. The results at nine to twelve years of the use of a hydroxyapatite-coated femoral stem. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82:378–382.
Article15. Park YS, Lim SJ. Long-term comparison of porous and hydroxyapatite sleeves in femoral revision using the S-ROM modular stem. Hip Int. 2010; 20:179–186.
Article16. Yee AJ, Kreder HK, Bookman I, Davey JR. A randomized trial of hydroxyapatite coated prostheses in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; 366:120–132.
Article17. Harris WH. Preliminary report of results of Harris total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973; 95:168–173.
Article18. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; 141:17–27.19. Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH. Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69:45–55.
Article20. Callaghan JJ, Salvati EA, Pellicci PM, Wilson PD Jr, Ranawat CS. Results of revision for mechanical failure after cemented total hip replacement, 1979 to 1982. A two to five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:1074–1085.
Article21. Furlong RJ, Osborn JF. Fixation of hip prostheses by hydroxyapatite ceramic coatings. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:741–745.
Article22. Geesink RG, de Groot K, Klein CP. Chemical implant fixation using hydroxyl-apatite coatings. The development of a human total hip prosthesis for chemical fixation to bone using hydroxyl-apatite coatings on titanium substrates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 225:147–170.23. Kim KS, Ko SH, Chung YY, et al. Total hip arthroplasty with hydroxyapatite-coated ABG(R) hip prosthesis: Minimum 5 year follow-up. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2003; 38:568–572.
Article24. Beksaç B, Salas A, González Della Valle A, Salvati EA. Wear is reduced in THA performed with highly cross-linked polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:1765–1772.
Article25. Bizot P, Nizard R, Hamadouche M, Hannouche D, Sedel L. Prevention of wear and osteolysis: alumina-on-alumina bearing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 393:85–93.26. Lazarinis S, Kärrholm J, Hailer NP. Effects of hydroxyapatite coating on survival of an uncemented femoral stem. A Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register study on 4,772 hips. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82:399–404.
Article27. Gandhi R, Davey JR, Mahomed NN. Hydroxyapatite coated femoral stems in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:38–42.28. Knight JL, Atwater RD, Guo J. Clinical results of the midstem porous-coated anatomic uncemented femoral stem in primary total hip arthroplasty: a five- to nine-year prospective study. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:535–545.
Article29. Rossi P, Sibelli P, Fumero S, Crua E. Short-term results of hydroxyapatite-coated primary total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; 310:98–102.
Article30. D'Antonio JA, Capello WN, Jaffe WL. Hydroxylapatite-coated hip three-year clinical and roentgenographic results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 285:102–115.31. Canales V, Panisello JJ, Herrera A, Sola A, Mateo JJ, Caballero MJ. Extensive osteolysis caused by polyethylene particle migration in an anatomical hydroxyapatite-coated hip prosthesis: 10 years' follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:1115–1124.
Article32. Oosterbos CJ, Rahmy AI, Tonino AJ, Witpeerd W. High survival rate of hydroxyapatite-coated hip prostheses: 100 consecutive hips followed for 10 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004; 75:127–133.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Hydroxyapatite-Coated Femoral stem. - Two-Year Clinical and Radiologic Follow-UP-
- Short-term Results after Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Fully Hydroxyapatite-coated Femoral Stem
- Total Hip Arthroplasty with Hydroxyapatite-Coated Anatomic Femoral Stem
- Clinical and Radiologic Results of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Hydroxyapatite - Coated Stem
- Early Postoperative Periprosthetic Radiological Findings in Cementless THRA : Comparison between Porous - coated Implant and Hydroxyapatite - coated Implant